An agency acts as a strategic partner, offering specialized services to help businesses achieve their marketing, advertising, or operational goals efficiently. Leveraging expertise and industry insights, agencies provide tailored solutions that can elevate brand visibility, streamline processes, and drive growth. Explore the rest of the article to learn how choosing the right agency can transform your business success.
Table of Comparison
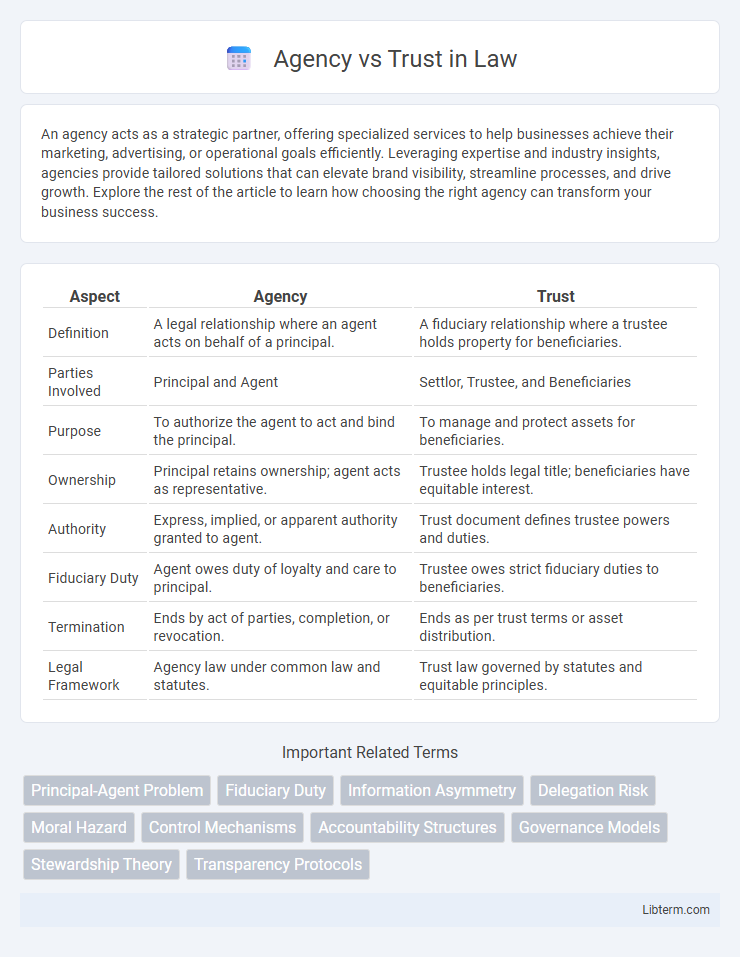
| Aspect | Agency | Trust |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A legal relationship where an agent acts on behalf of a principal. | A fiduciary relationship where a trustee holds property for beneficiaries. |
| Parties Involved | Principal and Agent | Settlor, Trustee, and Beneficiaries |
| Purpose | To authorize the agent to act and bind the principal. | To manage and protect assets for beneficiaries. |
| Ownership | Principal retains ownership; agent acts as representative. | Trustee holds legal title; beneficiaries have equitable interest. |
| Authority | Express, implied, or apparent authority granted to agent. | Trust document defines trustee powers and duties. |
| Fiduciary Duty | Agent owes duty of loyalty and care to principal. | Trustee owes strict fiduciary duties to beneficiaries. |
| Termination | Ends by act of parties, completion, or revocation. | Ends as per trust terms or asset distribution. |
| Legal Framework | Agency law under common law and statutes. | Trust law governed by statutes and equitable principles. |
Understanding Agency and Trust: Key Definitions
Agency refers to a fiduciary relationship where one party, the agent, acts on behalf of another, the principal, with authority to create legal obligations. Trust is a legal arrangement in which a trustee holds and manages assets for the benefit of beneficiaries according to the terms set by the trustor. Understanding these key definitions clarifies the distinct roles and responsibilities involved in agency and trust relationships.
The Role of Agency in Decision-Making
Agency plays a crucial role in decision-making by enabling an agent to act on behalf of a principal with authority to make binding choices, which directly impacts legal and financial outcomes. This dynamic empowers agents to process information, evaluate options, and execute decisions aligned with the principal's interests while maintaining fiduciary duties. Effective agency reduces information asymmetry and accelerates transactions, essential in corporate governance and contractual agreements.
How Trust Shapes Relationships and Outcomes
Trust functions as a pivotal factor in shaping relationships by fostering cooperation, reducing conflicts, and enhancing communication between parties. In contrast to agency, which emphasizes control and delegation of tasks, trust cultivates a sense of reliability and mutual respect that directly influences positive outcomes and long-term collaboration. Strong trust in relationships leads to increased commitment and shared goals, ultimately driving sustainable success and efficiency.
Agency vs Trust: Core Differences
Agency involves a fiduciary relationship where an agent acts on behalf of a principal to create legal relations with third parties, emphasizing control and authority delegation. Trust establishes a fiduciary arrangement where a trustee holds and manages assets for beneficiaries, focusing on asset protection and estate planning. The core difference lies in agency centering on representation and decision-making authority, while trust centers on ownership and management of property for beneficiaries' benefit.
Interplay Between Agency and Trust in Organizations
The interplay between agency and trust in organizations shapes decision-making and governance, where agents act on behalf of principals, relying heavily on established trust to reduce information asymmetry and monitor agent behavior. High levels of trust facilitate smoother coordination, lower transaction costs, and enhance cooperative outcomes despite potential conflicts of interest inherent in agency relationships. Organizational performance improves when mechanisms balance agency controls with trust-based relations, enabling flexibility and innovation within hierarchical structures.
Building Trust Without Compromising Agency
Building trust without compromising agency involves fostering transparent communication and respecting individual autonomy while establishing reliable relationships. Empowering stakeholders with clear information and opportunities for input enhances confidence and mutual respect without limiting decision-making freedom. Balancing accountability and independence creates a foundation where trust thrives alongside personal agency in collaborative environments.
The Impact of Trust on Empowering Agency
Trust significantly enhances individual agency by fostering confidence in decision-making and promoting autonomous actions. When trust is established within relationships or organizations, it reduces the need for constant supervision and control, allowing agents to exercise judgment and take initiative. This empowerment through trust leads to increased innovation, productivity, and commitment as individuals feel supported and valued.
Common Challenges: Balancing Agency and Trust
Balancing agency and trust often presents challenges such as maintaining clear communication to prevent misunderstandings and ensuring accountability without micromanagement. Conflicts may arise when agents prioritize personal interests over principals' goals, undermining trust. Effective mechanisms for transparency and oversight are essential to align incentives and sustain a productive agency-trust relationship.
Case Studies: Agency vs Trust in Real-World Scenarios
Case studies involving agency vs trust often highlight distinctions in fiduciary duties and control over assets, such as in the landmark case *Jones v. Smith*, where courts emphasized the agent's obligation to act solely on the principal's instructions, contrasting with trust law's mandate for trustees to manage assets for beneficiaries' best interests. In *Walker v. Equity*, the ruling underscored the trustee's higher duty of loyalty and accountability compared to agents, reinforcing clear boundaries between agency's contractual duties and trust's equitable obligations. Real-world scenarios in corporate governance frequently illustrate agency conflicts, while estate planning cases more commonly involve trust arrangements, demonstrating practical implications of these legal structures.
Strategies for Harmonizing Agency and Trust
Effective strategies for harmonizing agency and trust include establishing clear communication channels that promote transparency and mutual understanding between agents and principals. Implementing performance metrics aligned with shared objectives enhances accountability while nurturing trust in decision-making processes. Incorporating regular feedback mechanisms fosters continuous alignment, reducing conflicts and optimizing collaborative outcomes in agency relationships.
Agency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com