A waiver is a legal document that relinquishes your right to claim damages or certain legal rights, often used in contracts or agreements to limit liability. Understanding the implications of signing a waiver is crucial to protect yourself from unintended obligations or risks. Explore the rest of the article to learn how waivers affect your rights and when you should be cautious before signing one.
Table of Comparison
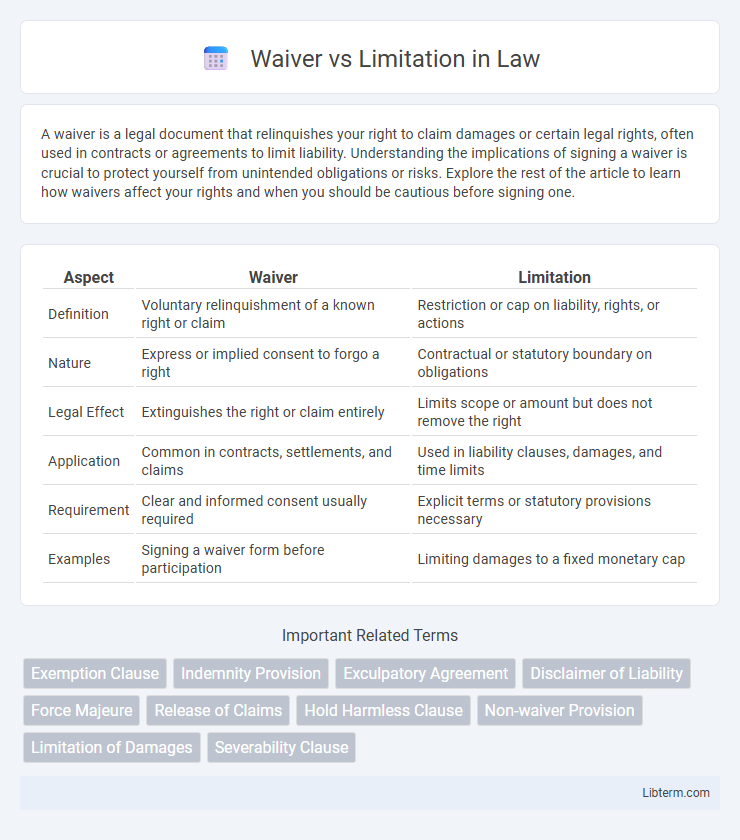
| Aspect | Waiver | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voluntary relinquishment of a known right or claim | Restriction or cap on liability, rights, or actions |
| Nature | Express or implied consent to forgo a right | Contractual or statutory boundary on obligations |
| Legal Effect | Extinguishes the right or claim entirely | Limits scope or amount but does not remove the right |
| Application | Common in contracts, settlements, and claims | Used in liability clauses, damages, and time limits |
| Requirement | Clear and informed consent usually required | Explicit terms or statutory provisions necessary |
| Examples | Signing a waiver form before participation | Limiting damages to a fixed monetary cap |
Understanding Waivers and Limitations
Waivers refer to the voluntary relinquishment of a known right, allowing parties to intentionally forgo certain claims or defenses, whereas limitations set predefined boundaries on obligations or liabilities within contracts or legal contexts. Understanding waivers involves recognizing explicit or implied consent to waive rights, often requiring clear language or conduct indicating such intent. Limitations typically establish restrictions such as time frames, monetary caps, or scope, helping manage risk and enforceable duties within agreements.
Legal Definitions: Waiver vs Limitation
Waiver refers to the voluntary relinquishment or surrender of a known right, claim, or privilege, effectively preventing the waiving party from enforcing it later. Limitation, in legal terms, typically denotes a restriction or cap on rights, liabilities, or claims, often defined by statutory timeframes such as statutes of limitations that set deadlines for filing legal actions. Understanding the distinction between waiver and limitation is crucial, as waiver involves intentional abandonment of rights, while limitation imposes legal boundaries on the period or scope within which those rights can be exercised.
Key Differences Between Waiver and Limitation
Waiver refers to the voluntary relinquishment of a known right, often resulting in the permanent loss of that right, whereas limitation involves restricting the scope or extent of a right without eliminating it entirely. Key differences include the effect on rights, with waiver causing complete abandonment and limitation merely imposing conditions or boundaries. Waivers require clear intent and consent, while limitations can be imposed by law, contract, or circumstance to control the exercise of rights.
Common Uses of Waivers in Contracts
Waivers are commonly used in contracts to voluntarily relinquish a known right, often seen in liability releases, non-compete agreements, and confidentiality clauses to prevent future claims. They serve to clarify that a party will not enforce certain contractual provisions, thereby reducing legal disputes and fostering trust between parties. Unlike limitations, which restrict the extent of liability or obligations, waivers explicitly forfeit specific rights or claims.
Limitations: Purpose and Application
Limitations define the scope and boundaries within which rights or claims can be exercised, serving to prevent abuse and ensure fairness in legal and contractual contexts. They establish clear temporal, quantitative, or procedural constraints, thereby providing predictability and reducing potential disputes between parties. In application, limitations protect vulnerable interests by setting conditions that must be met before rights can be enforced or waived.
Legal Implications of Waivers
Waivers involve the intentional relinquishment of a known right, which can legally prevent a party from pursuing claims related to the waived issue, often requiring clear, explicit language to be enforceable. Courts analyze the scope and clarity of waiver agreements to determine their validity, with ambiguous waivers typically interpreted against the drafter. Enforceable waivers can limit liability and reduce litigation risk, but they are scrutinized under public policy considerations, especially in cases involving negligence or intentional misconduct.
Enforceability of Limitations in Court
Limitations on liability are enforceable in court when clearly defined, reasonable, and not against public policy, ensuring parties understand the extent of their risk exposure. Courts scrutinize the specificity of limitation clauses and their applicability to the contract's subject matter, often invalidating overbroad or ambiguous provisions. Enforceability also depends on jurisdictional nuances, with some courts refusing to uphold limitations that exclude liability for gross negligence or willful misconduct.
Risks Associated with Waivers and Limitations
Waivers and limitations in contracts carry significant risks, including potential enforceability challenges and unintended forfeiture of critical rights. Waivers may expose parties to greater liability by voluntarily relinquishing claims, while limitations can restrict recovery amounts, potentially leaving damages uncompensated. Careful drafting and clear communication are essential to mitigate the risk of disputes and ensure both parties understand the scope and impact of these provisions.
How to Draft Effective Waiver and Limitation Clauses
Draft effective waiver and limitation clauses by clearly defining the scope and extent of rights being waived or limited, using precise and unambiguous language to avoid misinterpretation. Ensure compliance with applicable laws and tailor the clauses to specific contract contexts, addressing potential risks and allocating liabilities explicitly. Incorporate provisions for consent, severability, and duration to enhance enforceability and protect parties from unintended obligations or liabilities.
Best Practices: Choosing Between Waiver and Limitation
Choosing between waiver and limitation hinges on the risk tolerance and legal strategy of the parties involved. Waivers provide complete relinquishment of a known right, ideal when certainty and clarity are paramount, whereas limitations restrict liability to a defined scope, balancing protection with exposure. Best practice involves clearly drafting terms to avoid ambiguity and aligning the choice with the contract's overall risk management framework.
Waiver Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com