A joint venture combines resources and expertise from two or more parties to achieve a specific business goal, sharing risks and rewards. This strategic partnership enhances market reach, innovation, and operational efficiency, making it ideal for expanding your business presence. Discover how joint ventures can transform your growth strategy by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
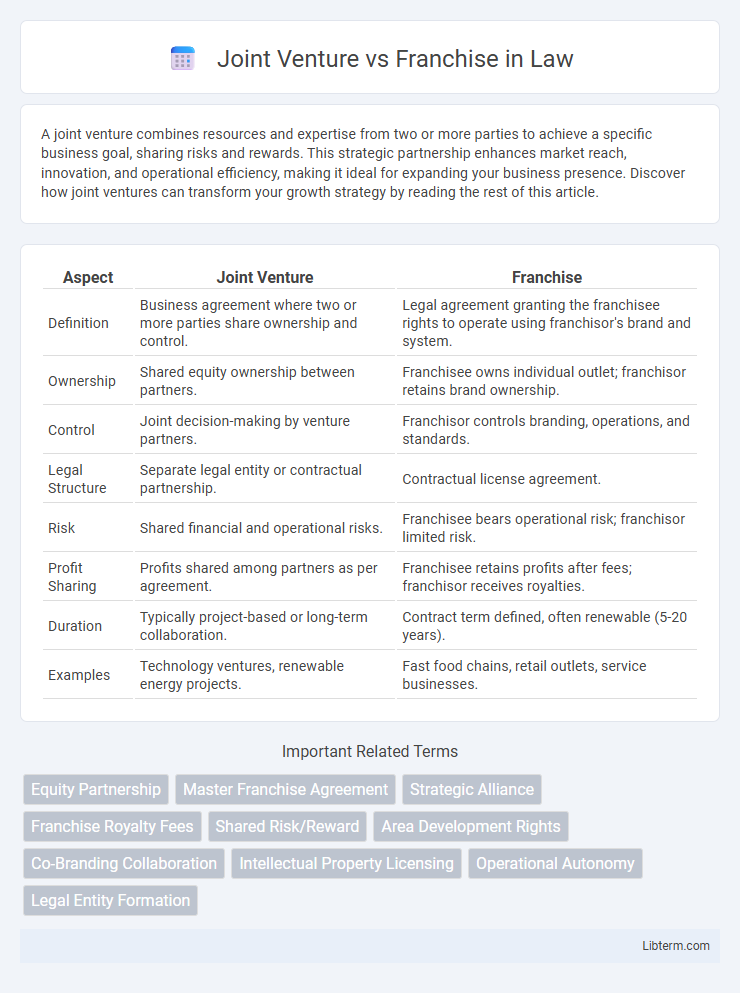
| Aspect | Joint Venture | Franchise |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Business agreement where two or more parties share ownership and control. | Legal agreement granting the franchisee rights to operate using franchisor's brand and system. |
| Ownership | Shared equity ownership between partners. | Franchisee owns individual outlet; franchisor retains brand ownership. |
| Control | Joint decision-making by venture partners. | Franchisor controls branding, operations, and standards. |
| Legal Structure | Separate legal entity or contractual partnership. | Contractual license agreement. |
| Risk | Shared financial and operational risks. | Franchisee bears operational risk; franchisor limited risk. |
| Profit Sharing | Profits shared among partners as per agreement. | Franchisee retains profits after fees; franchisor receives royalties. |
| Duration | Typically project-based or long-term collaboration. | Contract term defined, often renewable (5-20 years). |
| Examples | Technology ventures, renewable energy projects. | Fast food chains, retail outlets, service businesses. |
Introduction to Joint Ventures and Franchises
Joint ventures involve two or more parties pooling resources to pursue a specific business goal, sharing profits, losses, and control based on their agreement. Franchises enable individuals or entities to operate a business using the established brand, systems, and support of the franchisor in exchange for fees and royalties. Both models offer distinct approaches to expansion and collaboration, with joint ventures emphasizing partnership and shared ownership, while franchises focus on replicating a proven business format.
Definition and Key Features of a Joint Venture
A joint venture is a business arrangement where two or more parties collaborate by pooling resources, expertise, and capital to achieve a common goal while sharing profits, losses, and control. Key features include shared ownership, mutual decision-making, and a partnership established for a specific project or business activity, often with a defined duration. Unlike franchises, joint ventures involve direct collaboration and combined management rather than brand licensing and standardized operational methods.
Definition and Key Features of a Franchise
A franchise is a business model where a franchisor grants the franchisee the rights to operate under its brand, using its trademark, business system, and support services. Key features include standardized products or services, ongoing training, marketing assistance, and adherence to the franchisor's established operational guidelines. Unlike a joint venture, a franchise maintains brand consistency while allowing independent ownership and management by the franchisee.
Ownership Structure: Joint Venture vs Franchise
A joint venture involves shared ownership between two or more parties who contribute resources, share risks, and have mutual control over business operations. In contrast, a franchise is a licensing arrangement where the franchisee owns and operates individual outlets under the franchisor's established brand and business model but with limited autonomy. Ownership in joint ventures is collective and collaborative, whereas franchise ownership is independent but governed by franchisor agreements.
Control and Decision-Making Differences
Joint ventures involve shared control and collaborative decision-making between partners, allowing each party to influence operational strategies and resource allocation. Franchises maintain centralized control by the franchisor, who sets strict guidelines and standards, limiting the franchisee's autonomy in daily operations and marketing decisions. This distinction significantly impacts the level of independence and strategic input experienced by participants in each business model.
Legal Agreements and Obligations
Joint ventures require detailed legal agreements that define ownership shares, profit distribution, decision-making authority, and liability among partners, ensuring clear obligations and risk management. Franchise agreements establish the franchisor's control over brand use, operational standards, fees, and territorial rights, while imposing obligations on the franchisee to maintain brand consistency and comply with business practices. Both structures involve binding contractual commitments, but joint ventures emphasize shared management responsibilities, whereas franchises focus on brand licensing and operational compliance.
Financial Investment and Profit Sharing
Joint ventures typically require a substantial financial investment from all parties involved, with profits--and losses--shared according to each partner's equity stake, offering a direct impact on returns based on ownership percentage. Franchises demand an initial franchise fee plus ongoing royalties, creating a fixed cost structure where the franchisee retains most profits after fees, but operates under the franchisor's established brand and business model. Investment risk is generally higher and more variable in joint ventures, while franchises provide more predictable financial commitments and profit margins within a defined operational framework.
Risk and Liability Comparison
Joint ventures involve shared risk and liability between partners, with each party typically responsible for their contributions and obligations, spreading financial exposure and operational risks. Franchises place most liability on the franchisee, who assumes operational risks and financial responsibilities while the franchisor maintains overarching control and brand reputation risks. Liability in joint ventures can be more complex due to shared ownership, whereas franchise risk is more compartmentalized but depends heavily on the franchisee's management and compliance with franchise agreements.
Pros and Cons of Joint Ventures
Joint ventures offer strategic advantages such as shared resources, diversified expertise, and reduced financial risk, enabling entry into new markets with local partner insights. However, potential drawbacks include complex decision-making processes, conflicts of interest between partners, and challenges in aligning long-term business goals. Legal and financial liabilities are often shared, which can increase exposure if one partner underperforms or faces disputes.
Pros and Cons of Franchises
Franchises offer the advantage of established brand recognition, proven business models, and ongoing support from the franchisor, which reduces startup risks and accelerates market entry. However, franchises often require significant initial investment and ongoing royalty payments, limiting financial flexibility and profit potential for the franchisee. Strict operational guidelines and lack of autonomy can hinder innovation and adaptation to local market conditions.
Joint Venture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com