Civil law governs private relationships between individuals, organizations, and entities, covering areas such as contracts, property, family matters, and torts. Understanding how civil law applies to your situation can protect your rights and help resolve disputes effectively. Explore the full article to learn more about how civil law impacts your daily life and legal options.
Table of Comparison
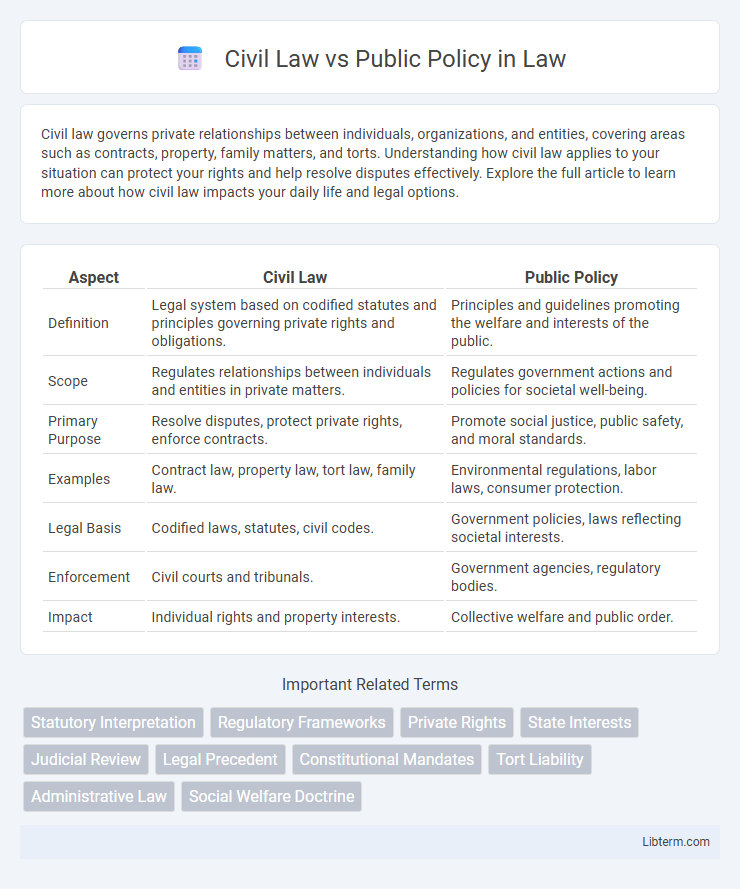
| Aspect | Civil Law | Public Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal system based on codified statutes and principles governing private rights and obligations. | Principles and guidelines promoting the welfare and interests of the public. |
| Scope | Regulates relationships between individuals and entities in private matters. | Regulates government actions and policies for societal well-being. |
| Primary Purpose | Resolve disputes, protect private rights, enforce contracts. | Promote social justice, public safety, and moral standards. |
| Examples | Contract law, property law, tort law, family law. | Environmental regulations, labor laws, consumer protection. |
| Legal Basis | Codified laws, statutes, civil codes. | Government policies, laws reflecting societal interests. |
| Enforcement | Civil courts and tribunals. | Government agencies, regulatory bodies. |
| Impact | Individual rights and property interests. | Collective welfare and public order. |
Introduction to Civil Law and Public Policy
Civil law governs private relationships between individuals and organizations, focusing on rights, obligations, and remedies in areas such as contracts, property, and torts. Public policy refers to the principles and standards enacted by governmental bodies to guide legal decisions and societal regulations for the common good. Understanding the intersection of civil law and public policy is essential for interpreting legal frameworks and resolving conflicts that affect both private interests and societal welfare.
Defining Civil Law: Key Principles
Civil law governs private rights and obligations between individuals and entities, emphasizing contracts, property, torts, and family law. Its key principles include the enforcement of legally binding agreements, protection of individual rights, and resolution of disputes through compensation rather than punishment. Civil law systems prioritize codified statutes and comprehensive legal codes to ensure consistency and predictability in judicial decisions.
Understanding Public Policy: Core Concepts
Public policy encompasses the principles and regulations established by governments to address societal issues and promote the public good. It shapes the framework within which civil law operates, influencing legislative priorities and judicial decisions. Understanding public policy involves recognizing its role in balancing individual rights with collective interests to achieve social order and justice.
Historical Evolution of Civil Law and Public Policy
The historical evolution of civil law traces back to ancient Roman law, particularly the Corpus Juris Civilis compiled under Emperor Justinian in the 6th century, which laid foundational principles for private law regulating relationships between individuals. Public policy emerged as a concept influencing legal interpretations by prioritizing societal interests, evolving significantly during the Enlightenment when state authority and the common good became central to legal frameworks. Over time, civil law systems incorporated public policy considerations to balance individual rights with communal welfare, shaping contemporary legal doctrines worldwide.
Major Differences Between Civil Law and Public Policy
Civil law governs disputes between private parties, emphasizing individual rights and legal remedies like compensation or injunctions, while public policy encompasses government principles aimed at maintaining societal order and welfare. Civil law is codified through statutes and judicial precedents, whereas public policy derives from legislative enactments, administrative regulations, and judicial interpretations shaping societal norms. The enforcement mechanisms differ as civil law relies on courts to resolve private disputes, whereas public policy initiatives involve government agencies implementing rules for the collective good.
Intersection of Civil Law and Public Policy
The intersection of civil law and public policy shapes legal frameworks that protect individual rights while promoting societal interests, influencing legislation on contracts, torts, and property rights. Civil law doctrines are often adapted to reflect evolving public policy goals such as social justice, economic fairness, and public safety. Courts balance private disputes with broader policy objectives, ensuring that civil law serves not only private parties but also the collective welfare of the community.
Case Studies: Civil Law Influencing Public Policy
Case studies reveal how civil law profoundly shapes public policy by setting legal standards that guide governmental actions and societal norms. Landmark civil cases, such as Brown v. Board of Education, have reversed discriminatory policies and promoted equality and human rights in public institutions. These cases demonstrate civil law's role in driving legislative reforms and reinforcing public policy priorities centered on justice and social welfare.
Impact of Public Policy on Civil Law Decisions
Public policy significantly influences civil law decisions by guiding courts to balance individual rights with societal interests, often shaping the interpretation and application of statutes. Courts may refuse to enforce contracts or legal actions that contravene public policy, thereby ensuring that civil law aligns with broader social norms and ethical standards. This dynamic interplay ensures that civil law evolves in response to changing public values and government priorities.
Challenges in Balancing Civil Law and Public Policy
Balancing civil law and public policy involves complex challenges such as reconciling individual rights with collective interests, ensuring legal consistency while adapting to evolving social values, and managing conflicts between judicial interpretations and legislative intent. Civil law frameworks must address public policy goals without undermining the predictability and fairness essential for legal stability. Courts often face difficulties in applying abstract policy principles to concrete cases, which can lead to divergent rulings and uncertainty in legal outcomes.
Future Trends in Civil Law and Public Policy
Future trends in civil law and public policy emphasize integrating advanced technology such as AI and blockchain to enhance legal processes and regulatory compliance. Emerging frameworks prioritize data privacy, cyber security, and environmental sustainability, reflecting shifting societal values and global challenges. Increased collaboration between lawmakers, technologists, and ethicists aims to create adaptive policies that address complex issues in digital governance and human rights protection.
Civil Law Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com