Quo warranto is a legal proceeding used to challenge an individual's right to hold a public office or exercise authority. This process ensures that public officials or entities have the legitimate authority granted by law to perform their duties. Explore the article to understand how quo warranto safeguards the rule of law and protects your rights.
Table of Comparison
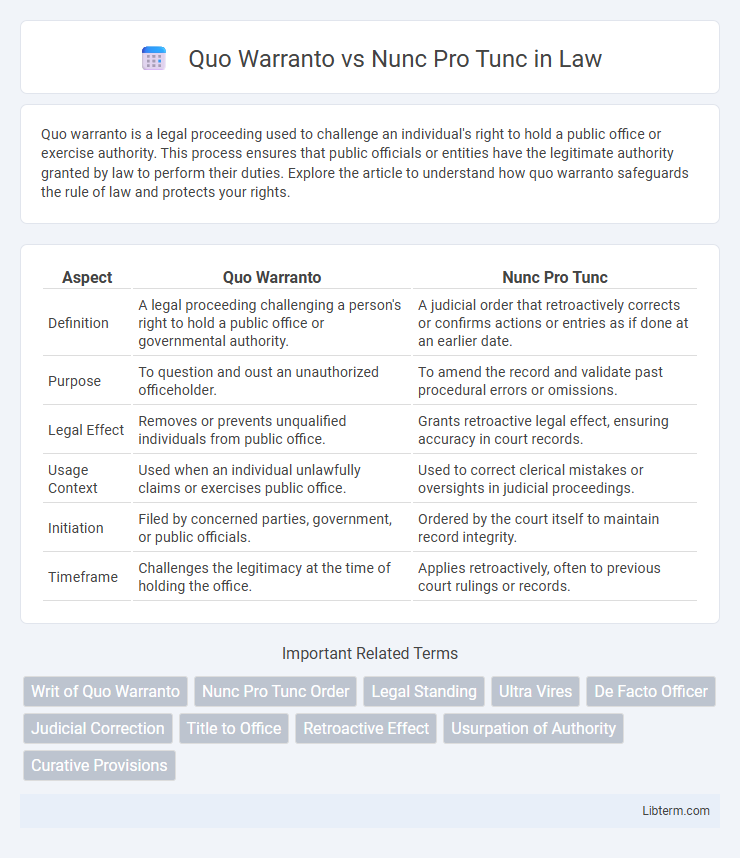
| Aspect | Quo Warranto | Nunc Pro Tunc |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A legal proceeding challenging a person's right to hold a public office or governmental authority. | A judicial order that retroactively corrects or confirms actions or entries as if done at an earlier date. |
| Purpose | To question and oust an unauthorized officeholder. | To amend the record and validate past procedural errors or omissions. |
| Legal Effect | Removes or prevents unqualified individuals from public office. | Grants retroactive legal effect, ensuring accuracy in court records. |
| Usage Context | Used when an individual unlawfully claims or exercises public office. | Used to correct clerical mistakes or oversights in judicial proceedings. |
| Initiation | Filed by concerned parties, government, or public officials. | Ordered by the court itself to maintain record integrity. |
| Timeframe | Challenges the legitimacy at the time of holding the office. | Applies retroactively, often to previous court rulings or records. |
Understanding Quo Warranto: Definition and Purpose
Quo Warranto is a legal proceeding used to challenge an individual's right to hold a public office or governmental authority, questioning the legitimacy of their claim. It serves to protect public interest by ensuring that officeholders meet the qualifications and have not usurped power unlawfully. This writ enforces accountability by requiring the accused to show by what warrant they hold the position.
Nunc Pro Tunc Explained: Meaning and Applications
Nunc Pro Tunc is a Latin legal term meaning "now for then," used to correct or retroactively amend a court record to reflect what should have been done at an earlier date. This procedural tool applies when clerical errors or omissions occur in judgments, orders, or other official documents, ensuring records align with the actual facts or intentions as of the original ruling date. Courts utilize Nunc Pro Tunc to preserve fairness, uphold legal accuracy, and avoid unjust consequences stemming from administrative mistakes without reopening substantive issues.
Historical Origins of Quo Warranto and Nunc Pro Tunc
Quo Warranto originated in medieval English law as a legal procedure used by the Crown to challenge individuals or corporations exercising authority without legal right, dating back to the 13th century. Nunc Pro Tunc, derived from Latin meaning "now for then," evolved within common law courts to allow retroactive judicial orders correcting earlier omissions or errors, ensuring fairness in legal records. Both doctrines have distinct historical foundations, with Quo Warranto centered on legitimacy of authority and Nunc Pro Tunc focused on the rectification of judicial record-keeping.
Legal Procedures for Filing Quo Warranto
The legal procedure for filing Quo Warranto involves submitting a verified petition to the appropriate court challenging a person's right to hold a public office or exercise a franchise, typically supported by evidence showing usurpation or illegal holding of authority. The court then issues a writ commanding the respondent to show by what authority they hold the office, ensuring protection of public interest and legality in public service. Nunc Pro Tunc, on the other hand, refers to a court's power to correct errors in its records retrospectively and does not substitute or affect the procedural requirements of filing a Quo Warranto petition.
How Nunc Pro Tunc Orders Are Issued
Nunc Pro Tunc orders are issued by courts to correct clerical or procedural errors in previous judgments, effectively retroactively validating actions as if they were performed on an earlier date. These orders apply when the court record fails to reflect what was actually decided or intended at the time of the original ruling. Unlike Quo Warranto, which challenges the legal right of a person to hold public office, Nunc Pro Tunc serves to amend official records without altering substantive legal rights.
Key Differences Between Quo Warranto and Nunc Pro Tunc
Quo Warranto challenges an individual's legal right to hold a public office or governmental position, focusing on the authority and legitimacy of the officeholder. Nunc Pro Tunc refers to court orders or judgments entered retroactively to correct clerical errors or oversights, effectively making records reflect what should have been done earlier. The key difference lies in Quo Warranto being a procedural action questioning authority, while Nunc Pro Tunc is a judicial mechanism for correcting past procedural mistakes without altering substantive rights.
Common Situations for Using Quo Warranto
Quo Warranto is commonly used to challenge a person's right to hold a public office or exercise authority when the legitimacy of such authority is in question. This legal writ is filed to prevent usurpation of official functions, often by questioning the qualifications, appointment procedures, or validity of tenure. Unlike Nunc Pro Tunc, which corrects clerical errors in court records retroactively, Quo Warranto serves as a proactive tool to uphold lawful governance and public accountability.
When to Seek a Nunc Pro Tunc Judgment
A Nunc Pro Tunc judgment is sought to correct clerical errors or omissions in a court's record, reflecting what was actually decided but not properly documented at the time. This type of judgment is appropriate when the court has already made a decision, but the official record fails to show it accurately, ensuring the judicial record aligns with the truth retroactively. In contrast, a Quo Warranto proceeding challenges a person's right to hold office or exercise authority, not merely the correction of court records.
Landmark Cases Involving Quo Warranto and Nunc Pro Tunc
Landmark cases involving Quo Warranto, such as *Marbury v. Madison* (1803), established the principle that courts can question the validity of a person's claim to public office or authority, reinforcing judicial oversight over governmental acts. In contrast, pivotal Nunc Pro Tunc cases like *United States v. Minker* (1958) demonstrated the court's power to retroactively correct clerical errors in judgments to uphold fairness and accuracy without affecting substantive rights. These cases collectively underscore the judiciary's role in both challenging unauthorized authority through Quo Warranto and ensuring procedural correctness via Nunc Pro Tunc orders.
Practical Implications in Modern Legal Practice
Quo Warranto actions challenge an individual's right to hold a public office, ensuring legal authority is properly validated, while Nunc Pro Tunc orders correct clerical errors in court records retroactively to reflect the true intent of prior rulings. In modern legal practice, Quo Warranto serves as a crucial mechanism for public accountability and legitimacy of government officials, whereas Nunc Pro Tunc facilitates procedural accuracy without altering substantive rights. Both tools optimize judicial efficiency by addressing distinct issues: one verifies authority, the other preserves record integrity.
Quo Warranto Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com