Liability refers to the legal responsibility one holds for actions or omissions that cause harm or damage to others. It plays a crucial role in protecting individuals and businesses by determining who must compensate for losses or injuries. Discover how understanding liability can safeguard your interests by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
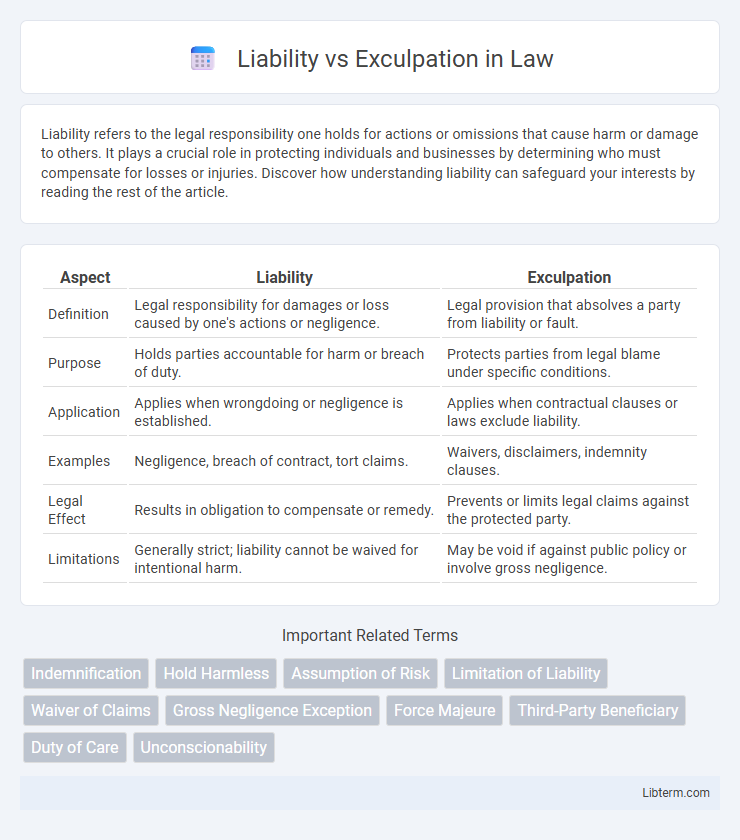
| Aspect | Liability | Exculpation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal responsibility for damages or loss caused by one's actions or negligence. | Legal provision that absolves a party from liability or fault. |
| Purpose | Holds parties accountable for harm or breach of duty. | Protects parties from legal blame under specific conditions. |
| Application | Applies when wrongdoing or negligence is established. | Applies when contractual clauses or laws exclude liability. |
| Examples | Negligence, breach of contract, tort claims. | Waivers, disclaimers, indemnity clauses. |
| Legal Effect | Results in obligation to compensate or remedy. | Prevents or limits legal claims against the protected party. |
| Limitations | Generally strict; liability cannot be waived for intentional harm. | May be void if against public policy or involve gross negligence. |
Understanding Liability: A Legal Overview
Understanding liability involves recognizing the legal responsibility one holds for actions or omissions that cause harm or damage to others. Liability can arise from negligence, breach of contract, or statutory violations, and it is essential to determine the extent to which a party is accountable for losses. Exculpation clauses in contracts attempt to limit or eliminate liability, but courts often scrutinize these provisions to ensure they are enforceable and not unconscionable.
What Is Exculpation? Key Definitions
Exculpation refers to the legal doctrine that absolves a party from liability or blame for a specific act or omission under certain conditions, often outlined in contracts or statutes. It involves demonstrating that the party was not responsible for the alleged wrongdoing, distinguishing it from liability, which imposes responsibility for damages or harm. Key definitions include "exculpatory clauses" in contracts that limit or eliminate a party's liability, and "exoneration," which legally clears one from fault or guilt.
Liability vs Exculpation: Core Differences
Liability refers to the legal responsibility one has for damages or wrongdoing, requiring compensation or rectification, while exculpation involves absolving a party from such responsibility, often through contractual clauses or legal defenses. The core difference lies in liability establishing accountability, whereas exculpation limits or eliminates that accountability under specific conditions. Understanding these distinctions is essential for drafting contracts and assessing legal risks in business and personal contexts.
Types of Liability in Law
Types of liability in law encompass tort liability, contract liability, and strict liability, each defining the scope of legal responsibility for damages or breaches. Tort liability arises from wrongful acts causing harm to others, including negligence and intentional misconduct, while contract liability stems from failure to fulfill contractual obligations. Strict liability imposes responsibility regardless of fault, often applied in cases involving inherently hazardous activities or defective products, contrasting with exculpation clauses that seek to limit or exempt parties from such liabilities.
Common Exculpatory Clauses and Their Uses
Common exculpatory clauses, such as waiver of liability, assumption of risk, and indemnity agreements, are designed to limit a party's liability in contracts, especially in high-risk activities or service agreements. These clauses shift responsibility away from one party by explicitly stating the other party accepts certain risks or agrees not to hold them liable for damages or injuries. Widely used in industries like recreational sports, real estate, and service providers, exculpatory clauses help manage legal exposure but must be clearly worded to be enforceable and not violate public policy.
How Liability Impacts Legal Agreements
Liability significantly shapes legal agreements by defining the responsibilities and potential financial burdens parties may face in case of breaches or damages. Clear liability clauses establish the extent to which each party is accountable, influencing risk management and insurance requirements. Understanding liability provisions helps parties allocate risks effectively, ensuring enforceable and balanced contractual obligations.
When and How Exculpation Applies
Exculpation applies when a party seeks to limit or eliminate liability for specific actions or omissions, often outlined in contracts or legal statutes to protect against claims arising from negligence or breach of duty. It generally applies in cases involving willful misconduct or gross negligence excepted, requiring clear and explicit language to be enforceable. Courts interpret exculpation clauses narrowly, focusing on the time frame, scope, and specific circumstances under which the party is relieved from liability.
Legal Limitations of Exculpatory Clauses
Exculpatory clauses attempt to limit or eliminate liability for damages or injuries, but legal limitations restrict their enforceability to protect public policy and fairness. Courts often invalidate exculpatory clauses in cases involving gross negligence, intentional misconduct, or when the clause conflicts with statutory regulations or public interests. The clarity, scope, and bargaining power between parties also influence whether an exculpatory clause is upheld under jurisdictional standards.
Balancing Risk: Liability Management Strategies
Liability management strategies focus on balancing risk by allocating responsibility through clear contractual terms, ensuring predictable financial exposure for all parties involved. Effective use of exculpation clauses limits liability by defining the scope of permissible actions and exclusions, reducing potential legal and financial repercussions. Combining indemnification provisions with risk transfer mechanisms, such as insurance, further strengthens defenses against undue liability while maintaining operational flexibility.
Practical Examples: Liability vs Exculpation in Action
In contract law, liability holds a party accountable for damages caused by their actions, such as a contractor responsible for faulty construction work. Exculpation clauses, often found in agreements, aim to limit or eliminate a party's liability, for instance, a service provider disclaiming responsibility for indirect losses. Courts scrutinize exculpation provisions to ensure they are clear and not against public policy, as seen in cases where gross negligence or intentional harm overrides such clauses.
Liability Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com