A verdict represents the final decision rendered by a judge or jury in a legal case, determining the outcome based on the evidence presented. Understanding the types of verdicts and their implications can clarify how justice is served and what consequences may follow. Explore the rest of the article to gain deeper insights into how verdicts impact your legal rights and responsibilities.
Table of Comparison
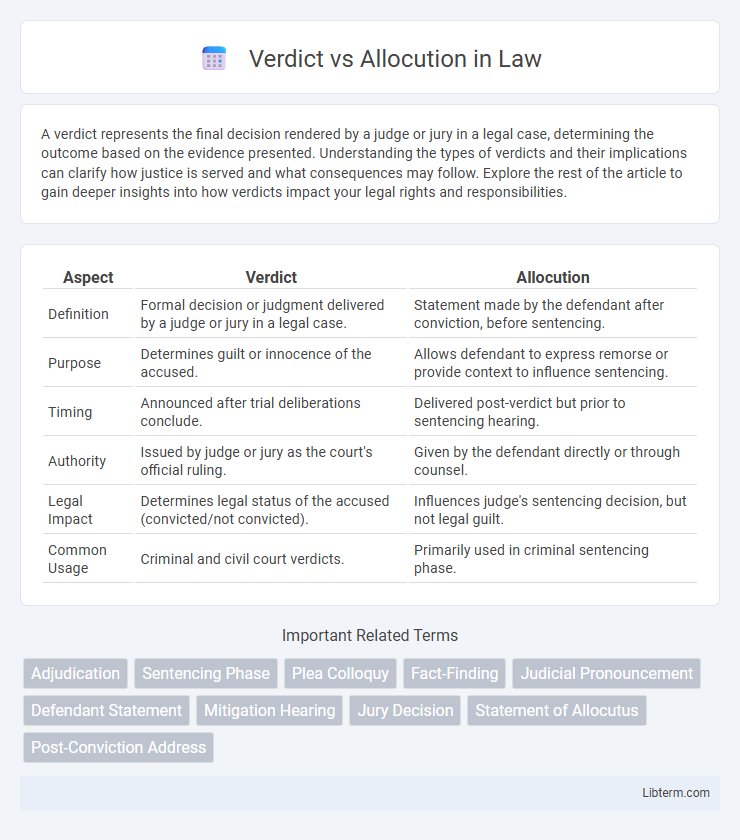
| Aspect | Verdict | Allocution |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal decision or judgment delivered by a judge or jury in a legal case. | Statement made by the defendant after conviction, before sentencing. |
| Purpose | Determines guilt or innocence of the accused. | Allows defendant to express remorse or provide context to influence sentencing. |
| Timing | Announced after trial deliberations conclude. | Delivered post-verdict but prior to sentencing hearing. |
| Authority | Issued by judge or jury as the court's official ruling. | Given by the defendant directly or through counsel. |
| Legal Impact | Determines legal status of the accused (convicted/not convicted). | Influences judge's sentencing decision, but not legal guilt. |
| Common Usage | Criminal and civil court verdicts. | Primarily used in criminal sentencing phase. |
Understanding the Concept of Verdict
A verdict is the formal decision or finding made by a judge or jury at the conclusion of a trial, determining the guilt or innocence of the defendant based on the evidence presented. It is a critical component of the judicial process that directly impacts the outcome of a case and the subsequent sentencing phase. Understanding the concept of verdict involves recognizing its role as the official resolution of legal disputes, distinct from allocution, which refers to the defendant's opportunity to speak before sentencing.
What is Allocution?
Allocution is a formal opportunity given to a defendant to speak directly to the court before sentencing, allowing them to express remorse, explain circumstances, or present mitigating factors. Unlike the verdict, which determines guilt or innocence, allocution focuses on influencing the judge's sentencing decision. This process aims to ensure a fair and personalized punishment based on the defendant's statements and attitude.
Key Differences Between Verdict and Allocution
A verdict is the formal decision or finding made by a judge or jury regarding the guilt or innocence of a defendant in a trial. Allocution occurs after the verdict, where the defendant has the opportunity to personally address the court before sentencing, often to express remorse or provide mitigating information. The key differences lie in purpose and timing: the verdict determines legal responsibility, while allocution influences sentencing outcomes.
The Role of Verdict in Criminal Trials
The verdict serves as the formal decision rendered by the jury or judge concerning the guilt or innocence of the defendant in criminal trials. This determination directly influences sentencing and the defendant's legal outcome, marking the culmination of evidence evaluation and legal arguments presented during the trial. The clarity and finality of the verdict ensure the administration of justice under the law and uphold the defendant's constitutional rights.
The Purpose of Allocution in Sentencing
Allocution serves as a critical opportunity for defendants to personally address the court before sentencing, allowing them to express remorse, provide explanations, or present mitigating factors. This process aims to humanize the defendant, offering judges a more comprehensive understanding beyond the verdict's factual findings. By enabling allocution, the court promotes fairness and individualized sentencing that takes into account the defendant's circumstances and attitude.
How Verdicts Are Reached
Verdicts are reached through a structured legal process where jurors evaluate evidence presented during a trial and apply the law as instructed by the judge. The jury deliberates to determine the facts and decides whether the defendant is guilty or not guilty based on the standard of proof beyond a reasonable doubt in criminal cases. This consensus culminates in a formal announcement of the verdict in court, concluding the fact-finding phase of the trial.
Allocution: The Defendant’s Right to Speak
Allocution gives defendants the essential right to address the court directly before sentencing, allowing them to express remorse, explain circumstances, or contest aspects of the verdict. This personal statement can influence the judge's sentencing decision by providing context that goes beyond the trial record. Unlike the verdict, which is the jury's determination of guilt, allocution emphasizes the defendant's voice in the judicial process.
Legal Implications of Verdict and Allocution
Verdict refers to the formal decision rendered by a judge or jury regarding the guilt or innocence of a defendant, directly impacting sentencing and further legal actions. Allocution is the defendant's opportunity to speak before sentencing, allowing for the presentation of mitigating factors that may influence the court's decision. The legal implications of a verdict establish the basis for conviction or acquittal, while allocution provides a critical chance to affect the severity of the sentence within the framework of criminal procedure.
Impact of Allocution on Sentencing Outcomes
Allocution significantly influences sentencing outcomes by providing defendants the opportunity to express remorse, clarify circumstances, and humanize themselves before the judge. This personal statement can lead to reduced sentences or alternative sentencing by fostering judicial empathy and mitigating perceived culpability. Unlike the verdict, which establishes guilt, allocution directly affects the judge's discretion during sentencing by presenting contextual factors and personal insights.
Verdict vs Allocution: Importance in Criminal Justice
Verdict and allocution serve distinct roles in criminal justice, with the verdict representing the jury's formal decision on the defendant's guilt or innocence, which directly determines the case outcome. Allocution occurs after the verdict, allowing the defendant to personally address the court before sentencing, often to express remorse or explain circumstances, potentially influencing the judge's sentencing decision. Understanding the importance of both ensures a comprehensive appreciation of procedural justice, where the verdict delivers the factual determination and allocution provides a platform for the defendant's voice in the sentencing phase.
Verdict Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com