An arbitration clause is a contractual provision requiring parties to resolve disputes through arbitration rather than court litigation. This clause helps streamline conflict resolution, saving time and legal expenses while ensuring confidentiality. Explore the rest of the article to understand how including an arbitration clause can protect Your interests in contracts.
Table of Comparison
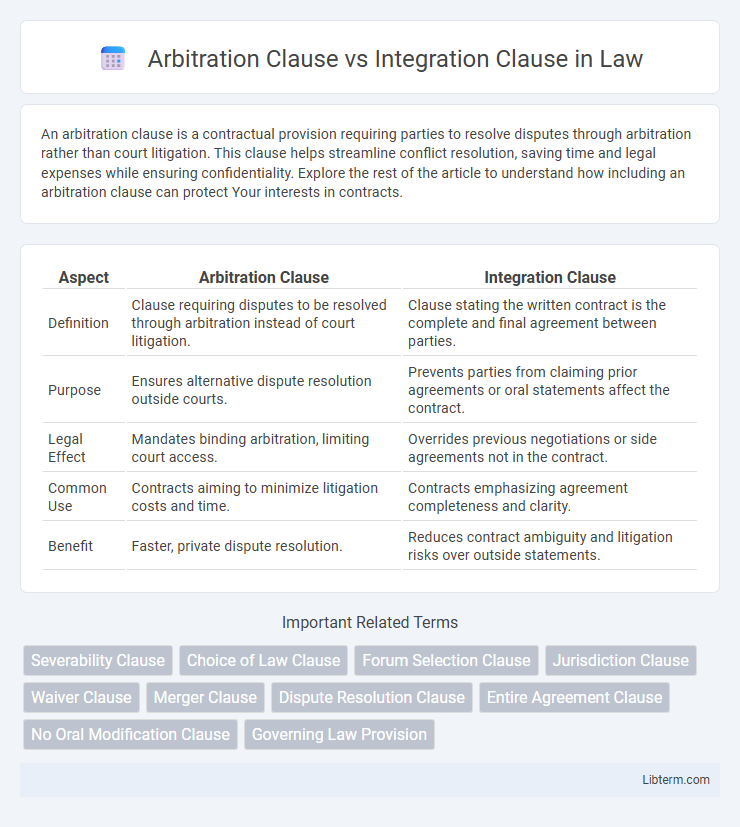
| Aspect | Arbitration Clause | Integration Clause |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Clause requiring disputes to be resolved through arbitration instead of court litigation. | Clause stating the written contract is the complete and final agreement between parties. |
| Purpose | Ensures alternative dispute resolution outside courts. | Prevents parties from claiming prior agreements or oral statements affect the contract. |
| Legal Effect | Mandates binding arbitration, limiting court access. | Overrides previous negotiations or side agreements not in the contract. |
| Common Use | Contracts aiming to minimize litigation costs and time. | Contracts emphasizing agreement completeness and clarity. |
| Benefit | Faster, private dispute resolution. | Reduces contract ambiguity and litigation risks over outside statements. |
Understanding Arbitration Clauses
Arbitration clauses require disputes to be resolved through arbitration rather than court litigation, specifying the arbitration process, location, and governing rules. Understanding arbitration clauses involves recognizing their role in limiting legal risks and controlling dispute resolution costs by avoiding lengthy court procedures. These clauses often complement integration clauses, which confirm that the contract represents the entire agreement, preventing parties from introducing external evidence that could alter the arbitration terms.
Defining Integration Clauses
Integration clauses explicitly state that a written contract represents the complete and final agreement between parties, preventing the admission of prior or contemporaneous external agreements. Arbitration clauses, by contrast, specify that disputes arising from the contract will be resolved through arbitration rather than litigation. Defining integration clauses is crucial for ensuring contractual clarity and limiting the scope of admissible evidence during dispute resolution.
Purpose of Arbitration Clauses in Contracts
Arbitration clauses in contracts establish a mechanism for resolving disputes outside of court, promoting faster and more cost-effective conflict resolution. These clauses specify that parties agree to submit disputes to arbitration, ensuring confidentiality and minimizing litigation risks. By defining the arbitration process, they provide clarity and predictability, which helps maintain business relationships and reduces the uncertainty associated with traditional lawsuits.
Role of Integration Clauses in Agreements
Integration clauses play a crucial role in agreements by establishing that the written contract represents the complete and final understanding between the parties, preventing any external statements or prior agreements from altering its terms. This clause helps limit disputes by ensuring all obligations and agreements are contained within the document, supporting clarity and enforcement. While arbitration clauses focus on dispute resolution methods, integration clauses emphasize the integrity and exclusivity of the contractual terms themselves.
Key Differences Between Arbitration and Integration Clauses
Arbitration clauses require parties to resolve disputes through arbitration rather than court litigation, specifying binding arbitration as the exclusive dispute resolution method. Integration clauses, also known as merger clauses, establish that the written contract represents the entire agreement between parties, excluding any prior or external agreements from influencing contract interpretation. The key difference lies in arbitration clauses governing how disputes are settled, while integration clauses define the completeness and exclusivity of the contract's terms.
Legal Implications of Arbitration Clauses
Arbitration clauses legally mandate that disputes arising from a contract be resolved through arbitration rather than court litigation, significantly limiting parties' access to judicial remedies and appeal rights. These clauses often expedite dispute resolution, reduce legal costs, and maintain confidentiality, but can also restrict discovery processes and may enforce arbitration even when one party is unwilling. Courts typically enforce arbitration agreements strictly under the Federal Arbitration Act, emphasizing arbitration's role in promoting efficient and final dispute settlement while potentially impacting the parties' substantive and procedural legal rights.
Enforceability of Integration Clauses
Enforceability of integration clauses hinges on their ability to clearly state that the written contract is the complete and final agreement between the parties, effectively excluding prior or contemporaneous oral or written statements. Courts generally uphold integration clauses to prevent parties from introducing extrinsic evidence that contradicts or adds to the contract, thereby promoting contractual certainty and reducing disputes. However, if ambiguity exists or if there is evidence of fraud, mistake, or duress, courts may limit enforcement of the integration clause to ensure fairness in contractual obligations.
Common Misconceptions About Arbitration vs Integration Clauses
Arbitration clauses often lead to confusion as many assume they are interchangeable with integration clauses, but their functions are distinct; arbitration clauses mandate dispute resolution through arbitration, while integration clauses confirm the contract as the complete and final agreement. A common misconception is that inclusion of an integration clause negates the need for arbitration clauses, yet the two serve complementary roles in contract interpretation and enforcement. Understanding these differences is crucial in contract drafting to avoid disputes over jurisdiction and the admissibility of external evidence.
Best Practices for Drafting Arbitration and Integration Clauses
For best practices in drafting arbitration and integration clauses, clearly define the scope of disputes subject to arbitration and specify the arbitration rules and seat to ensure enforceability. An integration clause should explicitly state that the written contract constitutes the entire agreement, preventing reliance on prior negotiations or agreements. Precise language that avoids ambiguity helps minimize litigation risks and facilitates smoother dispute resolution.
Choosing the Right Clause for Your Contract
Selecting the appropriate clause for your contract depends on your priorities; an arbitration clause ensures disputes are resolved through binding arbitration, offering confidentiality and faster resolution compared to court litigation. An integration clause, also known as a merger clause, confirms that the written contract represents the entire agreement, preventing reliance on prior negotiations or statements. Carefully evaluate whether dispute resolution mechanism or contractual clarity is more critical to your agreement's enforceability and long-term effectiveness.
Arbitration Clause Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com