A private sale offers exclusive access to products or assets not available to the general public, ensuring a more personalized and confidential transaction. This approach often provides better negotiation opportunities and tailored terms to suit Your specific needs. Explore the rest of the article to understand how private sales can benefit You and how to navigate them effectively.
Table of Comparison
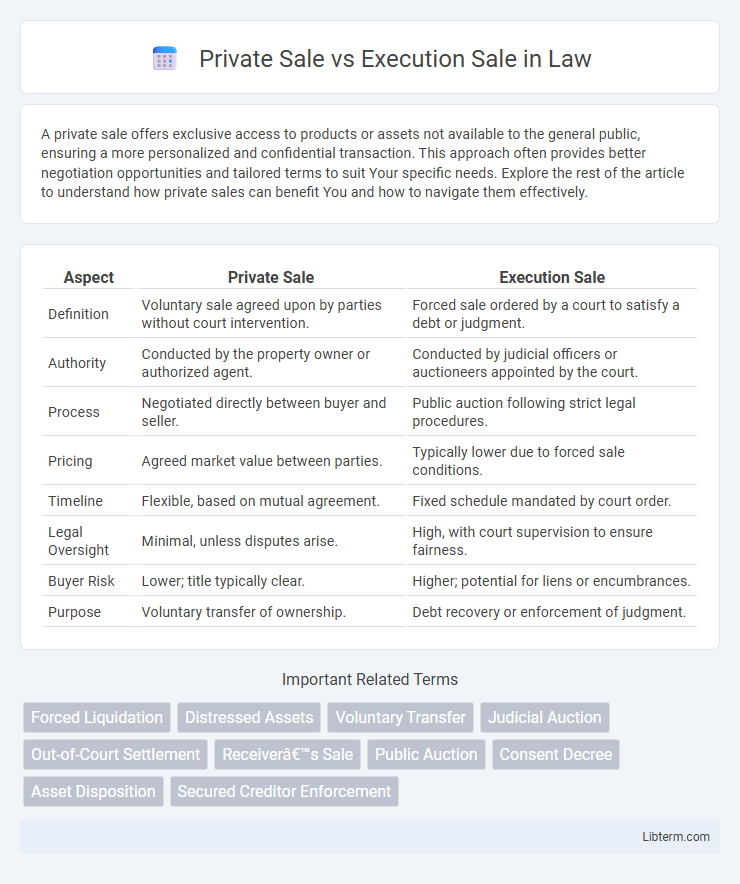
| Aspect | Private Sale | Execution Sale |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voluntary sale agreed upon by parties without court intervention. | Forced sale ordered by a court to satisfy a debt or judgment. |
| Authority | Conducted by the property owner or authorized agent. | Conducted by judicial officers or auctioneers appointed by the court. |
| Process | Negotiated directly between buyer and seller. | Public auction following strict legal procedures. |
| Pricing | Agreed market value between parties. | Typically lower due to forced sale conditions. |
| Timeline | Flexible, based on mutual agreement. | Fixed schedule mandated by court order. |
| Legal Oversight | Minimal, unless disputes arise. | High, with court supervision to ensure fairness. |
| Buyer Risk | Lower; title typically clear. | Higher; potential for liens or encumbrances. |
| Purpose | Voluntary transfer of ownership. | Debt recovery or enforcement of judgment. |
Understanding Private Sale: Definition and Process
A private sale involves the direct transaction of assets between parties without a public auction, often negotiated confidentially to maximize value. The process requires agreement on terms, price, and conditions, typically facilitated by brokers or legal advisors to ensure compliance and smooth transfer. Private sales offer flexibility and privacy, contrasting with execution sales, which are court-ordered public asset liquidations following default or legal proceedings.
What is an Execution Sale?
An Execution Sale refers to the court-ordered sale of a debtor's property to satisfy a judgment debt, typically conducted through a public auction or sheriff's sale. This process ensures the creditor obtains funds by legally transferring ownership of assets seized from the debtor. Unlike Private Sales, Execution Sales are regulated by court procedures, offering transparency and competitive bidding to maximize recovery.
Key Differences Between Private and Execution Sales
Private sale involves the direct negotiation and transfer of property between a willing buyer and seller without court intervention, often allowing for flexible terms and confidentiality. Execution sale, by contrast, is a court-ordered public auction of assets or property to satisfy outstanding debts or judgments, ensuring a transparent and legally regulated process. Key differences include the involvement of judicial authority in execution sales, the typically faster timeline of private sales, and the impact on price determination, with execution sales often reflecting market-driven bidding outcomes.
Legal Framework Governing Sales Methods
The legal framework governing private sales and execution sales varies significantly, with private sales typically governed by contract law and requiring explicit consent between parties, while execution sales are strictly regulated by judicial authority under enforcement laws to satisfy court judgments. Execution sales are conducted through court orders and adhere to procedural rules ensuring transparency and creditor rights, whereas private sales allow more flexibility but may lack stringent oversight, potentially affecting the validity of the transaction. Jurisdictions often impose specific statutory requirements for public notification and bidding processes in execution sales, which do not generally apply to private sales.
Advantages of Private Sale
Private sales offer advantages such as greater control over negotiation terms, allowing sellers to set prices and conditions directly with buyers without public bidding pressures. This method accelerates transactions by reducing procedural delays common in execution sales, which often require court approval or formal auction processes. Private sales also maintain confidentiality, protecting sensitive information and minimizing market exposure that could affect asset value.
Benefits of Execution Sale
Execution sales offer a transparent process where assets are sold under court supervision, ensuring fair market value and reducing fraudulent activities. The public nature of execution sales attracts competitive bidding, often resulting in quicker liquidation and better pricing for creditors. Unlike private sales, execution sales provide a legally enforceable framework that protects the interests of all parties involved.
Risks and Challenges in Private Sales
Private sales carry significant risks including lack of transparency, limited market exposure, and potential undervaluation of assets due to the absence of competitive bidding. Challenges include difficulty in verifying buyer credibility and enforcing contractual terms, increasing the likelihood of disputes or fraud. The non-regulated environment often results in less protection for sellers compared to execution sales conducted through formal auction processes.
Pitfalls of Execution Sales
Execution sales often involve court-ordered auctions where properties are sold to satisfy creditors, which can lead to lower sale prices due to limited buyer interest and rushed timelines. The lack of thorough property inspections and transparency during execution sales increases the risk of undisclosed liens, structural issues, or legal complications for buyers. In contrast, private sales provide more controlled negotiation environments, enabling buyers and sellers to address concerns proactively and avoid the pitfalls linked to execution sales.
Choosing the Right Sale Method: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right sale method involves evaluating factors such as asset liquidity, time constraints, and market conditions. Private sales offer confidentiality and potentially quicker negotiations, ideal for selling specialized or high-value assets to targeted buyers. Execution sales, typically through auctions or court-mandated processes, prioritize transparency and competitive bidding, suitable when maximizing market exposure and price realization is essential.
Case Studies: Private Sale vs Execution Sale in Practice
Case studies reveal that private sales often result in quicker transactions with negotiated prices tailored to specific parties, exemplified by real estate deals where sellers seek confidentiality and speed. Execution sales, typically court-ordered or through auctions, tend to prioritize fair market value transparency, as demonstrated in foreclosure scenarios where assets are sold publicly to satisfy creditors. Analysis of these cases indicates private sales may achieve higher net proceeds for sellers, while execution sales provide structured, legally regulated processes ensuring creditor rights.
Private Sale Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com