Judicial activism occurs when judges interpret laws and the Constitution in a way that reflects personal views or contemporary values, rather than adhering strictly to precedent or original intent. This approach often influences significant social and political changes through landmark court decisions. Explore the article to understand how judicial activism shapes legal landscapes and impacts your rights.
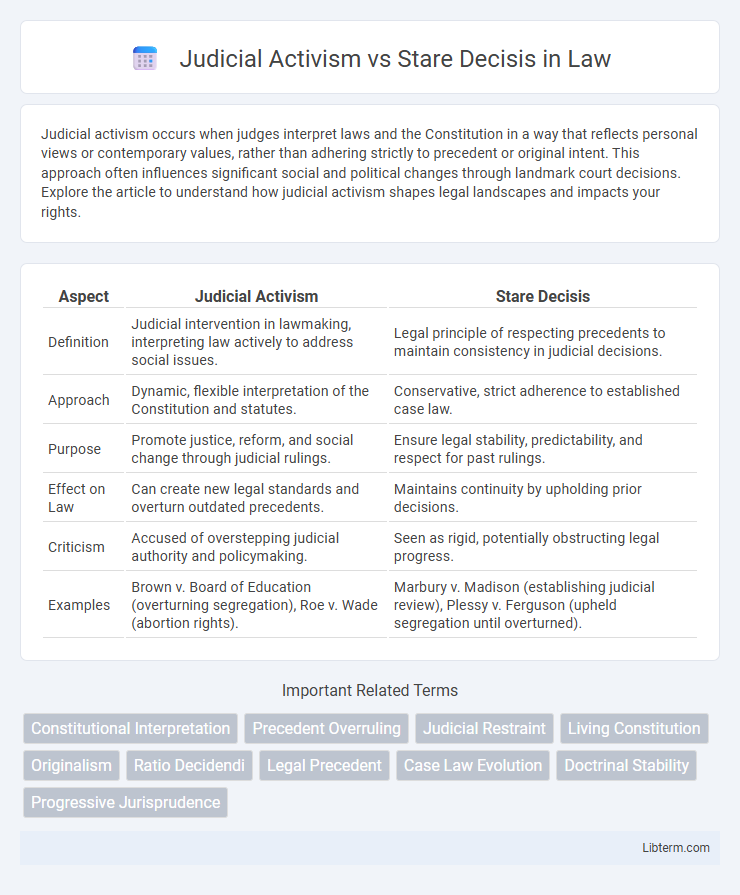
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Judicial Activism | Stare Decisis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Judicial intervention in lawmaking, interpreting law actively to address social issues. | Legal principle of respecting precedents to maintain consistency in judicial decisions. |
| Approach | Dynamic, flexible interpretation of the Constitution and statutes. | Conservative, strict adherence to established case law. |
| Purpose | Promote justice, reform, and social change through judicial rulings. | Ensure legal stability, predictability, and respect for past rulings. |
| Effect on Law | Can create new legal standards and overturn outdated precedents. | Maintains continuity by upholding prior decisions. |
| Criticism | Accused of overstepping judicial authority and policymaking. | Seen as rigid, potentially obstructing legal progress. |
| Examples | Brown v. Board of Education (overturning segregation), Roe v. Wade (abortion rights). | Marbury v. Madison (establishing judicial review), Plessy v. Ferguson (upheld segregation until overturned). |
Introduction to Judicial Activism and Stare Decisis
Judicial activism refers to courts actively interpreting the Constitution or laws to address contemporary issues, often leading to new policy directions, while stare decisis emphasizes adhering to precedent to ensure legal stability and predictability. This principle of precedent binds courts to previous decisions, promoting consistency across judicial rulings. The tension between these approaches shapes judicial decision-making by balancing legal innovation with respect for established case law.
Defining Judicial Activism: Meaning and Scope
Judicial activism refers to the proactive role of judges in interpreting the constitution and laws to address social issues and protect individual rights, often leading to significant changes in public policy. It contrasts with judicial restraint, where courts limit their intervention and adhere closely to legislative intent or precedent. The scope of judicial activism encompasses decisions that go beyond traditional interpretations, reflecting judges' willingness to challenge existing norms for justice and societal progress.
Understanding Stare Decisis: Doctrine of Legal Precedent
Stare decisis, the doctrine of legal precedent, mandates courts to follow established rulings to ensure consistency and predictability in the law. This principle reinforces judicial restraint by binding judges to prior decisions unless compelling reasons warrant departure. Understanding stare decisis is crucial to grasp how judicial activism challenges or upholds legal stability through selective adherence to precedent.
Historical Evolution of Judicial Activism
Judicial activism historically emerged during the early 20th century as courts began interpreting the Constitution more flexibly to address social and economic changes, moving beyond strict adherence to precedent. Key moments include the Warren Court era (1953-1969), which expanded civil rights and liberties through bold judicial rulings, exemplifying activism against traditional stare decisis principles. This evolution reflects a shift from passive judicial restraint to proactive engagement in shaping public policy when legislative or executive branches fail to act.
Landmark Cases Illustrating Stare Decisis
Landmark cases illustrating stare decisis include *Plessy v. Ferguson* (1896), which established the "separate but equal" doctrine, later overturned by *Brown v. Board of Education* (1954) to correct racial segregation in public schools. Another key case is *Roe v. Wade* (1973), where the Supreme Court recognized a constitutional right to abortion, and subsequent cases have largely adhered to this precedent despite ongoing debate. These examples demonstrate the principle of stare decisis, ensuring legal stability by adhering to prior judicial decisions unless compelling reasons prompt a shift.
Judicial Activism: Advantages and Criticisms
Judicial activism allows courts to adapt legal principles to contemporary societal needs, promoting social justice and protecting minority rights when legislative action is absent or inadequate. It enables judges to interpret the constitution flexibly, fostering progressive change and addressing evolving social values. Critics argue that judicial activism undermines the principle of stare decisis, leads to judicial overreach, and compromises the separation of powers by allowing unelected judges to make policy decisions better suited for legislatures.
Stare Decisis: Benefits and Limitations
Stare decisis, the doctrine of adhering to precedent, ensures consistency and predictability in judicial decisions, fostering legal stability and public confidence in the rule of law. It minimizes judicial bias by compelling courts to follow established rulings, promoting fairness and equality in legal interpretation. Nonetheless, stare decisis may perpetuate outdated or erroneous decisions, limiting the judiciary's ability to adapt the law to evolving societal values and circumstances.
Impact of Judicial Activism on Legal Consistency
Judicial activism often disrupts legal consistency by allowing judges to interpret laws based on personal or contemporary views rather than established precedents, which contrasts with the principle of stare decisis that prioritizes stability and predictability in the legal system. This approach can lead to dynamic legal developments but may also introduce uncertainty, as previously settled rulings may be overturned or significantly altered. The tension between these approaches influences how courts balance the need for legal evolution with the importance of maintaining coherent and reliable jurisprudence.
Balancing Judicial Innovation with Precedent Respect
Judicial activism promotes legal innovation by allowing courts to adapt laws to contemporary society, while stare decisis emphasizes maintaining consistency through adherence to precedent. Balancing these principles requires judges to carefully evaluate when deviating from precedent serves justice without undermining legal stability. This dynamic interplay ensures the judiciary evolves thoughtfully, preserving both fairness and predictability in the legal system.
Conclusion: Navigating the Tension Between Judicial Activism and Stare Decisis
Balancing judicial activism and stare decisis requires courts to respect precedent while adapting legal interpretations to evolving societal values. Effective navigation involves prudent discernment, ensuring that departures from established rulings address contemporary injustices without undermining legal stability. This dynamic tension shapes a responsive yet predictable judicial system, essential for maintaining legitimacy and public trust.
Judicial Activism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com