Jurisdiction defines the legal authority of a court or governing body to hear and decide cases within a specific geographic area or over certain types of legal matters. Understanding jurisdiction is crucial for ensuring your case is filed in the correct court, avoiding delays or dismissals. Explore the article to learn more about different types of jurisdiction and their impact on legal proceedings.
Table of Comparison
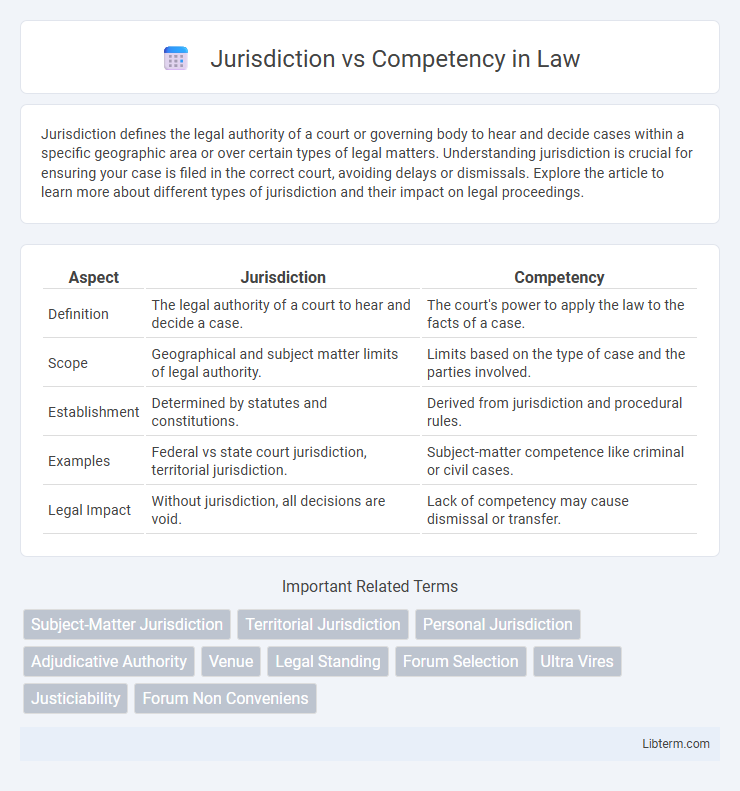
| Aspect | Jurisdiction | Competency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The legal authority of a court to hear and decide a case. | The court's power to apply the law to the facts of a case. |
| Scope | Geographical and subject matter limits of legal authority. | Limits based on the type of case and the parties involved. |
| Establishment | Determined by statutes and constitutions. | Derived from jurisdiction and procedural rules. |
| Examples | Federal vs state court jurisdiction, territorial jurisdiction. | Subject-matter competence like criminal or civil cases. |
| Legal Impact | Without jurisdiction, all decisions are void. | Lack of competency may cause dismissal or transfer. |
Understanding Jurisdiction and Competency
Jurisdiction refers to the legal authority granted to a court or tribunal to hear and decide cases within a specific geographic area or subject matter. Competency, on the other hand, defines the court's power to adjudicate a particular type of case or issue based on legal capacity and procedural requirements. Understanding jurisdiction and competency is essential for determining which court has the rightful authority to preside over a legal dispute and ensure valid, enforceable judgments.
Definitions: Jurisdiction vs Competency
Jurisdiction refers to the legal authority granted to a court to hear and decide cases within a specific geographic area or over particular types of legal matters. Competency, on the other hand, relates to a court's power to adjudicate cases based on the subject matter or the qualifications of the parties involved, ensuring proper authority and capacity to render judgment. Understanding the distinctions between jurisdiction and competency is crucial for determining the validity of a court's decision-making power in various legal proceedings.
Types of Jurisdiction in Law
Jurisdiction in law refers to a court's authority to hear and decide cases, categorized into subject-matter jurisdiction, personal jurisdiction, and territorial jurisdiction. Subject-matter jurisdiction defines the specific types of cases a court can adjudicate, such as criminal, civil, or family law matters. Personal jurisdiction involves the court's power over the parties involved, while territorial jurisdiction restricts authority to a particular geographic area.
Types of Competency in Legal Proceedings
Jurisdiction defines a court's authority to hear a case based on geographic location or subject matter, while competency refers to the court's ability to properly adjudicate a case considering procedural and substantive criteria. Types of competency in legal proceedings include subject-matter competency, which ensures the court can decide the issue presented; territorial competency, determining if the court's geographic scope covers the case; and personal competency, ensuring the court has authority over the parties involved. Competency also encompasses functional competency, addressing whether the court can exercise specific powers in the proceeding, and temporal competency, evaluating if the timing of the court's intervention aligns with procedural rules.
Key Differences Between Jurisdiction and Competency
Jurisdiction defines the court's legal authority to hear and decide a case based on geographic area or subject matter, while competency refers to the court's procedural power to adjudicate a case properly. Jurisdiction is generally established by law or constitution, determining if a court can exercise power over persons or property involved. Competency ensures the court meets all procedural and substantive requirements to render a valid judgment within its jurisdictional scope.
Importance of Jurisdiction in Legal Cases
Jurisdiction determines the authority of a court to hear and decide a case, making it a fundamental aspect of the legal process. Without proper jurisdiction, any judgment rendered may be declared void or unenforceable, emphasizing its critical role in upholding the rule of law. Legal disputes must be initiated in courts with subject-matter and territorial jurisdiction to ensure fairness and procedural validity.
The Role of Competency in Court Decisions
Competency plays a critical role in court decisions by determining whether a court has the legal capacity to hear and decide a specific case based on the subject matter, parties involved, or geographic area. Unlike jurisdiction, which defines the court's overall authority, competency ensures that the court is the proper venue to adjudicate issues fairly and effectively. Courts lacking competency may dismiss or transfer cases, safeguarding judicial process integrity and preventing improper adjudication.
Jurisdiction and Competency: Examples in Practice
Jurisdiction refers to a court's legal authority to hear and decide a case, often defined by geographic location or subject matter, such as a family court handling divorce cases within a specific state. Competency involves the court's or judge's ability to properly manage and rule on a case, including factors like the mental capacity of parties or the appropriateness of the procedure. For example, a state court may have jurisdiction over a contract dispute occurring within its borders, while competency issues arise if a party is deemed legally incapable of representing themselves during the trial.
Challenges in Determining Jurisdiction and Competency
Challenges in determining jurisdiction and competency often arise from overlapping legal authorities and ambiguous statutory provisions, causing confusion over which court or tribunal has the power to hear a case. Conflicting interpretations of jurisdictional boundaries can delay proceedings and increase litigation costs, while competency issues related to a court's subject matter expertise may impact the quality and fairness of judicial decisions. Ensuring clear legislative guidelines and consistent jurisdictional doctrines is critical to resolving disputes effectively and maintaining judicial efficiency.
Impact of Jurisdiction and Competency on Legal Outcomes
Jurisdiction determines the court's authority to hear a case, directly influencing where a legal dispute is resolved and ensuring the applicable laws are correctly applied. Competency refers to the court's power to decide specific types of cases, affecting the validity and enforceability of its judgments. Misalignment or lack of proper jurisdiction and competency can lead to dismissal, retrial, or appeals, significantly altering legal outcomes and procedural efficiency.
Jurisdiction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com