Judicial error occurs when a court makes a mistake in applying the law, interpreting evidence, or procedural rulings that impact the outcome of a case. These errors can lead to unfair verdicts, misinterpretation of legal principles, and potential miscarriages of justice. Explore the rest of the article to understand how judicial errors affect legal proceedings and what remedies are available to protect your rights.
Table of Comparison
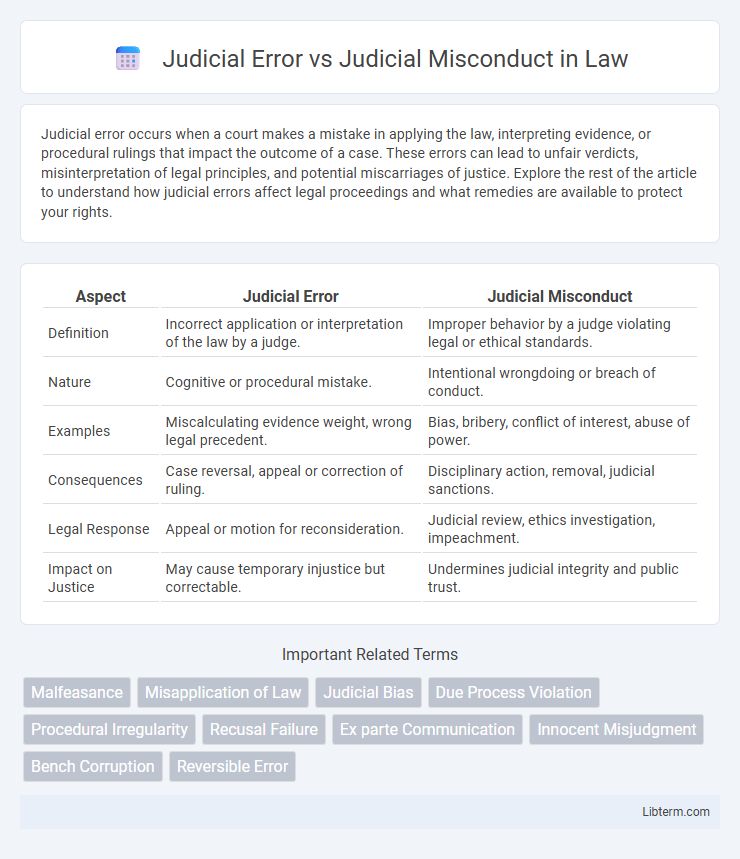
| Aspect | Judicial Error | Judicial Misconduct |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Incorrect application or interpretation of the law by a judge. | Improper behavior by a judge violating legal or ethical standards. |
| Nature | Cognitive or procedural mistake. | Intentional wrongdoing or breach of conduct. |
| Examples | Miscalculating evidence weight, wrong legal precedent. | Bias, bribery, conflict of interest, abuse of power. |
| Consequences | Case reversal, appeal or correction of ruling. | Disciplinary action, removal, judicial sanctions. |
| Legal Response | Appeal or motion for reconsideration. | Judicial review, ethics investigation, impeachment. |
| Impact on Justice | May cause temporary injustice but correctable. | Undermines judicial integrity and public trust. |
Understanding Judicial Error: Definition and Examples
Judicial error refers to a mistake or oversight made by a judge in interpreting or applying the law, often occurring during trials or legal rulings. Examples include errors in evidentiary rulings, misapplication of legal standards, or procedural mistakes that do not involve ethical violations or intentional wrongdoing. Understanding judicial error helps distinguish these unintentional mistakes from judicial misconduct, which involves unethical or illegal behavior by judges.
What Constitutes Judicial Misconduct?
Judicial misconduct refers to actions by judges that violate ethical standards, such as bias, corruption, or abuse of authority, undermining the integrity of the judicial process. It involves intentional or reckless behavior that compromises a judge's impartiality, including accepting bribes, engaging in conflicts of interest, or demonstrating prejudice during proceedings. Unlike judicial error, which pertains to mistakes in applying the law or fact-finding, judicial misconduct involves unethical or illegal conduct that can lead to disciplinary measures or removal from office.
Key Differences Between Judicial Error and Judicial Misconduct
Judicial error refers to mistakes or incorrect decisions made by judges during legal proceedings, often arising from misinterpretation of law or factual inaccuracies, whereas judicial misconduct involves unethical or illegal behavior such as bias, corruption, or abuse of authority. The key difference lies in intent and ethical violation: judicial error is usually unintentional and subject to correction through appeals, while judicial misconduct undermines judicial integrity and may result in disciplinary action or removal. Understanding this distinction is critical for maintaining trust in the justice system and ensuring accountability among judiciary members.
Causes of Judicial Error in the Legal System
Judicial error in the legal system often stems from misinterpretation of laws, inadequate evidence evaluation, or cognitive biases affecting judges' decisions. These errors can arise due to insufficient legal knowledge, procedural mistakes, or external pressures influencing judicial impartiality. Understanding causes like flawed fact-finding, reliance on incorrect legal precedents, and communication breakdowns is essential to improve judicial accuracy and fairness.
Common Forms of Judicial Misconduct
Common forms of judicial misconduct include bias or prejudice, abuse of power, improper communication with parties involved in a case, and failure to disqualify oneself from proceedings where a conflict of interest exists. Unlike judicial error, which involves mistakes in legal reasoning or procedure, judicial misconduct undermines the integrity and impartiality of the judiciary. Examples also encompass accepting bribes, violating judicial codes of ethics, and engaging in discriminatory behavior.
Legal Consequences of Judicial Error
Judicial error involves mistakes made by a judge in applying the law or assessing facts, which can lead to the reversal or remand of a case on appeal. The legal consequences typically include the correction of the error through appellate review without necessarily implying wrongdoing or ethical violations. Judicial misconduct, by contrast, involves unethical or illegal actions by a judge that may result in disciplinary proceedings, removal from office, or sanctions beyond case retrial or reversal.
Disciplinary Measures for Judicial Misconduct
Judicial misconduct refers to improper behavior or unethical actions by judges that violate codes of judicial ethics, distinct from judicial errors which are mistakes in legal judgment. Disciplinary measures for judicial misconduct include censure, suspension, removal from office, and in severe cases, criminal prosecution. These sanctions are enforced by judicial conduct commissions or oversight bodies to uphold judicial integrity and public trust.
Impact on Public Trust: Error vs. Misconduct
Judicial error involves unintentional mistakes in legal decision-making that may temporarily affect case outcomes but generally do not erode public trust significantly when corrected through appeals. In contrast, judicial misconduct, characterized by unethical or illegal behavior such as bias or corruption, severely damages public confidence in the justice system and undermines its legitimacy. Maintaining transparency and accountability in addressing misconduct is crucial to restoring faith in judicial institutions.
Prevention Strategies for Judicial Error and Misconduct
Effective prevention strategies for judicial error and misconduct include comprehensive judicial training programs focusing on ethical standards, procedural accuracy, and bias awareness. Implementing robust oversight mechanisms such as independent review boards and regular performance evaluations ensures accountability and early detection of errors or misconduct. Enhancing transparency through open court proceedings and accessible complaint systems empowers stakeholders to report concerns promptly, fostering a culture of judicial integrity.
Case Studies Highlighting Error and Misconduct in the Judiciary
Case studies reveal that judicial error often stems from misinterpretation of law or procedural mistakes, as seen in the wrongful conviction of Anthony Ray Hinton due to flawed ballistic evidence evaluation. Judicial misconduct, by contrast, involves unethical behaviors like bias, corruption, or conflicts of interest, exemplified by the scandal surrounding former judge Mark Ciavarella, who accepted kickbacks for imposing harsh sentences. These cases underscore the critical need for judicial accountability mechanisms to prevent miscarriages of justice caused by both error and misconduct.
Judicial Error Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com