Charging an hourly fee ensures you pay only for the actual time spent on your project, providing transparent and flexible billing. This method is ideal for tasks with variable scopes or ongoing consultations, allowing adjustments as work progresses. Discover how choosing the right hourly fee can benefit your budget and project management by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
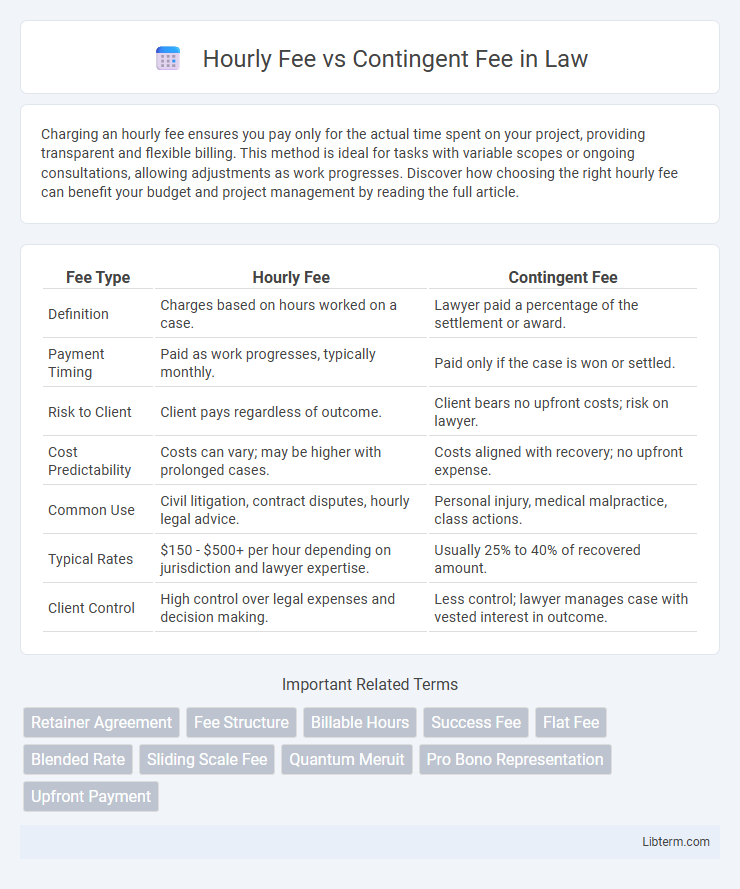
| Fee Type | Hourly Fee | Contingent Fee |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Charges based on hours worked on a case. | Lawyer paid a percentage of the settlement or award. |
| Payment Timing | Paid as work progresses, typically monthly. | Paid only if the case is won or settled. |
| Risk to Client | Client pays regardless of outcome. | Client bears no upfront costs; risk on lawyer. |
| Cost Predictability | Costs can vary; may be higher with prolonged cases. | Costs aligned with recovery; no upfront expense. |
| Common Use | Civil litigation, contract disputes, hourly legal advice. | Personal injury, medical malpractice, class actions. |
| Typical Rates | $150 - $500+ per hour depending on jurisdiction and lawyer expertise. | Usually 25% to 40% of recovered amount. |
| Client Control | High control over legal expenses and decision making. | Less control; lawyer manages case with vested interest in outcome. |
Understanding Hourly Fee Structures
Hourly fee structures charge clients based on the exact time professionals spend on services, typically recorded in increments such as 0.1 or 0.25 hours, ensuring transparent billing aligned with effort. These fees vary widely depending on the industry, expertise level, and geographic location, with legal and consulting rates often ranging from $100 to $500 per hour or more. Understanding the predictability and potential cost fluctuations of hourly fees helps clients assess budgeting needs compared to contingent fees, where payment depends on case outcomes or results.
What Is a Contingent Fee?
A contingent fee is a payment arrangement where a lawyer only receives a fee if the case is won or settled successfully, typically calculated as a percentage of the awarded amount. This fee structure aligns the attorney's interests with the client's outcome, often used in personal injury, workers' compensation, and other civil cases. Unlike hourly fees, contingent fees eliminate upfront costs, making legal services accessible to clients who might not afford hourly billing.
Key Differences Between Hourly and Contingent Fees
Hourly fees involve clients paying an agreed-upon rate for each hour of legal work performed, ensuring payment regardless of case outcome, while contingent fees depend on winning the case, with the lawyer receiving a percentage of the settlement or judgment. Hourly fees provide predictable billing based on time, suitable for cases requiring extensive input or ongoing consultation, whereas contingent fees align the lawyer's incentive with success, often used in personal injury or class action lawsuits. Understanding these key differences helps clients choose the best payment structure for their legal needs and financial situation.
Pros and Cons of Hourly Fee Arrangements
Hourly fee arrangements provide transparent billing based on actual time worked, ensuring clients pay only for services rendered. This model offers flexibility and control over costs but may result in unpredictable expenses if the scope of work expands. Hourly fees can create potential conflicts of interest if extended hours benefit the service provider more than the client.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Contingent Fees
Contingent fees offer the advantage of no upfront cost, making legal services accessible to clients who might otherwise be unable to afford representation, as lawyers are paid only upon winning the case. This fee structure aligns the attorney's interests with the client's success but can lead to higher overall costs if the case is won, often a percentage of the settlement or judgment. However, contingent fees may disadvantage complex or less likely cases, as lawyers might be hesitant to take high-risk cases without guaranteed compensation.
Cost Predictability: Hourly vs Contingent Fee
Hourly fees provide clear cost predictability by charging clients for actual time spent on a case, allowing for detailed tracking of legal expenses. Contingent fees, typically a percentage of the settlement or judgment, offer less upfront cost but result in variable total expenses depending on case outcomes. Clients seeking precise budgeting favor hourly fees, while those aiming to minimize initial outlay may prefer contingent fee arrangements despite cost uncertainty.
Impact on Client-Attorney Relationship
Hourly fees create a transparent billing structure that may encourage frequent communication yet can cause clients to worry about escalating costs, potentially straining trust. Contingent fees align attorney incentives with client outcomes, fostering a partnership atmosphere but may lead clients to feel less control over legal strategies. Understanding these fee arrangements is crucial for managing expectations and building a strong, collaborative client-attorney relationship.
Situations Best Suited for Each Fee Model
Hourly fees are ideal for legal cases requiring ongoing consultation or when the scope of work is unpredictable, such as complex corporate matters or contract negotiations. Contingent fees suit plaintiffs in personal injury or wrongful termination cases where payment depends on winning or securing a settlement. Choosing the appropriate fee model depends on case complexity, financial risk tolerance, and predictability of legal outcomes.
How to Choose the Right Fee Structure
Selecting the right fee structure depends on the nature of your legal case and financial situation. Hourly fees offer transparency and predictability for ongoing legal services, while contingent fees align lawyer payment with case success, common in personal injury suits. Evaluate case complexity, risk tolerance, and expected outcomes to decide which fee model maximizes value and minimizes financial uncertainty.
Frequently Asked Questions About Legal Fee Agreements
Hourly fee arrangements require clients to pay lawyers based on the actual time spent, typically recorded in increments of six minutes, offering transparency and control over legal costs. Contingent fee agreements involve lawyers receiving a percentage, often between 25% to 40%, of the settlement or judgment amount only if the case is won, common in personal injury and civil litigation. Clients often ask about cost predictability, the impact of case outcomes on fees, and whether additional expenses are included or billed separately in each fee structure.
Hourly Fee Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com