A conservator specializes in preserving and restoring cultural heritage, artwork, and historical artifacts to ensure their longevity for future generations. Their expertise involves meticulous analysis and application of conservation techniques tailored to each item's unique materials and condition. Discover how conservators safeguard our shared history and why their work is essential by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
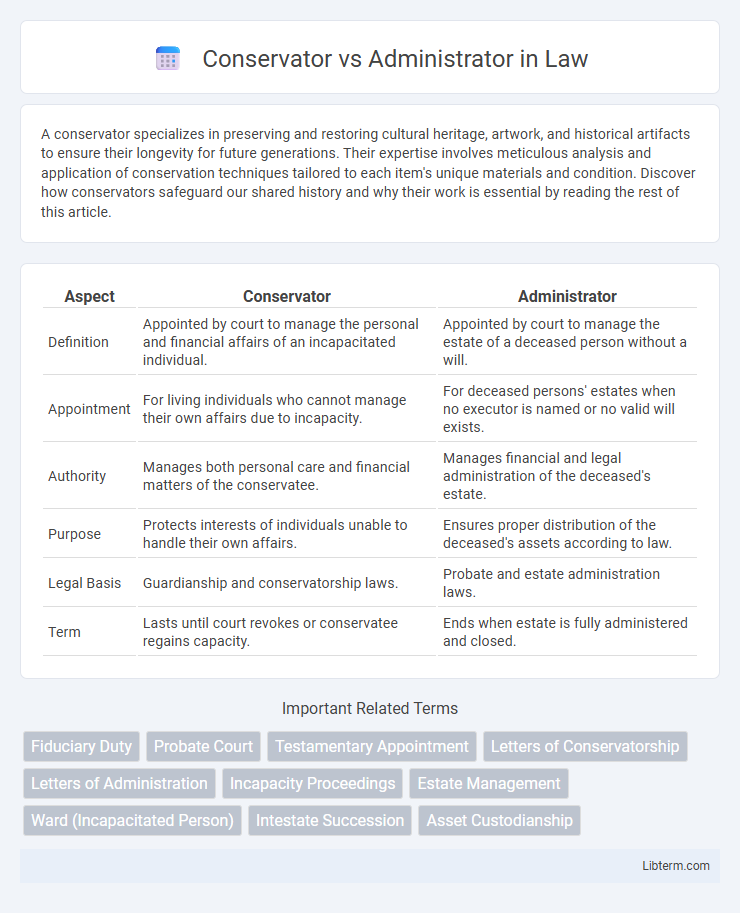
| Aspect | Conservator | Administrator |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Appointed by court to manage the personal and financial affairs of an incapacitated individual. | Appointed by court to manage the estate of a deceased person without a will. |
| Appointment | For living individuals who cannot manage their own affairs due to incapacity. | For deceased persons' estates when no executor is named or no valid will exists. |
| Authority | Manages both personal care and financial matters of the conservatee. | Manages financial and legal administration of the deceased's estate. |
| Purpose | Protects interests of individuals unable to handle their own affairs. | Ensures proper distribution of the deceased's assets according to law. |
| Legal Basis | Guardianship and conservatorship laws. | Probate and estate administration laws. |
| Term | Lasts until court revokes or conservatee regains capacity. | Ends when estate is fully administered and closed. |
Introduction to Conservator and Administrator Roles
A conservator is appointed by a court to manage the financial affairs and physical well-being of an individual who is unable to do so due to incapacity or disability. An administrator, on the other hand, is responsible for managing and distributing the estate of a deceased person who died without a will, following state probate laws. Both roles require fiduciary duties to act in the best interest of the person or estate they oversee.
Legal Definitions: Conservator vs Administrator
A conservator is a court-appointed individual responsible for managing the personal and financial affairs of an incapacitated adult, while an administrator is appointed to manage and distribute the estate of a deceased person without a will. Conservatorship involves ongoing oversight to protect the interests of a living person who cannot care for themselves, whereas administration pertains to settling an estate according to state laws when no executor exists. Legal definitions clearly distinguish conservators as guardians of living individuals' well-being, and administrators as fiduciaries handling post-mortem asset distribution.
Scope of Authority: Key Differences
A conservator primarily manages the personal and financial affairs of an incapacitated individual, focusing on day-to-day decisions and asset protection within a court-approved scope. An administrator is appointed to handle the estate of a deceased person, overseeing tasks like asset distribution, debt settlement, and legal compliance according to probate laws. The key difference lies in conservatorship addressing ongoing care and financial management for the living, while administration involves executing a decedent's estate post-mortem.
Situations Requiring a Conservator
Situations requiring a conservator typically involve individuals who are unable to manage their personal or financial affairs due to physical or mental incapacitation, such as elderly adults with dementia or individuals with severe brain injuries. Unlike an administrator who manages estates of deceased persons, a conservator is appointed to protect and oversee the well-being and assets of living persons who lack decision-making capacity. Courts often require a clear demonstration of incapacity and the need for protection before appointing a conservator to ensure proper care and financial stewardship.
Cases Needing an Administrator
Cases needing an administrator typically arise when a deceased person leaves no valid will, prompting the court to appoint an administrator to manage estate distribution according to state laws. Unlike a conservator, who oversees financial or personal affairs for an incapacitated individual, an administrator handles probate matters for intestate estates. Courts prioritize qualified administrators in complex estates involving multiple heirs, unresolved debts, or unclear asset ownership.
Appointment Process for Each Role
The appointment process for a conservator involves a court hearing where a judge evaluates evidence of an individual's incapacity and determines the need to appoint a conservator to manage personal and financial affairs. In contrast, an administrator is appointed through probate court when a person dies intestate, with the court selecting a qualified individual, often a close relative, to distribute the deceased's estate according to state laws. Both roles require formal court orders, but conservatorship focuses on managing a living person's affairs, while administration handles estate settlement after death.
Duties and Responsibilities Compared
A conservator manages the personal and financial affairs of an individual deemed incapable of doing so, focusing on daily care, healthcare decisions, and property management. An administrator, appointed by a probate court, oversees the distribution of a deceased person's estate, ensuring debts are paid and assets are properly allocated according to the law. Both roles require fiduciary responsibility, but conservatorship centers on ongoing care, whereas administration emphasizes estate settlement.
Rights of the Protected Individual
Conservators hold the legal authority to make personal, financial, and medical decisions on behalf of the protected individual, ensuring their well-being and managing assets with fiduciary responsibility. Administrators, appointed after a person's death, manage and distribute the decedent's estate according to probate laws, without rights to make decisions for a living individual. The protected individual's rights include receiving adequate care, privacy, and the right to petition the court for modification or termination of conservatorship to regain autonomy.
Duration and Termination of Each Role
A conservator typically serves for a fixed period determined by the court, often until the conservatee regains capacity or the conservatorship is no longer necessary, whereas an administrator's role lasts until the estate is fully settled and distributed according to probate laws. Termination of a conservatorship occurs through court order based on evaluations of the conservatee's ability to manage their affairs, while administration ends after the final accounting and court approval of the estate's closure. The process for ending a conservatorship can be more dynamic, reflecting changes in the individual's condition, whereas administration follows a procedural timeline governed by legal requirements.
Choosing Between a Conservator and Administrator
Choosing between a conservator and an administrator depends on the specific needs of the estate and the individual's capacity to manage their affairs. A conservator is appointed to manage the personal and financial matters of someone who is incapacitated, while an administrator is responsible for distributing assets of a deceased person's estate when no will exists. Legal criteria, court involvement, and the scope of authority differ significantly, making it essential to evaluate the beneficiary's condition and estate status before deciding.
Conservator Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com