A sheriff's deed is a legal document issued after a property is sold at a sheriff's sale, typically due to foreclosure or unpaid taxes. It transfers ownership from the previous owner to the winning bidder, often subject to redemption rights and other legal conditions. Explore the rest of this article to understand how a sheriff's deed impacts your property rights and the buying process.
Table of Comparison
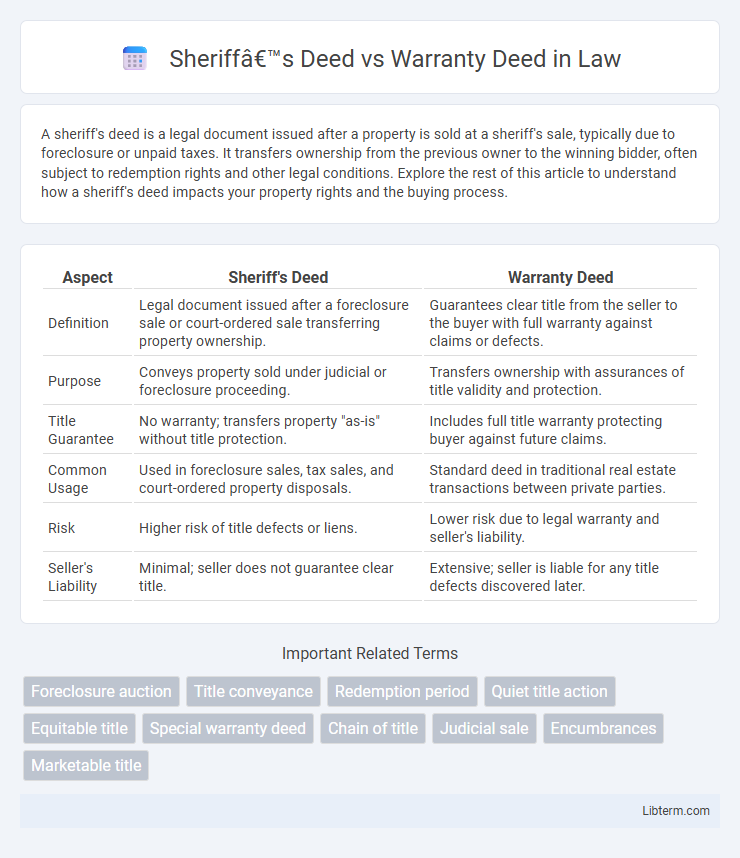
| Aspect | Sheriff's Deed | Warranty Deed |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal document issued after a foreclosure sale or court-ordered sale transferring property ownership. | Guarantees clear title from the seller to the buyer with full warranty against claims or defects. |
| Purpose | Conveys property sold under judicial or foreclosure proceeding. | Transfers ownership with assurances of title validity and protection. |
| Title Guarantee | No warranty; transfers property "as-is" without title protection. | Includes full title warranty protecting buyer against future claims. |
| Common Usage | Used in foreclosure sales, tax sales, and court-ordered property disposals. | Standard deed in traditional real estate transactions between private parties. |
| Risk | Higher risk of title defects or liens. | Lower risk due to legal warranty and seller's liability. |
| Seller's Liability | Minimal; seller does not guarantee clear title. | Extensive; seller is liable for any title defects discovered later. |
Understanding Deed Types: Sheriff’s Deed vs Warranty Deed
A Sheriff's Deed conveys property ownership typically resulting from a foreclosure or auction sale, often providing limited or no warranties about title quality, making it riskier for buyers. In contrast, a Warranty Deed guarantees clear title and protects the buyer against future claims or encumbrances, ensuring the seller has full ownership. Understanding these deed types is crucial for assessing legal protections and potential title issues in real estate transactions.
What Is a Sheriff’s Deed?
A sheriff's deed is a legal document issued after a property is sold at a court-ordered foreclosure auction, transferring ownership from the previous owner to the highest bidder. This deed typically provides limited or no warranty against title defects, meaning the buyer assumes greater risk regarding liens or claims on the property. Sheriff's deeds are commonly used to satisfy judgments or unpaid debts, distinguishing them from warranty deeds that guarantee clear title protection.
What Is a Warranty Deed?
A Warranty Deed is a legal document that guarantees the seller holds clear title to a property and has the right to sell it, providing the buyer with protection against future claims or liens. It includes warranties that the property is free from encumbrances and that the seller will defend the buyer against any title defects. This type of deed offers the highest level of buyer security compared to a Sheriff's Deed, which typically conveys property sold at a government auction without such guarantees.
Key Differences Between Sheriff’s Deed and Warranty Deed
A Sheriff's Deed transfers property ownership following a foreclosure or court-ordered sale, often providing no warranties against title defects. In contrast, a Warranty Deed guarantees clear title and protects the buyer from any claims or liens arising before the sale. These fundamental differences affect the level of buyer protection and potential risks associated with property transactions.
Legal Protections Offered by Sheriff’s Deed
A Sheriff's Deed provides limited legal protections, transferring property ownership without warranties against title defects or claims from prior owners. Unlike a Warranty Deed, which guarantees clear title and protects the buyer from any undisclosed encumbrances, a Sheriff's Deed usually accompanies foreclosure sales and is subject to existing liens or title issues. Buyers relying on a Sheriff's Deed must conduct thorough title searches and may need title insurance to mitigate potential legal risks.
Legal Protections Offered by Warranty Deed
A Warranty Deed provides the strongest legal protections for the buyer by guaranteeing clear title and defending against any future claims or liens on the property, unlike a Sheriff's Deed, which often comes with no warranties and sells the property "as-is." The warranty deed ensures the seller has full ownership and the right to sell, offering recourse if title defects arise. This legal safeguard significantly reduces risks in real estate transactions compared to the limited protections of a sheriff's deed.
Typical Situations for Using a Sheriff’s Deed
Sheriff's deeds typically arise during foreclosure sales, where properties are sold to satisfy unpaid debts or court judgments. These deeds transfer ownership without guaranteeing clear title, reflecting the court-ordered sale through sheriff's or trustee's auctions. Buyers use sheriff's deeds primarily to acquire distressed properties, often accepting higher risk for lower purchase prices compared to warranty deeds.
Typical Situations for Using a Warranty Deed
Warranty deeds are typically used in real estate transactions where the seller guarantees clear ownership and full legal rights to the property, offering buyers protection against future title disputes. Common situations include traditional home sales, refinancing, and property transfers requiring a high level of buyer security. These deeds are crucial when buyers seek assurance that the title is free of liens, encumbrances, or claims, backed by a comprehensive warranty from the seller.
Risks and Benefits: Sheriff’s Deed vs Warranty Deed
A Sheriff's Deed transfers property ownership following a court-ordered sale, often as a result of foreclosure, and carries risks such as unclear title or unresolved liens, requiring thorough title research. Warranty Deeds provide buyers with legal guarantees, including a clear title and protection against future claims, significantly reducing ownership risks and offering peace of mind. Buyers choosing a Sheriff's Deed may benefit from lower purchase prices, but face potential title defects, whereas Warranty Deeds offer stronger legal protections at typically higher costs.
Choosing the Right Deed for Your Property Transaction
Choosing the right deed for your property transaction depends on the level of protection and warranty you require. A warranty deed guarantees clear title and provides legal protection against potential claims, making it ideal for traditional home sales. In contrast, a sheriff's deed is issued after a foreclosure sale, offering no warranties on title, and is best suited for buyers willing to assume higher risk for potentially lower prices.
Sheriff’s Deed Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com