Forfeiture is a legal process where an individual loses ownership rights to property due to illegal activity or breach of contract. This includes both criminal forfeiture tied to crimes and civil forfeiture involving property connected to unlawful acts. Explore the article to understand how forfeiture may affect your rights and assets.
Table of Comparison
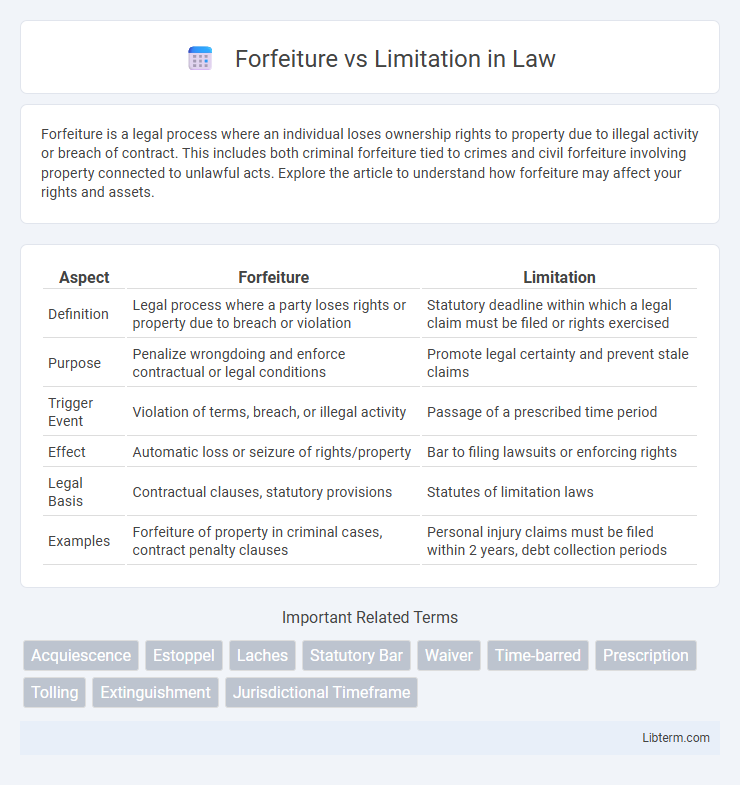
| Aspect | Forfeiture | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal process where a party loses rights or property due to breach or violation | Statutory deadline within which a legal claim must be filed or rights exercised |
| Purpose | Penalize wrongdoing and enforce contractual or legal conditions | Promote legal certainty and prevent stale claims |
| Trigger Event | Violation of terms, breach, or illegal activity | Passage of a prescribed time period |
| Effect | Automatic loss or seizure of rights/property | Bar to filing lawsuits or enforcing rights |
| Legal Basis | Contractual clauses, statutory provisions | Statutes of limitation laws |
| Examples | Forfeiture of property in criminal cases, contract penalty clauses | Personal injury claims must be filed within 2 years, debt collection periods |
Understanding Forfeiture and Limitation
Forfeiture refers to the loss of a right or property as a penalty for breach of legal duty or contract, often resulting in an automatic surrender without court intervention. Limitation pertains to the statutory period within which legal action must be brought, after which claims are barred to ensure timely justice and legal certainty. Understanding the distinctions between forfeiture and limitation helps clarify how rights are lost either through breach or expiration of time limits under the law.
Legal Definitions: Forfeiture vs Limitation
Forfeiture refers to the legal process by which a party loses rights or property due to breach of legal obligation or wrongdoing, often as a penalty or consequence of violating contractual or statutory duties. Limitation pertains to the statutory time frame within which a legal claim or action must be initiated, after which the right to enforce the claim is barred by law. Understanding the distinction between forfeiture, which involves the loss of rights through fault or breach, and limitation, which restricts the period for legal claims, is essential in both civil and criminal law contexts.
Key Differences Between Forfeiture and Limitation
Forfeiture involves the loss of rights or property due to a breach of contract or legal condition, often resulting from intentional or negligent actions by a party. Limitation refers to the restriction of legal claims within a specified timeframe, governed by statutes of limitations that prevent outdated lawsuits. Key differences include forfeiture being a penalty triggered by conduct, whereas limitation serves as a procedural deadline to ensure timely enforcement of rights.
Circumstances Leading to Forfeiture
Forfeiture arises when a party fails to perform contractual obligations due to intentional breaches, fraud, or willful misconduct, resulting in the loss of rights or property. Circumstances leading to forfeiture typically include non-payment, abandonment, or violation of specific contract terms explicitly stated as conditions. In contrast, limitation refers to the restriction of claims within a prescribed time frame without necessarily involving misconduct or breach.
Situations Where Limitation Applies
Limitation applies primarily in legal contexts where a fixed deadline restricts the time within which a party can assert a claim or right, typically defined by statute of limitations periods ranging from one to several years depending on jurisdiction and case type. Situations include filing lawsuits for breach of contract, personal injury claims, and property disputes, where failure to initiate action within the prescribed limitation period bars legal recourse. Unlike forfeiture, limitation does not depend on the party's conduct but strictly imposes temporal boundaries to ensure timely resolution and legal certainty.
Effects of Forfeiture on Legal Rights
Forfeiture results in the automatic loss or surrender of legal rights or property due to a breach of conditions or failure to meet obligations, significantly impacting contract enforcement and ownership claims. The effect of forfeiture often means that the party losing rights cannot reclaim them, even if the breach is later remedied, leading to permanent deprivation of entitlements. This creates a strong incentive to comply with contractual terms and legal duties, as forfeiture enforces strict consequences for non-performance.
Impact of Limitation Periods on Claims
Limitation periods establish a statutory timeframe within which claims must be initiated, directly impacting the enforceability of legal rights by barring actions filed after expiration. These time constraints ensure legal certainty and prevent the indefinite threat of litigation, thereby promoting timely resolution of disputes. Failure to file a claim within the prescribed limitation period typically results in dismissal, regardless of the claim's merit, underscoring the critical importance of understanding applicable limitation laws.
Forfeiture and Limitation in Contract Law
Forfeiture in contract law occurs when a party loses a right or property as a consequence of breaching a contractual obligation, often resulting in the cancellation of certain benefits or rights under the agreement. Limitation refers to the statutory time period within which a party must enforce or bring a claim arising from a contract, after which the right to sue or seek remedy expires. Understanding the distinction between forfeiture and limitation is crucial for enforcing contract terms and protecting parties' legal interests effectively.
Judicial Interpretations: Forfeiture vs Limitation
Judicial interpretations distinguish forfeiture as the voluntary and intentional surrender of a legal right, whereas limitation refers to the expiration of the right due to the lapse of time as prescribed by statute. Courts emphasize that forfeiture results from the party's conduct, showing waiver or abandonment, while limitation periods impose mandatory deadlines to file claims or enforce rights, ensuring legal certainty. This differentiation impacts the enforcement and defenses in litigation, with forfeiture often requiring proof of intent and limitation being governed by rigid statutory provisions.
Practical Implications for Litigants
Forfeiture occurs when a party loses a right due to failing to assert it in a timely manner, while limitation involves statutory deadlines restricting when claims can be filed. Litigants must act promptly to avoid forfeiture, ensuring key rights and defenses are preserved during litigation. Understanding these distinctions helps prevent procedural dismissals and supports effective case strategy.
Forfeiture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com