Understanding the legality of any action or product is crucial to ensure compliance with laws and avoid potential penalties. Laws vary by region, so it's important to be aware of the specific regulations that apply to your situation. Explore the rest of this article to learn more about key legal considerations and how they might impact you.
Table of Comparison
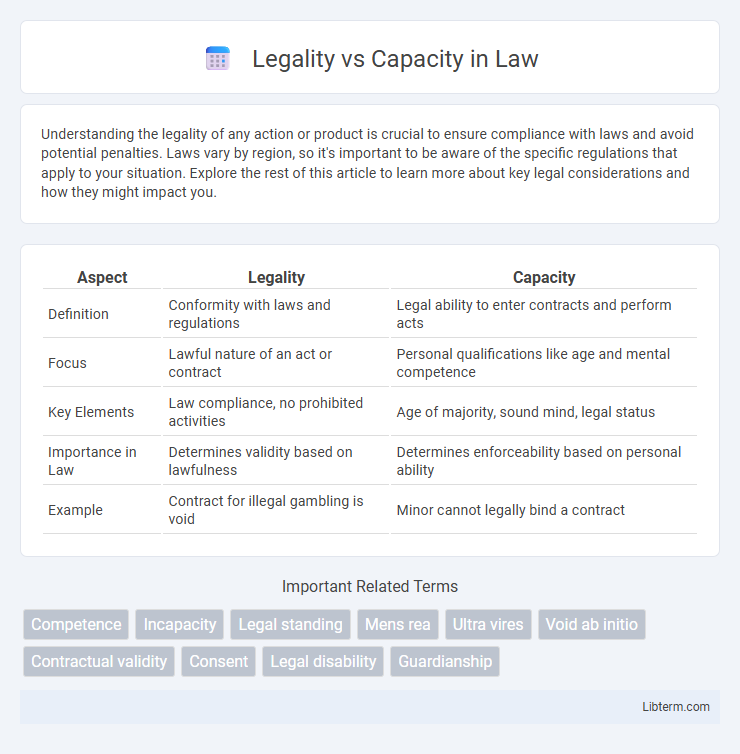
| Aspect | Legality | Capacity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conformity with laws and regulations | Legal ability to enter contracts and perform acts |
| Focus | Lawful nature of an act or contract | Personal qualifications like age and mental competence |
| Key Elements | Law compliance, no prohibited activities | Age of majority, sound mind, legal status |
| Importance in Law | Determines validity based on lawfulness | Determines enforceability based on personal ability |
| Example | Contract for illegal gambling is void | Minor cannot legally bind a contract |
Understanding the Concept of Legality
Legality refers to the conformity of an act, contract, or transaction with established laws and regulations, ensuring that it is legally permissible and enforceable. It involves assessing whether the subject matter, purpose, and terms of an agreement comply with statutory requirements and public policy. Understanding legality is crucial for validating contracts and preventing agreements that involve illegal activities or objectives.
Defining Capacity in Legal Contexts
Capacity in legal contexts refers to an individual's recognized ability to enter into binding contracts, make decisions, or engage in legal transactions. It is determined by criteria such as age, mental competence, and soundness of mind, ensuring that the person understands the nature and consequences of the act. Without sufficient capacity, legal agreements may be declared void or voidable due to the individual's inability to comprehend or consent knowingly.
Key Differences Between Legality and Capacity
Legality refers to the compliance of an agreement or action with established laws, ensuring it does not violate statutory regulations or public policy. Capacity involves the legal ability of an individual or entity to enter into a contract, typically requiring sound mind and legal age. Key differences include that legality concerns the nature of the contract's content, while capacity pertains to the parties' qualifications to engage legally in that contract.
Importance of Legality in Contract Formation
Legality is a fundamental requirement in contract formation, ensuring that agreements comply with laws and public policy to be enforceable. Contracts involving illegal acts or objectives lack validity, rendering them void and unenforceable in court. Upholding legality protects parties from engaging in unlawful transactions and fosters trust in contractual relationships.
Assessing Capacity: Who Is Competent to Contract?
Assessing capacity to contract involves determining whether an individual possesses the legal ability and mental competence to enter into a binding agreement. Competency typically requires that the person is of legal age, understands the nature and consequences of the contract, and is not impaired by mental illness, intoxication, or other factors affecting judgment. Legal frameworks often place the burden of proof on the party claiming incapacity, emphasizing the importance of clear evidence when contesting a party's contractual competence.
Legal Implications of Lacking Capacity
Lacking capacity in legal terms often results in contracts or agreements being voidable or unenforceable, as the individual may not fully comprehend the nature or consequences of the transaction. Courts assess capacity based on mental competency, age, and understanding, which directly influences the validity of any legal commitments made. Entities or parties dealing with individuals lacking capacity face increased risks of disputes, necessitating careful evaluation to ensure compliance with legal standards and protection against potential liabilities.
Case Studies: Legality vs Capacity in Court Decisions
Court decisions often hinge on differentiating legality from capacity, as seen in landmark cases like *Bank of Montreal v. Innovation Credit Corp.*, where contract validity was challenged based on mental capacity rather than legal compliance. Judgments in *In re Estate of Reynolds* illustrate how courts prioritize an individual's capacity to understand and consent over mere legality when assessing testamentary documents. These case studies highlight judicial emphasis on nuanced evaluations of mental capacity to ensure just enforcement of legal agreements.
Consequences of Invalid Contracts
Invalid contracts result in legal consequences such as unenforceability, meaning the parties cannot seek court remedies to enforce the agreement. Lack of legality or capacity typically voids the contract, preventing parties from claiming damages or specific performance. Courts may also require restitution to prevent unjust enrichment when an invalid contract involves exchange of benefits.
Remedies for Breach of Legality or Capacity
Remedies for breach of legality often involve voiding the contract or enforcing restitution to restore parties to their original positions, as illegal agreements are generally unenforceable under contract law. In cases of capacity, courts may allow rescission or ratification depending on whether the incapacitated party seeks to confirm or void the contract, with minors typically having the right to disaffirm agreements to protect their interests. Specific performance or damages are rare remedies for illegality or incapacity because the law prioritizes public policy and the protection of vulnerable parties over enforcing problematic contracts.
Practical Tips for Ensuring Valid Contracts
Ensuring valid contracts requires verifying both legality and capacity, as contracts must involve lawful subject matter and parties legally competent to contract. Practical tips include confirming all parties are of legal age, mentally sound, and not under duress or undue influence, while avoiding agreements involving illegal activities or terms violating public policy. Proper documentation and clear communication help prevent disputes related to contract validity.
Legality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com