Legislative processes establish the foundation for creating, amending, and enforcing laws that govern society. Understanding how bills become laws, the roles of legislators, and the impact of legislative decisions is essential for civic engagement. Explore the rest of this article to gain insight into how legislative systems shape your community and country.
Table of Comparison
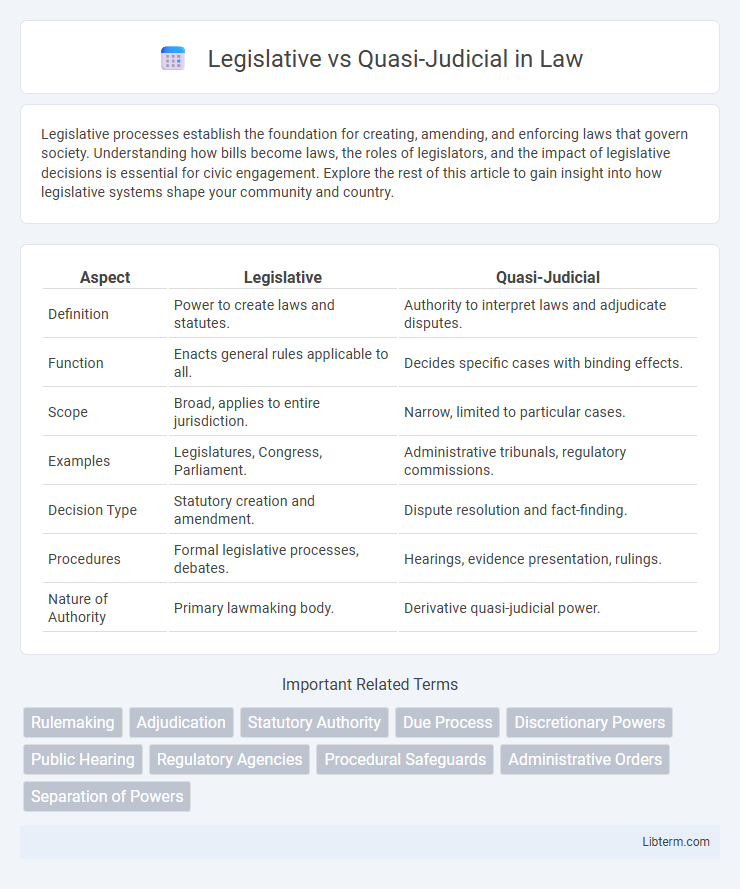
| Aspect | Legislative | Quasi-Judicial |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Power to create laws and statutes. | Authority to interpret laws and adjudicate disputes. |
| Function | Enacts general rules applicable to all. | Decides specific cases with binding effects. |
| Scope | Broad, applies to entire jurisdiction. | Narrow, limited to particular cases. |
| Examples | Legislatures, Congress, Parliament. | Administrative tribunals, regulatory commissions. |
| Decision Type | Statutory creation and amendment. | Dispute resolution and fact-finding. |
| Procedures | Formal legislative processes, debates. | Hearings, evidence presentation, rulings. |
| Nature of Authority | Primary lawmaking body. | Derivative quasi-judicial power. |
Introduction to Legislative and Quasi-Judicial Functions
Legislative functions involve creating, amending, or repealing laws and policies by authorized government bodies, ensuring governance aligns with societal needs. Quasi-judicial functions entail administrative agencies interpreting laws and resolving disputes through formal proceedings resembling judicial processes. Understanding these distinct roles helps clarify the separation of powers and efficient government functioning.
Defining Legislative Powers
Legislative powers involve the authority to create, amend, or repeal laws through formal statutes and ordinances passed by elected bodies such as parliaments or city councils. These powers are distinct from quasi-judicial functions, where decisions are made based on applying existing laws to specific cases. Defining legislative powers clarifies the scope of lawmaking authority, ensuring separation of powers and appropriate governance.
Understanding Quasi-Judicial Authorities
Quasi-judicial authorities possess the power to interpret laws and make decisions similar to courts but are typically limited to specific administrative matters. Unlike legislative bodies that create laws, quasi-judicial entities focus on adjudicating disputes, enforcing regulations, and ensuring compliance within their jurisdiction. These authorities operate under legal frameworks that grant them the ability to assess evidence, conduct hearings, and issue rulings binding on affected parties.
Key Differences Between Legislative and Quasi-Judicial Processes
Legislative processes involve the creation, amendment, or repeal of laws by a governing body, emphasizing policy-making and broad applicability, whereas quasi-judicial processes focus on resolving specific disputes or adjudicating individual cases based on existing laws. Legislative bodies, such as parliaments or city councils, engage in public hearings and debates to formulate general rules, while quasi-judicial entities, including administrative tribunals or regulatory commissions, conduct formal hearings, evaluate evidence, and issue binding decisions. The key distinction lies in legislative actions shaping future governance versus quasi-judicial proceedings applying laws to particular fact patterns with limited scope.
Legal Basis for Legislative and Quasi-Judicial Actions
Legislative actions are grounded in statutory authority granted by constitutions or legislative bodies, enabling the creation or amendment of laws and regulations with broad applicability. Quasi-judicial actions derive their legal basis from specific laws or administrative codes empowering agencies to adjudicate disputes, make findings, and issue orders affecting individual rights. The distinction lies in legislative powers focusing on lawmaking, while quasi-judicial powers emphasize the interpretation and enforcement of those laws through fact-finding and adjudication.
Procedures in Legislative vs Quasi-Judicial Proceedings
Legislative proceedings involve the creation and enactment of laws through formal processes such as debates, readings, and voting within legislative bodies. Quasi-judicial proceedings follow structured procedures resembling judicial trials, including evidence presentation, witness examination, and impartial decision-making by administrative agencies. The key procedural difference lies in the legislative process's focus on policy formulation, while quasi-judicial procedures emphasize fact-finding and adjudication based on established legal standards.
Role of Public Participation in Both Functions
Public participation in legislative functions primarily involves the inclusion of community input during the drafting and amendment of laws, ensuring democratic representation and transparency. In quasi-judicial functions, public participation is typically limited to hearings where affected parties present evidence and arguments, emphasizing fairness and due process in specific cases. Both functions rely on public engagement to uphold accountability, but the scope and nature of participation differ based on their decision-making roles.
Impact on Rights and Liberties
Legislative actions establish broad policies and laws that shape the rights and liberties of individuals within a jurisdiction by creating, modifying, or repealing statutes. Quasi-judicial decisions, made by administrative agencies or boards, directly affect individual rights through specific rulings or adjudications, often determining entitlements or penalties based on established laws. The legislative process offers general regulation impacting society at large, while quasi-judicial processes provide targeted legal resolutions that protect or limit individual freedoms based on case-specific evidence and procedure.
Case Studies Illustrating Legislative and Quasi-Judicial Distinctions
Case studies such as *Chevron U.S.A., Inc. v. Natural Resources Defense Council, Inc.* highlight legislative bodies' role in rulemaking and policy formulation, emphasizing broad, prospective regulations, whereas quasi-judicial examples like *Goldberg v. Kelly* illustrate adjudicative decisions affecting specific parties based on individual facts. Legislative actions typically involve statutory enactments or administrative rules created via formal procedures, while quasi-judicial decisions apply existing laws to disputes, offering adjudication reminiscent of court proceedings. These distinctions clarify the separation of powers in administrative law, with legislative function focusing on rule creation and quasi-judicial function centered on resolving contested cases.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Legislative and Quasi-Judicial Approaches
Selecting between legislative and quasi-judicial approaches depends on the need for policy formulation or dispute resolution. Legislative processes are ideal for creating broad regulations and establishing general rules affecting large populations. Quasi-judicial methods are better suited for applying established laws to specific cases, providing individualized decisions with procedural safeguards.
Legislative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com