Understanding your motive is crucial for achieving clarity and purpose in any endeavor. A clear motive drives focused actions and influences outcomes significantly. Explore the rest of the article to discover how identifying your motive can transform your goals.
Table of Comparison
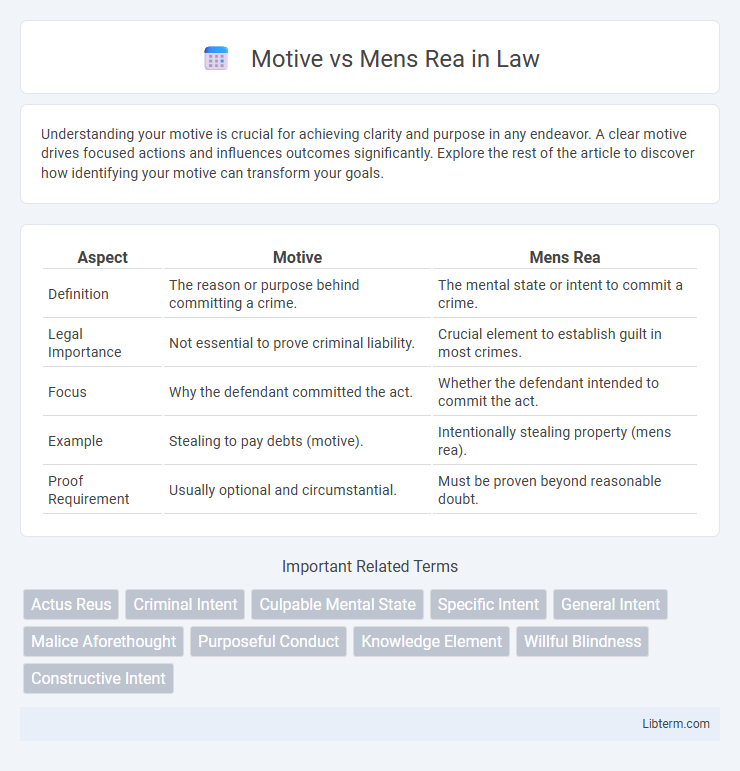
| Aspect | Motive | Mens Rea |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The reason or purpose behind committing a crime. | The mental state or intent to commit a crime. |
| Legal Importance | Not essential to prove criminal liability. | Crucial element to establish guilt in most crimes. |
| Focus | Why the defendant committed the act. | Whether the defendant intended to commit the act. |
| Example | Stealing to pay debts (motive). | Intentionally stealing property (mens rea). |
| Proof Requirement | Usually optional and circumstantial. | Must be proven beyond reasonable doubt. |
Understanding the Concepts: Motive and Mens Rea
Motive refers to the reason behind a person's actions, while mens rea denotes the mental state or intent to commit a crime. Understanding mens rea is crucial for establishing criminal liability, as it reflects knowledge, recklessness, or purposefulness in the defendant's conduct. Motive, although it can explain why a crime was committed, is not essential to prove the defendant's guilt under criminal law.
Defining Motive in Criminal Law
Motive in criminal law refers to the reason why a person commits a crime, revealing the underlying purpose or goal behind the illegal act. Unlike mens rea, which denotes the defendant's mental state or intent to commit a crime, motive explains the cause that drives the behavior. Understanding motive can aid in establishing the context of the crime but is not required to prove criminal liability.
Explaining Mens Rea: The Guilty Mind
Mens rea, the Latin term for "guilty mind," refers to the mental state a person must have to be legally responsible for a crime, encompassing intent, knowledge, recklessness, or negligence. It distinguishes unlawful acts committed with a culpable state of mind from those done accidentally or without criminal intent. Understanding mens rea is crucial for establishing criminal liability, as it ensures that only individuals who intentionally or knowingly engage in wrongdoing face punishment.
Key Differences Between Motive and Mens Rea
Motive refers to the underlying reason or desire driving an individual to commit a crime, while mens rea denotes the mental state or intent required to establish criminal liability. Mens rea involves specific cognitive elements such as intent, knowledge, recklessness, or negligence that determine the culpability of the defendant. Courts prioritize proving mens rea to establish guilt, whereas motive helps explain why the crime was committed but is not essential for conviction.
Role of Motive in Criminal Trials
Motive refers to the reason behind a defendant's actions, whereas mens rea denotes the defendant's mental state or intent to commit a crime. In criminal trials, establishing mens rea is crucial for proving guilt, but motive is not an essential element to secure a conviction; however, motive can provide context and help explain behavior, influencing jury perception and sentencing decisions. Courts often consider motive as circumstantial evidence to support mens rea but rely primarily on direct proof of intent to determine criminal responsibility.
Importance of Mens Rea in Legal Proceedings
Mens Rea, or the "guilty mind," is a crucial element in criminal law that determines the defendant's mental state at the time of the offense, which is essential for establishing criminal liability. Unlike motive, which explains why a crime was committed, mens rea directly affects the classification and severity of charges, influencing judgments in trials and sentencing. Courts prioritize mens rea to ensure that only those with intentional or reckless states of mind are held criminally responsible, thereby upholding principles of justice and fairness in legal proceedings.
Motive vs Mens Rea: Impact on Criminal Liability
Motive refers to the underlying reason a person commits a crime, while mens rea signifies the mental intent to engage in unlawful conduct, a crucial element for establishing criminal liability. The presence of mens rea confirms the defendant's culpability, whereas motive, although influential in understanding behavior or intent, generally does not determine legal guilt. Courts prioritize proving mens rea to hold individuals accountable, making motive more relevant to sentencing and context than to the core determination of criminal liability.
Examples to Illustrate Motive and Mens Rea
Motive refers to the reason behind an individual's actions, such as financial gain driving someone to commit theft, while mens rea is the mental state of intent or knowledge of wrongdoing, like knowingly stealing a wallet. For example, a person who steals to feed their family illustrates a clear motive, whereas mens rea is demonstrated when they understand their act is illegal and deliberately proceed. Courts often require proof of mens rea to establish criminal liability, whereas motive helps explain why the crime occurred but is not always necessary for conviction.
Judicial Interpretation of Motive and Mens Rea
Judicial interpretation distinguishes motive as the reason behind committing an act, while mens rea pertains to the defendant's mental state or intent to commit a crime. Courts emphasize mens rea as a crucial element for establishing criminal liability, requiring proof that the defendant had the intent, knowledge, or recklessness regarding the crime. Motive, although informative for understanding why a crime was committed, is generally not required to prove mens rea but can influence sentencing and jury decisions.
Conclusion: The Distinction and Its Legal Significance
Motive explains why a person commits a crime, whereas mens rea refers to the mental state or intent to commit the act. The legal system prioritizes mens rea in establishing criminal liability, as it directly relates to the defendant's culpability and responsibility. Understanding this distinction is crucial for accurate application of criminal law, ensuring fair judgments and appropriate sentencing.
Motive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com