A plurality opinion represents the view supported by the largest number of judges or justices but lacks a majority. This opinion helps clarify the court's reasoning when no single rationale commands a majority, impacting legal interpretations and future rulings. Explore the rest of the article to understand how plurality opinions influence judicial decisions and your legal rights.
Table of Comparison
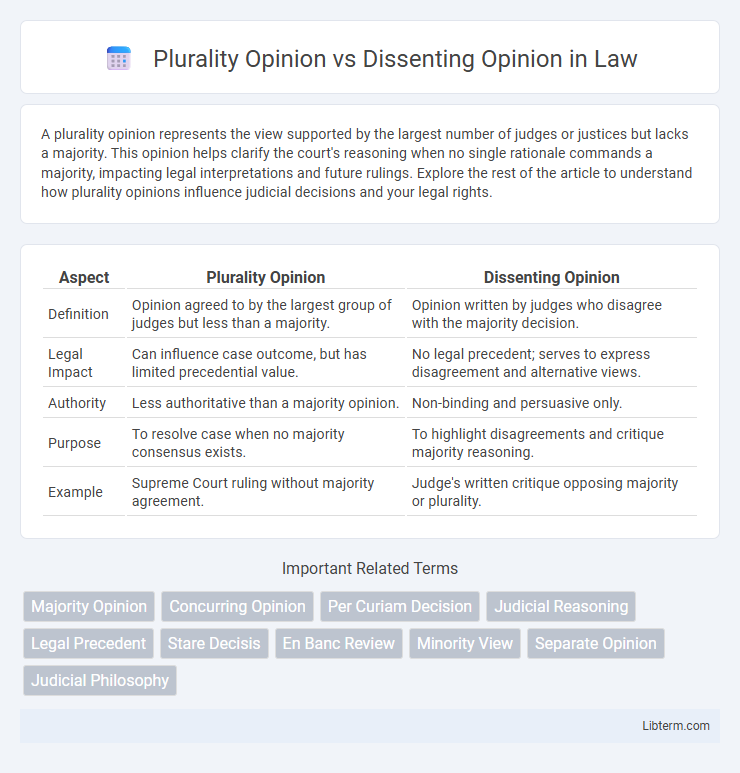
| Aspect | Plurality Opinion | Dissenting Opinion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Opinion agreed to by the largest group of judges but less than a majority. | Opinion written by judges who disagree with the majority decision. |
| Legal Impact | Can influence case outcome, but has limited precedential value. | No legal precedent; serves to express disagreement and alternative views. |
| Authority | Less authoritative than a majority opinion. | Non-binding and persuasive only. |
| Purpose | To resolve case when no majority consensus exists. | To highlight disagreements and critique majority reasoning. |
| Example | Supreme Court ruling without majority agreement. | Judge's written critique opposing majority or plurality. |
Understanding Plurality and Dissenting Opinions
Plurality opinions occur when a majority of judges agree on the outcome but not on the reasoning, resulting in no single rationale commanding a majority, which can complicate legal precedents. Dissenting opinions express disagreement with the majority's decision and reasoning, offering alternative legal interpretations that may influence future cases. Understanding the distinction helps clarify how courts reach decisions and the impact of differing judicial views on case law development.
Definition of a Plurality Opinion
A plurality opinion occurs when no single rationale receives a majority of the justices' support, resulting in the opinion with the most votes but less than a majority. It represents the court's decision without establishing a binding precedent for lower courts. Unlike dissenting opinions, which express disagreement, a plurality opinion reflects the controlling outcome when the court cannot produce a majority consensus.
Key Features of Plurality Opinions
Plurality opinions occur when no single opinion receives a majority of the judges' support, resulting in the opinion with the most votes serving as the court's decision without establishing binding precedent. These opinions provide key insights into the reasoning of several judges but lack the authoritative weight of a majority opinion, often leading to interpretative challenges in lower courts. Plurality opinions contrast with dissenting opinions, where judges express disagreement with the majority's ruling rather than contributing to the controlling judgment.
What is a Dissenting Opinion?
A dissenting opinion is a written statement by one or more judges expressing disagreement with the majority or plurality opinion in a court case. It provides an alternative legal reasoning or interpretation of the law, often highlighting different views on the facts or the application of legal principles. Unlike the majority opinion, a dissenting opinion does not have binding authority but can influence future legal arguments and judicial decisions.
Core Characteristics of Dissenting Opinions
Dissenting opinions express disagreement with the majority ruling, providing alternative legal reasoning that challenges the Court's interpretation of law or facts. They do not establish binding precedent but can influence future cases by highlighting different perspectives on constitutional or statutory issues. The core characteristics of dissenting opinions include their role in fostering judicial debate, preserving minority viewpoints, and shaping legal evolution over time.
Major Differences Between Plurality and Dissenting Opinions
Plurality opinions occur when no single rationale gains majority support, resulting in the opinion with the most votes but less than a majority, while dissenting opinions reflect disagreement with the majority's decision. Plurality opinions influence legal precedent with limited authoritative value compared to majority opinions, whereas dissenting opinions do not hold precedential weight but can impact future legal reasoning and reforms. The core difference lies in plurality opinions representing a fractured majority's rationale, contrasted by dissenting opinions expressing outright opposition to the outcome.
Legal Impact of Plurality vs Dissenting Opinions
Plurality opinions hold the most votes but lack a majority, limiting their precedential value and often leading lower courts to treat them as persuasive rather than binding authority. Dissenting opinions, while not legally binding, can influence future legal reasoning, legislative changes, and eventual majority rulings by highlighting alternative interpretations or critiques of the majority's legal rationale. The legal impact of plurality opinions is generally narrower and more uncertain, whereas dissenting opinions serve as important tools for legal evolution and doctrinal development over time.
Historical Examples in Supreme Court Cases
Plurality opinions in Supreme Court cases, such as in the 1973 case *Regents of the University of California v. Bakke*, reflect the views of the largest group of justices when no majority is reached, shaping legal interpretations without creating binding precedent. Dissenting opinions, exemplified by Justice John Marshall Harlan's famous dissent in *Plessy v. Ferguson* (1896), play a crucial role by challenging the Court's majority and influencing future legal developments. These opinions highlight the dynamic interplay between consensus and conflict within the Court's history, impacting constitutional law and societal values.
Implications for Future Legal Precedent
Plurality opinions, which lack a majority agreement, hold less precedential weight and often lead to ambiguity in future legal rulings. Dissenting opinions, while not legally binding, can influence future jurisprudence by highlighting alternative interpretations and prompting later courts to reconsider established laws. The distinction between plurality and dissenting opinions plays a critical role in shaping the stability and evolution of legal precedent.
Importance of Both Opinions in Judicial Decisions
Plurality opinions, representing the judgment without a majority agreement on reasoning, clarify the controlling legal principles in complex cases, guiding lower courts and future decisions. Dissenting opinions highlight alternative legal interpretations and potential consequences, fostering robust judicial debate and influencing the evolution of case law over time. Both opinions are essential for a balanced legal system, as they contribute to transparency, development of legal doctrine, and protection of minority viewpoints within the judiciary.
Plurality Opinion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com