Discovery drives innovation by unveiling new insights and expanding our understanding of the world. It fuels progress across various fields, from science and technology to art and culture, reshaping how we solve problems and create opportunities. Explore the rest of the article to learn how discovery can transform your perspective and impact your life.
Table of Comparison
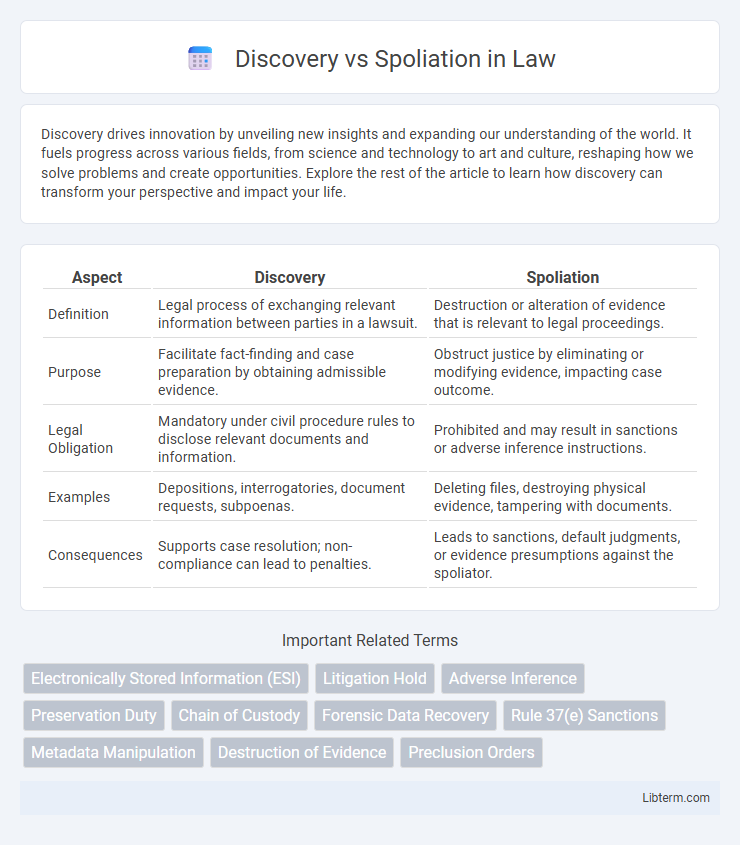
| Aspect | Discovery | Spoliation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal process of exchanging relevant information between parties in a lawsuit. | Destruction or alteration of evidence that is relevant to legal proceedings. |
| Purpose | Facilitate fact-finding and case preparation by obtaining admissible evidence. | Obstruct justice by eliminating or modifying evidence, impacting case outcome. |
| Legal Obligation | Mandatory under civil procedure rules to disclose relevant documents and information. | Prohibited and may result in sanctions or adverse inference instructions. |
| Examples | Depositions, interrogatories, document requests, subpoenas. | Deleting files, destroying physical evidence, tampering with documents. |
| Consequences | Supports case resolution; non-compliance can lead to penalties. | Leads to sanctions, default judgments, or evidence presumptions against the spoliator. |
Introduction to Discovery and Spoliation
Discovery is the pre-trial process in civil litigation where parties exchange relevant information and evidence to build their cases. Spoliation occurs when a party intentionally destroys, alters, or fails to preserve evidence that is crucial to the litigation. Courts impose sanctions for spoliation to deter misconduct and ensure fair access to information during discovery.
Legal Definitions: Discovery vs Spoliation
Discovery refers to the legal process where parties in a lawsuit exchange relevant information and evidence to prepare for trial, governed by specific rules to ensure fairness and transparency. Spoliation entails the intentional, reckless, or negligent destruction, alteration, or concealment of evidence that is relevant to litigation, resulting in legal sanctions such as adverse inference instructions or dismissal of claims. Courts strictly enforce discovery rules to prevent spoliation, protecting the integrity of the judicial process and ensuring that all pertinent evidence is preserved and available.
Importance of Discovery in Litigation
Discovery is crucial in litigation as it enables both parties to obtain essential evidence, clarify facts, and assess the strengths and weaknesses of their cases. Effective discovery reduces surprises at trial, promotes fair settlements, and ensures judicial efficiency by narrowing the issues for adjudication. Failure to properly engage in discovery can lead to spoliation sanctions, severely impacting a party's credibility and case outcome.
Understanding Spoliation of Evidence
Spoliation of evidence refers to the intentional, reckless, or negligent destruction, alteration, or concealment of relevant information during the discovery phase of litigation. Courts impose severe sanctions for spoliation to preserve the integrity of the judicial process, including adverse inference instructions or default judgments against the offending party. Understanding spoliation is critical, as it directly impacts case outcomes and underscores the need for stringent evidence preservation protocols during discovery.
Key Differences Between Discovery and Spoliation
Discovery involves the legal process of exchanging relevant information and evidence between parties in a lawsuit, aiming to ensure transparency and fairness. Spoliation refers to the intentional destruction, alteration, or failure to preserve evidence that is relevant to ongoing or anticipated litigation. The key difference lies in discovery facilitating access to evidence, whereas spoliation obstructs justice by compromising or eliminating critical information.
Common Discovery Methods in Legal Cases
Common discovery methods in legal cases include interrogatories, which are written questions requiring written answers under oath, and depositions, where witnesses provide sworn testimony orally before trial. Requests for production compel parties to submit documents, electronically stored information (ESI), and tangible items relevant to the case. Requests for admission obtain parties' acknowledgment of specific facts to streamline trial issues and reduce evidentiary disputes related to spoliation claims.
Consequences of Spoliation in Court
Spoliation of evidence in court can result in severe consequences such as adverse inference instructions, where the jury is allowed to presume that the destroyed evidence was unfavorable to the spoliator's case. Courts may also impose sanctions including fines, dismissal of claims, or default judgments against the party responsible for spoliation. These penalties encourage preservation of relevant information and uphold the integrity of the judicial process.
Preventing Spoliation During Discovery Process
Preventing spoliation during the discovery process requires implementing robust data preservation protocols, including issuing timely litigation hold notices to relevant parties and ensuring continuous monitoring of electronic evidence. Utilizing advanced data management tools and conducting regular audits helps maintain the integrity and authenticity of critical documents, reducing the risk of inadvertent destruction or alteration. Effective coordination between legal teams and IT departments streamlines compliance with discovery obligations and minimizes potential sanctions linked to spoliation.
Landmark Cases on Discovery and Spoliation
Landmark cases such as Zubulake v. UBS Warburg and Pension Committee of the University of Montreal Pension Plan v. Banc of America Securities LLC have significantly shaped the legal landscape of discovery and spoliation, establishing clear standards for electronic evidence preservation and sanctions. These cases emphasize the duty to preserve relevant evidence once litigation is anticipated and outline remedies for failure to prevent spoliation, including adverse inference instructions and monetary penalties. The rulings underscore the critical role of proactive litigation holds and thorough document management in avoiding spoliation-related consequences.
Best Practices for Managing Evidence and Discovery
Effective management of evidence and discovery requires implementing strict protocols for preserving data integrity and chain of custody to prevent spoliation. Utilizing advanced e-discovery tools supports thorough collection, processing, and review of electronic evidence, reducing the risk of data loss or alteration. Documenting every step of evidence handling ensures compliance with legal standards and strengthens the defensibility of the discovery process.
Discovery Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com