Merge two or more datasets efficiently by aligning them based on common keys or attributes to create a unified, comprehensive dataset. This process enhances data analysis accuracy and helps reveal deeper insights by combining relevant information from different sources. Explore the rest of this article to learn how you can master various merge techniques and optimize your data integration workflow.
Table of Comparison
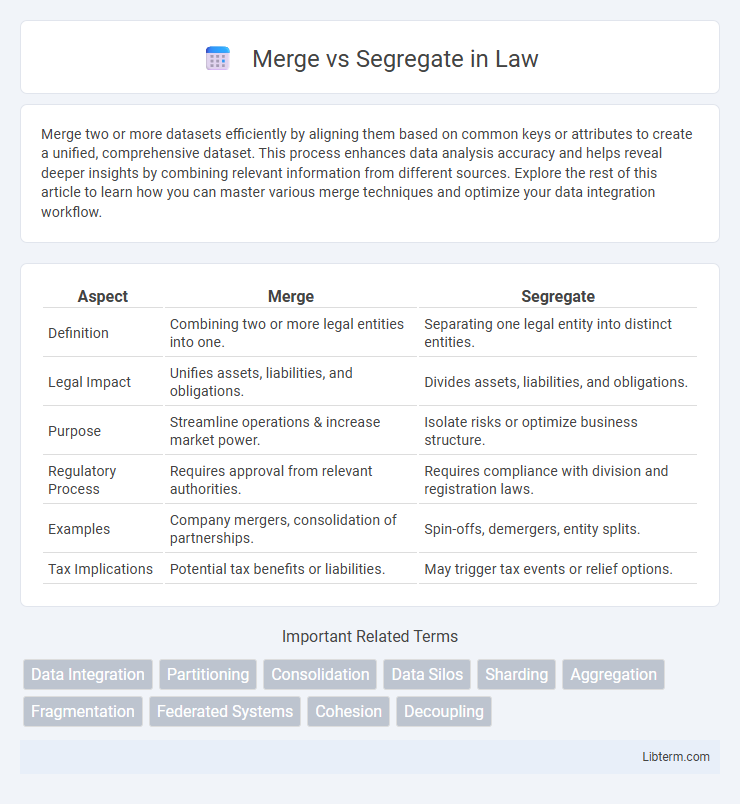
| Aspect | Merge | Segregate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining two or more legal entities into one. | Separating one legal entity into distinct entities. |
| Legal Impact | Unifies assets, liabilities, and obligations. | Divides assets, liabilities, and obligations. |
| Purpose | Streamline operations & increase market power. | Isolate risks or optimize business structure. |
| Regulatory Process | Requires approval from relevant authorities. | Requires compliance with division and registration laws. |
| Examples | Company mergers, consolidation of partnerships. | Spin-offs, demergers, entity splits. |
| Tax Implications | Potential tax benefits or liabilities. | May trigger tax events or relief options. |
Introduction to Merge and Segregate
Merge combines multiple datasets or systems into a unified whole to improve data consistency, reduce redundancy, and enhance operational efficiency. Segregate separates data or processes into distinct groups to increase security, simplify management, and minimize the risk of cross-contamination. Understanding the fundamental differences between merging and segregating aids in selecting the optimal strategy for data integration or isolation based on organizational goals and compliance needs.
Defining Merge: Concept and Applications
Merge refers to the process of combining two or more entities, data sets, or systems into a unified whole, enhancing efficiency and coherence across applications. In data management, merge operations consolidate records to eliminate duplication and create comprehensive datasets, essential for database management, version control, and machine learning. Common applications include software development for code integration, business mergers for strategic growth, and data analytics to improve decision-making through aggregated insights.
Understanding Segregate: Overview and Benefits
Segregate in data management involves isolating data sets to improve security and enhance organization by reducing overlap and potential errors. This approach benefits industries like finance and healthcare by ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations and streamlining access control. Clear segregation facilitates targeted analysis and boosts operational efficiency by minimizing data redundancy and improving system performance.
Key Differences Between Merge and Segregate
Merge combines two or more datasets, files, or entities into a single, unified structure, enhancing integration and data consolidation. Segregate separates data or elements based on specific criteria, ensuring distinct classification and organization for clarity and targeted analysis. Key differences lie in their purpose: merging emphasizes unity and aggregation, while segregation prioritizes division and differentiation.
Advantages of Merging Data/Processes
Merging data and processes enhances operational efficiency by eliminating redundancies and streamlining workflows, leading to faster decision-making and reduced costs. Integrated data sets improve accuracy and consistency, providing a unified source of truth that supports comprehensive analytics and reporting. Consolidated processes foster better collaboration across departments, resulting in improved resource allocation and innovation opportunities.
Benefits of Segregating Systems or Information
Segregating systems or information enhances security by limiting access to sensitive data, reducing the risk of unauthorized breaches. It improves system performance through dedicated resources tailored for specific tasks, minimizing cross-system interference. This approach also simplifies compliance with regulatory requirements by isolating data according to privacy and governance standards.
Use Cases: When to Merge vs When to Segregate
Merging is ideal for use cases where data consolidation improves analysis efficiency, such as combining customer records from multiple sources to create a unified profile. Segregation suits scenarios requiring data isolation for security or compliance, like separating sensitive financial information from general user data. Choosing between merge and segregate depends on factors like data sensitivity, analysis goals, and regulatory requirements.
Challenges and Risks: Merge vs Segregate
Merging systems or data pools often introduces challenges such as data inconsistencies, integration complexities, and increased risk of system downtime. Segregating functions or datasets can reduce these risks by isolating failures and simplifying management but may lead to resource duplication and increased operational costs. Balancing these trade-offs requires thorough risk assessment to optimize integration benefits while minimizing security vulnerabilities and scalability issues.
Best Practices for Merging or Segregating
Best practices for merging involve thorough data validation to ensure consistency, proper mapping of fields to avoid data loss, and maintaining backups before integration. Segregating requires clear criteria for data partitioning, preserving referential integrity, and implementing access controls to prevent unauthorized data mixing. Employing automated tools and continuous monitoring enhances accuracy and efficiency in both merging and segregating processes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Selecting between merge and segregate approaches depends on data integration goals and system complexity. Merging promotes unified data views and streamlined processing, ideal for consolidated reporting and analysis. Segregation enhances data security and modular management, suitable for environments requiring distinct data boundaries and compliance.
Merge Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com