Case law interpretation involves analyzing judicial decisions to understand how laws are applied in various contexts, ensuring consistent legal outcomes. Courts rely on precedents set by previous rulings to guide their judgments, which is essential for maintaining the rule of law. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding of how case law shapes legal interpretation and affects your rights.
Table of Comparison
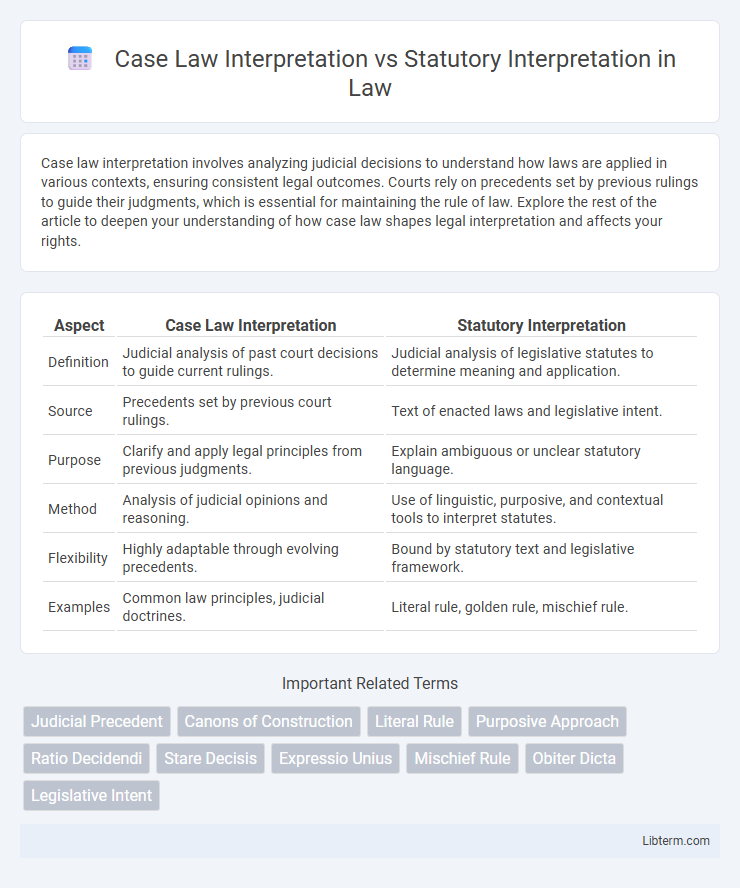
| Aspect | Case Law Interpretation | Statutory Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Judicial analysis of past court decisions to guide current rulings. | Judicial analysis of legislative statutes to determine meaning and application. |
| Source | Precedents set by previous court rulings. | Text of enacted laws and legislative intent. |
| Purpose | Clarify and apply legal principles from previous judgments. | Explain ambiguous or unclear statutory language. |
| Method | Analysis of judicial opinions and reasoning. | Use of linguistic, purposive, and contextual tools to interpret statutes. |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable through evolving precedents. | Bound by statutory text and legislative framework. |
| Examples | Common law principles, judicial doctrines. | Literal rule, golden rule, mischief rule. |
Introduction to Legal Interpretation
Legal interpretation involves deciphering the meaning and application of laws through two primary methods: case law interpretation and statutory interpretation. Case law interpretation relies on judicial decisions, where courts analyze precedents and apply principles from previous rulings to current disputes, emphasizing flexibility and evolving jurisprudence. Statutory interpretation focuses on understanding and implementing the language of written statutes, statutes' legislative intent, and applying canonical rules such as the literal, golden, and purposive approaches to clarify ambiguities.
Defining Case Law Interpretation
Case law interpretation involves analyzing judicial decisions to clarify and apply legal principles within previous rulings. It relies on precedents established by higher courts to resolve ambiguities and guide the application of laws in specific cases. This method contrasts with statutory interpretation, which focuses primarily on the explicit language and intent of legislative texts.
Defining Statutory Interpretation
Statutory interpretation involves the process by which courts analyze and apply legislation to specific cases, ensuring laws are understood and enforced according to legislative intent. It relies heavily on the text of statutes, legislative history, and principles such as the plain meaning, purposive approach, and ejusdem generis. Defining statutory interpretation centers on clarifying ambiguous language or gaps within statutes to provide precise legal guidance and maintain consistency in judicial decisions.
Purpose and Importance of Interpretation
Case law interpretation focuses on understanding judicial decisions to apply legal principles to specific circumstances, ensuring consistency and fairness across future rulings. Statutory interpretation involves analyzing legislative texts to ascertain the legislature's intent, providing clarity and guiding proper application of the law. Both are essential for resolving ambiguities, maintaining legal certainty, and adapting laws to evolving societal contexts.
Methods Used in Case Law Interpretation
Case law interpretation employs methods such as the literal rule, where judges interpret statutes by their plain, ordinary meaning, and the purposive approach, which considers the legislative intent behind the law. The golden rule allows modification of the literal meaning to avoid absurd or unjust outcomes, while the mischief rule focuses on remedying the specific issue the statute aimed to address. These interpretative techniques enable courts to apply legal principles flexibly, ensuring that statutory provisions are implemented effectively in varying contexts.
Approaches to Statutory Interpretation
Approaches to statutory interpretation include the literal, golden, and purposive rules, each prioritizing different methods to ascertain legislative intent. The literal approach emphasizes the ordinary meaning of statutory language, while the golden rule allows modification of words to avoid absurd outcomes. The purposive approach seeks to fulfill the legislature's intended purpose, often resorting to extrinsic materials to guide interpretation.
Key Differences Between the Two
Case law interpretation relies on judicial decisions and precedents to clarify legal principles, emphasizing how courts apply laws in specific situations. Statutory interpretation focuses on the legislative text, examining the language, context, and purpose of statutes to determine lawmakers' intent. Key differences include case law's reliance on past rulings versus statutory interpretation's emphasis on textual analysis and legislative history.
Challenges in Legal Interpretation
Challenges in legal interpretation arise from the inherent complexity and ambiguity of both case law and statutory texts, requiring judges to discern legislative intent and apply precedent consistently. Statutory interpretation faces difficulty due to broad or vague language in statutes, necessitating contextual analysis and balancing literal versus purposive approaches. Case law interpretation challenges include reconciling conflicting precedents and adapting past rulings to evolving social and legal contexts while maintaining judicial coherence.
Landmark Cases Illustrating Both Approaches
Landmark cases such as Marbury v. Madison emphasize case law interpretation, where judicial decisions establish precedents guiding future rulings. Statutory interpretation is exemplified in Chevron U.S.A., Inc. v. Natural Resources Defense Council, Inc., which highlights courts deferring to agency expertise in ambiguous statutory language. These cases illustrate the distinct roles of judiciary in shaping law through precedent and clarifying legislative intent via statutory analysis.
Conclusion: Balancing Case Law and Statutory Interpretation
Balancing case law and statutory interpretation ensures that courts respect legislative intent while adapting legal principles to evolving societal contexts. Case law provides precedent that guides consistent judicial decisions, whereas statutory interpretation clarifies ambiguous or broad legislative language. Effective legal analysis requires integrating both approaches to maintain a coherent and dynamic legal system.
Case Law Interpretation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com