Professional negligence occurs when a service provider fails to perform their duties to the required standard, causing harm or loss to a client. Understanding the legal obligations and common examples of professional negligence can help you protect your rights and seek appropriate compensation. Explore the rest of the article to learn more about identifying, proving, and addressing professional negligence cases effectively.
Table of Comparison
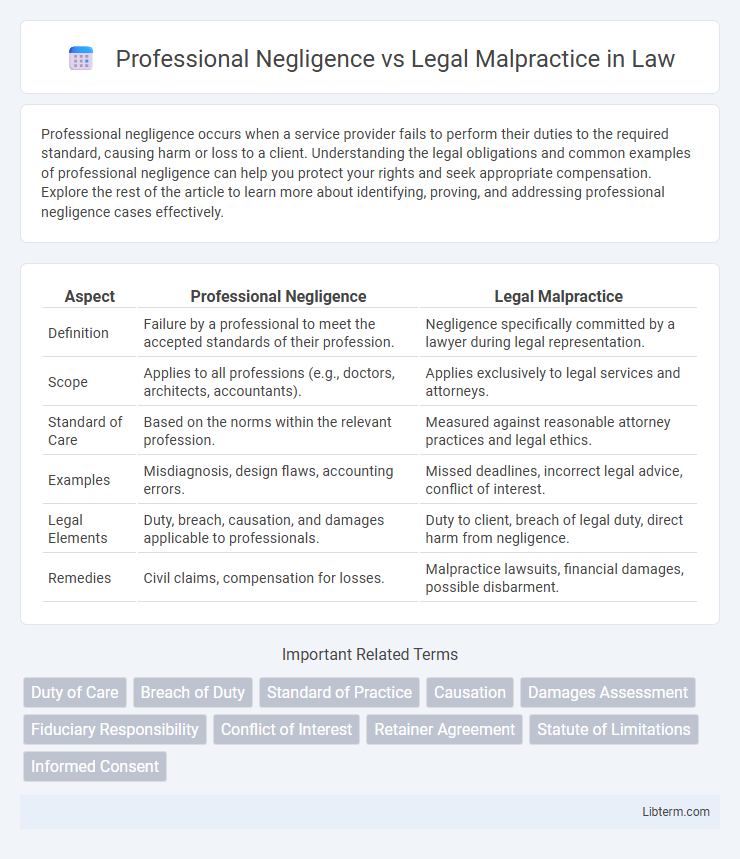
| Aspect | Professional Negligence | Legal Malpractice |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Failure by a professional to meet the accepted standards of their profession. | Negligence specifically committed by a lawyer during legal representation. |
| Scope | Applies to all professions (e.g., doctors, architects, accountants). | Applies exclusively to legal services and attorneys. |
| Standard of Care | Based on the norms within the relevant profession. | Measured against reasonable attorney practices and legal ethics. |
| Examples | Misdiagnosis, design flaws, accounting errors. | Missed deadlines, incorrect legal advice, conflict of interest. |
| Legal Elements | Duty, breach, causation, and damages applicable to professionals. | Duty to client, breach of legal duty, direct harm from negligence. |
| Remedies | Civil claims, compensation for losses. | Malpractice lawsuits, financial damages, possible disbarment. |
Understanding Professional Negligence
Professional negligence occurs when a professional fails to perform their duties to the accepted standard of care, resulting in harm or loss to a client. This concept applies across various fields, including medicine, accounting, and engineering, where specialized knowledge is essential. Understanding professional negligence requires recognizing the breach of duty and direct causation of damages within the professional-client relationship.
Defining Legal Malpractice
Legal malpractice is a specific type of professional negligence that occurs when an attorney fails to provide competent and diligent representation, resulting in harm to the client. It involves breaches such as missed deadlines, conflicts of interest, or inadequate legal advice that compromise the client's case. Unlike general professional negligence, legal malpractice requires proving attorney-client relationship, duty, breach, causation, and damages specific to legal services.
Key Differences Between Professional Negligence and Legal Malpractice
Professional negligence refers to a breach of duty by any licensed professional, such as doctors, architects, or accountants, resulting in harm to a client, whereas legal malpractice specifically pertains to attorneys failing to meet the legal standard of care in their representation. Legal malpractice claims often involve issues like missed deadlines, conflict of interest, or inadequate legal advice, whereas professional negligence covers a broader range of professions and errors. The statute of limitations and types of damages recoverable can also vary significantly between professional negligence and legal malpractice cases.
Elements Required to Prove Professional Negligence
Professional negligence requires establishing duty of care, breach of that duty, causation linking the breach to damages, and actual harm suffered by the plaintiff. The plaintiff must demonstrate that the professional failed to meet the standard of care expected in their specific field. Unlike legal malpractice, which specifically involves attorneys, professional negligence applies broadly across professions such as medicine, engineering, and accounting.
Legal Malpractice: Essential Components
Legal malpractice involves a breach of duty by an attorney who fails to perform according to the professional standards expected in the legal field, resulting in harm to the client. Essential components include the existence of an attorney-client relationship, a duty breached through negligence or misconduct, causation linking the breach to the client's damages, and actual damages suffered. Proving legal malpractice requires demonstrating that the attorney's actions fell below the standard of care and directly caused financial or legal harm to the client.
Common Examples of Professional Negligence
Professional negligence occurs when a professional fails to provide the standard of care expected in their field, leading to harm or financial loss for a client. Common examples of professional negligence include medical misdiagnosis, engineering design errors causing structural failures, and accounting mistakes resulting in significant tax penalties. Legal malpractice, a subset of professional negligence, specifically involves attorneys who fail to competently represent their clients, such as missing filing deadlines or providing incorrect legal advice.
Typical Scenarios of Legal Malpractice
Legal malpractice typically occurs when an attorney fails to provide the standard level of care expected in the profession, resulting in harm to the client. Common scenarios include missing crucial deadlines such as statutes of limitations, inadequate investigation of the case, and conflicts of interest that compromise the lawyer's duty of loyalty. These breaches lead to financial loss or jeopardize the client's legal rights, distinguishing legal malpractice from broader professional negligence in other fields.
Legal Ramifications and Remedies
Legal malpractice specifically refers to negligence by attorneys, resulting in harm to clients through breach of duty, whereas professional negligence encompasses similar failures across various professions. Legal ramifications of legal malpractice include damages awards for financial losses, potential disciplinary actions by bar associations, and reputational damage impacting future practice. Remedies often involve compensatory damages, case retrials, or settlements, with preventive measures such as improved client communication and rigorous adherence to legal standards.
Preventing Professional Negligence and Legal Malpractice
Preventing professional negligence and legal malpractice requires rigorous adherence to industry standards and continuous education to maintain competence in one's field. Implementing clear communication protocols, thorough documentation, and risk management strategies helps minimize errors and ensure accountability. Regular audits and professional liability insurance also provide critical safeguards against potential claims.
Choosing the Right Legal Representation
Selecting the right legal representation requires understanding the distinction between professional negligence and legal malpractice, as both impact case outcomes differently. Legal malpractice specifically involves breaches of duty by lawyers that directly harm clients, whereas professional negligence can pertain to various professions failing to meet standard care. Hiring attorneys experienced in handling legal malpractice claims ensures specialized advocacy and maximizes the likelihood of favorable results.
Professional Negligence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com