An appellant is an individual or party who formally challenges a decision made by a lower court, seeking a higher court's review and reversal of that ruling. This legal role is crucial in the judicial process, ensuring that errors or injustices in initial judgments can be addressed. Discover how the appellant's responsibilities and rights affect your legal case by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
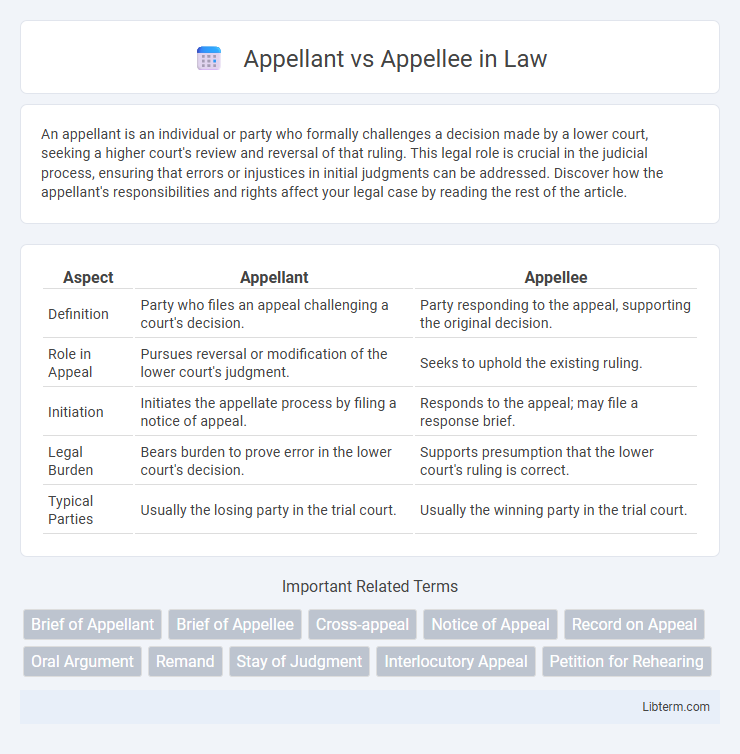
| Aspect | Appellant | Appellee |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Party who files an appeal challenging a court's decision. | Party responding to the appeal, supporting the original decision. |
| Role in Appeal | Pursues reversal or modification of the lower court's judgment. | Seeks to uphold the existing ruling. |
| Initiation | Initiates the appellate process by filing a notice of appeal. | Responds to the appeal; may file a response brief. |
| Legal Burden | Bears burden to prove error in the lower court's decision. | Supports presumption that the lower court's ruling is correct. |
| Typical Parties | Usually the losing party in the trial court. | Usually the winning party in the trial court. |
Introduction to Appellant and Appellee
The appellant is the party who initiates an appeal by challenging a trial court's decision, seeking a review and reversal of the judgment. The appellee, also known as the respondent, is the party who responds to the appeal, advocating for the trial court's ruling to be upheld. Understanding the roles of appellant and appellee is essential for navigating appellate court procedures and legal arguments.
Key Definitions: Appellant vs Appellee
The appellant is the party who initiates an appeal by challenging the decision of a lower court, seeking a reversal or modification of the judgment. The appellee, also known as the respondent, is the party who opposes the appeal and argues for the affirmance of the lower court's decision. Understanding these key definitions is crucial for navigating appellate procedure and ensuring proper legal representation in higher courts.
Roles in the Appeals Process
The appellant initiates the appeals process by challenging a lower court's decision, seeking reversal or modification based on alleged legal errors. The appellee responds by defending the original ruling and arguing why the decision should be upheld. Both parties submit briefs and may present oral arguments, with their roles centered on persuading the appellate court to rule in their favor.
Legal Rights and Responsibilities
The appellant holds the legal right to challenge a lower court's decision by filing an appeal, seeking reversal or modification based on alleged errors in the trial or application of law. The appellee is responsible for defending the original judgment, presenting arguments to uphold the lower court's ruling and demonstrating its correctness. Both parties must adhere to procedural rules, including timely submission of briefs and evidence, to ensure a fair appellate review process.
How an Appeal is Initiated
An appeal is initiated when the appellant files a notice of appeal with the appropriate appellate court, signaling their intention to challenge the trial court's decision. The appellant, typically the party dissatisfied with the judgment, must adhere to strict deadlines and procedural rules to ensure the appeal is accepted. Following the notice, the appellant prepares and submits an appellate brief outlining legal errors alleged in the lower court's ruling for the appellee to respond.
Common Grounds for Appeal
Common grounds for appeal typically involve legal errors made during the trial, such as misinterpretation of the law or improper admission of evidence. Appellants often argue that the trial court abused its discretion or that factual findings lack sufficient evidentiary support. Issues related to due process violations and incorrect jury instructions commonly serve as bases for appellate review between appellants and appellees.
The Appellant’s Burden of Proof
The appellant's burden of proof requires demonstrating that the lower court committed a significant legal error affecting the case outcome. This burden involves presenting clear and convincing evidence or showing a substantial procedural mistake that justifies reversing or modifying the decision. Failure to meet this burden typically results in the appellate court affirming the original judgment.
Response Strategies of the Appellee
The appellee employs response strategies centered on affirming the trial court's judgment by highlighting the appellant's failure to demonstrate reversible error. Emphasis is placed on precedent and statutory interpretations that support the original decision, alongside detailed factual rebuttals to the appellant's claims. Effective appellee responses often include robust legal arguments and meticulous record citations to reinforce the validity of the lower court's ruling.
Court Procedures and Legal Arguments
The appellant initiates the appeal by filing a notice to challenge the trial court's decision, presenting legal arguments centered on alleged errors of law or procedural mistakes that affected the verdict. The appellee responds by defending the lower court's ruling, emphasizing the record's evidence and arguing that the trial was fair and legally sound. Both parties submit briefs to the appellate court, which reviews these documents and oral arguments to determine whether to uphold, reverse, or remand the case based on the legal standards governing appellate review.
Outcomes and Implications for Both Parties
Appellant and appellee represent opposing parties in an appeal, where the appellant seeks to overturn a lower court's decision, while the appellee aims to uphold it. Outcomes favoring the appellant result in reversal or modification of the original judgment, potentially leading to retrials or altered legal standards. Conversely, a ruling in favor of the appellee confirms the lower court's ruling, reinforcing established legal precedents and affirming the appellee's position or entitlement.
Appellant Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com