Partitioning your hard drive can significantly improve system organization and data management by separating operating system files from personal data and applications. Proper partitioning enhances security and can simplify backup processes, reducing the risk of data loss and system crashes. Explore the full article to learn how to effectively partition your drive and optimize your computer's performance.
Table of Comparison
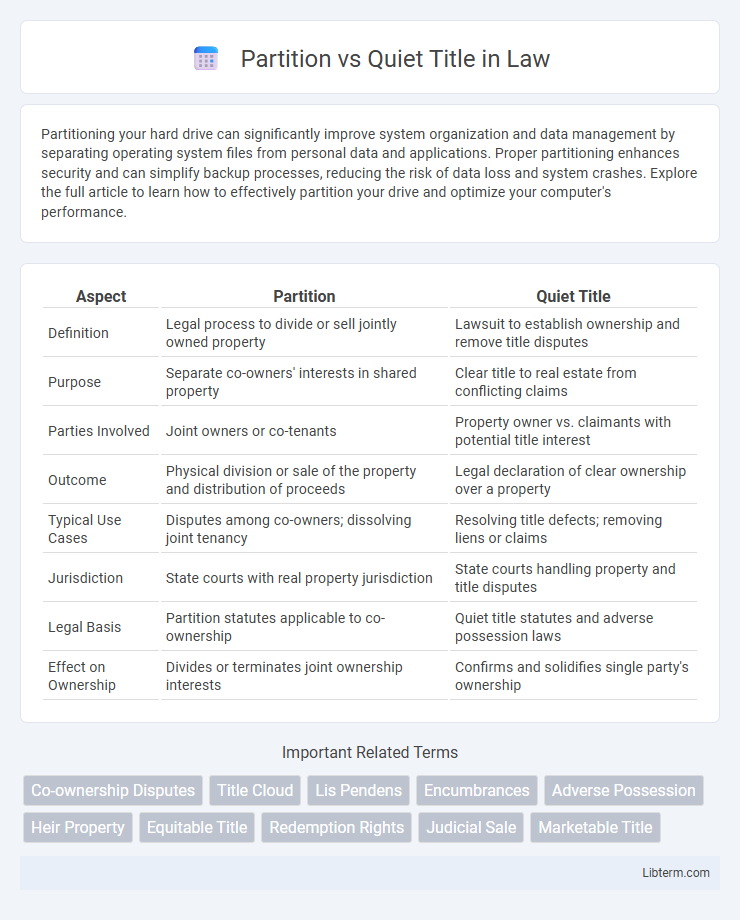
| Aspect | Partition | Quiet Title |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal process to divide or sell jointly owned property | Lawsuit to establish ownership and remove title disputes |
| Purpose | Separate co-owners' interests in shared property | Clear title to real estate from conflicting claims |
| Parties Involved | Joint owners or co-tenants | Property owner vs. claimants with potential title interest |
| Outcome | Physical division or sale of the property and distribution of proceeds | Legal declaration of clear ownership over a property |
| Typical Use Cases | Disputes among co-owners; dissolving joint tenancy | Resolving title defects; removing liens or claims |
| Jurisdiction | State courts with real property jurisdiction | State courts handling property and title disputes |
| Legal Basis | Partition statutes applicable to co-ownership | Quiet title statutes and adverse possession laws |
| Effect on Ownership | Divides or terminates joint ownership interests | Confirms and solidifies single party's ownership |
Understanding Partition and Quiet Title Actions
Partition actions involve dividing jointly owned property among co-owners, either physically or through sale, to resolve ownership disputes and ensure fair distribution. Quiet title actions serve to establish or clarify property ownership by removing clouds, liens, or claims against the title, securing clear legal proof of ownership. Understanding the specific goals and procedures of both helps property owners effectively resolve different types of ownership conflicts.
Key Differences Between Partition and Quiet Title
Partition resolves disputes by physically dividing or selling property among co-owners to distribute ownership shares, while quiet title focuses on establishing clear ownership and removing claims or liens on a property. Key differences include that partition actions involve multiple parties seeking to separate joint interests, whereas quiet title suits typically address a single owner's effort to confirm legal title. Partition results in the division or sale of property, but quiet title produces a judicial declaration clarifying rights without altering property possession.
When to File a Partition Lawsuit
A partition lawsuit should be filed when co-owners of real property cannot agree on how to divide or sell the shared property, often due to disagreements about usage, responsibilities, or disposition. This legal action is appropriate when physical division of the property is feasible or a sale is necessary to distribute proceeds fairly among owners. Timing is critical, as filing occurs after failed negotiations, ensuring the court can equitably resolve ownership disputes and prevent prolonged conflicts.
Situations Warranting a Quiet Title Action
Quiet title actions are warranted in situations where property ownership is disputed, unclear, or burdened by a cloud on the title due to claims, liens, or legal defects. This legal remedy is essential for resolving ownership disputes without dividing the property, unlike partition actions that physically separate co-owned real estate. Quiet title is particularly used when a single party seeks to establish clear title against adverse claims, boundary disputes, or title defects after inheritance, foreclosure, or tax sales.
Legal Procedures for Partition Cases
Partition cases initiate legal procedures that require filing a lawsuit to divide jointly owned property among co-owners, often resulting in physical division or sale with proceeds distributed accordingly. The court examines ownership interests, property valuation, and potential buyout options while ensuring equitable division based on recorded deeds or agreements. Unlike quiet title actions that seek to resolve ownership disputes, partition suits focus on the physical or financial separation of property interests through formal judicial intervention.
Legal Steps in a Quiet Title Lawsuit
A quiet title lawsuit involves filing a complaint in the appropriate court to establish clear ownership of contested property by resolving disputes over claims or liens. Legal steps include providing evidence of ownership, notifying all parties with potential claims, and obtaining a court order that declares the plaintiff as the rightful owner, thereby removing any conflicting claims. This process differs from partition actions, which focus on dividing property among co-owners rather than eliminating competing ownership interests.
Common Disputes in Partition Actions
Common disputes in partition actions often involve disagreements over property boundaries, unequal contributions to property improvements, and conflicting claims to ownership shares. Partition suits may also arise when co-owners cannot agree on whether to sell or divide the property physically. In contrast, quiet title actions primarily address disputes over the validity of title or ownership claims rather than the division or use of the property itself.
Typical Issues Resolved by Quiet Title
Quiet title actions typically resolve disputes over property ownership, such as unclear titles caused by forgery, liens, or conflicting claims from heirs or contractors. These legal proceedings help clear title defects, enabling owners to sell, refinance, or develop property without ownership challenges. Quiet title is particularly effective in settling boundary disagreements, removing clouds on title, and confirming rightful ownership.
Pros and Cons: Partition vs. Quiet Title
Partition actions allow multiple property owners to divide or sell shared real estate based on their ownership interests, providing a clear resolution to ownership disputes but often resulting in lengthy and costly court proceedings. Quiet title suits those seeking to establish or confirm clear ownership by removing adverse claims or liens on a property with potentially faster resolution, though it may not physically divide the property or address disputes among co-owners. Choosing partition offers a physical division of property but can increase expenses and complexity, whereas quiet title prioritizes legal clarity without altering property boundaries, possibly leaving co-ownership conflicts unresolved.
Choosing the Right Legal Remedy for Property Disputes
Partition suits divide co-owned property among owners by physically splitting or selling assets, ideal for resolving disputes among multiple parties with shared interests. Quiet title actions eliminate adverse claims by confirming clear ownership, often used when ownership disputes stem from unclear titles or conflicting records. Selecting the right legal remedy hinges on whether the goal is to physically separate ownership interests or to clarify title and remove clouds on property ownership.
Partition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com