A preliminary hearing is a crucial step in the criminal justice process where a judge determines if there is enough evidence to proceed to trial. This hearing allows Your attorney to challenge the prosecution's case and helps protect your rights by preventing unnecessary trials. Discover more about what happens during a preliminary hearing and how it can affect your case by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
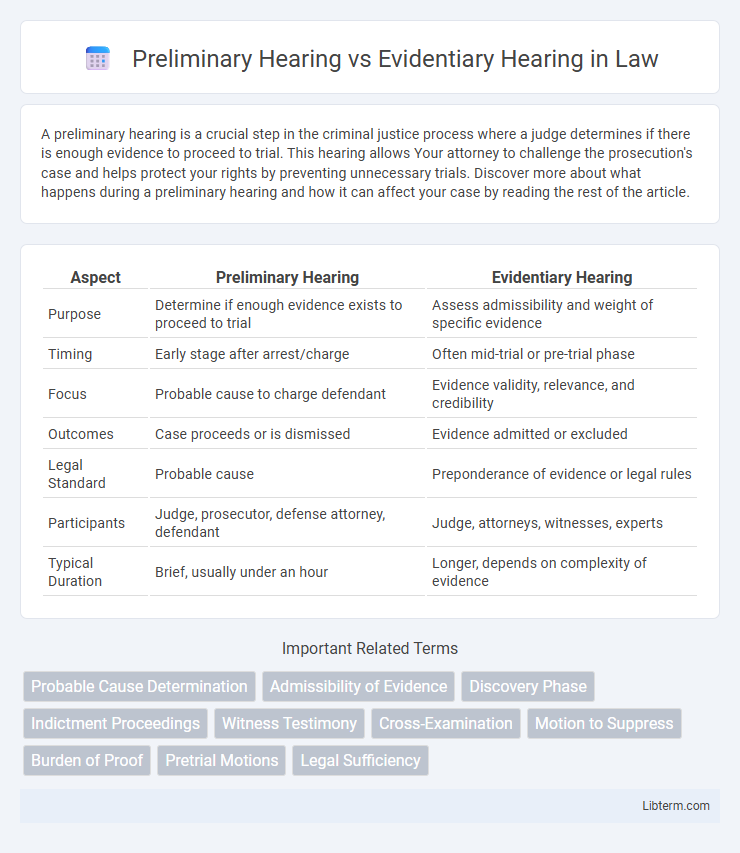
| Aspect | Preliminary Hearing | Evidentiary Hearing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Determine if enough evidence exists to proceed to trial | Assess admissibility and weight of specific evidence |
| Timing | Early stage after arrest/charge | Often mid-trial or pre-trial phase |
| Focus | Probable cause to charge defendant | Evidence validity, relevance, and credibility |
| Outcomes | Case proceeds or is dismissed | Evidence admitted or excluded |
| Legal Standard | Probable cause | Preponderance of evidence or legal rules |
| Participants | Judge, prosecutor, defense attorney, defendant | Judge, attorneys, witnesses, experts |
| Typical Duration | Brief, usually under an hour | Longer, depends on complexity of evidence |
Introduction to Preliminary and Evidentiary Hearings
Preliminary hearings serve to determine whether sufficient evidence exists to proceed with a criminal trial, acting as a safeguard against unwarranted prosecutions. Evidentiary hearings focus on resolving specific legal issues by examining evidence and witness testimony, often influencing trial admissibility or case outcomes. Both hearings play distinct roles in the judicial process, with preliminary hearings emphasizing probable cause and evidentiary hearings addressing the validity of evidence or procedural disputes.
Legal Definitions: Preliminary vs Evidentiary Hearings
Preliminary hearings are legal proceedings that occur early in a criminal case to determine if there is enough evidence to proceed to trial, focusing on probable cause. Evidentiary hearings, however, are conducted to resolve specific factual or legal issues by examining the admissibility of evidence or witness testimony before or during trial. The primary difference lies in their purpose: preliminary hearings assess whether the case should move forward, while evidentiary hearings address detailed evidentiary disputes within the case.
Purpose of a Preliminary Hearing
A Preliminary Hearing serves to determine if there is sufficient evidence to proceed to trial by evaluating whether probable cause exists that the defendant committed the alleged crime. This hearing acts as a safeguard against unwarranted prosecutions, ensuring the prosecution presents enough factual basis before a full trial. Unlike an Evidentiary Hearing, which focuses on resolving specific factual disputes or evidentiary issues, the Preliminary Hearing primarily assesses the legitimacy of the charges to justify continuing the legal process.
Purpose of an Evidentiary Hearing
An evidentiary hearing serves to evaluate the admissibility and credibility of evidence before trial, ensuring that only relevant and reliable information is presented to the court. Unlike a preliminary hearing, which determines whether there is probable cause to proceed with charges, the evidentiary hearing scrutinizes specific facts and legal issues, such as disputes over witness testimony or the exclusion of certain evidence. This process helps streamline the trial by resolving evidentiary conflicts early, preserving judicial efficiency and protecting the rights of all parties involved.
Key Differences Between Preliminary and Evidentiary Hearings
Preliminary hearings primarily determine whether probable cause exists to proceed with a criminal trial, focusing on evidence sufficiency to justify charges, while evidentiary hearings evaluate the admissibility and credibility of specific evidence or witnesses within an ongoing trial. Preliminary hearings involve a judge assessing prosecution evidence against the defendant's defense without deciding guilt, whereas evidentiary hearings address legal disputes about evidence that can significantly impact trial outcomes. The scope of preliminary hearings is broad, aimed at screening cases early, whereas evidentiary hearings are narrow, targeting fact-finding or legal interpretation within the trial process.
When is Each Hearing Used in Criminal Proceedings?
Preliminary hearings occur early in criminal proceedings to determine if there is probable cause to proceed to trial, typically following an arrest and before indictment. Evidentiary hearings take place later and focus on resolving specific legal or factual issues, such as the admissibility of evidence or witness credibility, before or during the trial. The preliminary hearing safeguards against unwarranted prosecutions, while the evidentiary hearing ensures trial fairness by addressing critical trial-related disputes.
Rights of the Defendant in Each Hearing
During a Preliminary Hearing, the defendant's rights center on the opportunity to challenge the sufficiency of the prosecution's evidence and to avoid unnecessary trials by ensuring probable cause exists. In an Evidentiary Hearing, the defendant focuses on the right to present and contest evidence related to specific legal issues, such as suppression of evidence or admissibility questions. Both hearings safeguard due process, but the Preliminary Hearing emphasizes establishing a prima facie case, while the Evidentiary Hearing addresses detailed factual disputes impacting the trial.
Outcomes and Implications of Each Hearing
Preliminary hearings determine if sufficient evidence exists to proceed to trial, often resulting in charges being dismissed or bound over for trial, which impacts the defendant's immediate legal status. Evidentiary hearings assess the admissibility and sufficiency of specific evidence, shaping the trial's scope by excluding or allowing critical proof, ultimately influencing case strategy and potential verdicts. Both hearings significantly affect case progression and defense tactics, with preliminary hearings focusing on probable cause and evidentiary hearings addressing evidentiary validity.
Role of Evidence in Preliminary vs Evidentiary Hearings
In a preliminary hearing, evidence primarily serves to establish probable cause that a crime was committed and that the defendant is likely responsible, often relying on summaries and hearsay to determine if the case should proceed to trial. Evidentiary hearings involve a more detailed and formal examination of admissible evidence, where witnesses may be called and cross-examined to resolve specific factual disputes or legal issues before trial. The role of evidence is more limited and cursory in preliminary hearings, whereas evidentiary hearings require stricter adherence to rules of evidence and are crucial for shaping the scope and substance of the trial.
Frequently Asked Questions about Preliminary and Evidentiary Hearings
Preliminary hearings determine if sufficient evidence exists to proceed to trial, often addressing probable cause in criminal cases, while evidentiary hearings focus on resolving specific legal issues through evidence examination before the main trial. Common questions include the timing of each hearing, differences in burden of proof, and whether witnesses testify during the proceedings. Understanding that preliminary hearings assess case viability and evidentiary hearings clarify factual disputes helps clarify their distinct legal purposes.
Preliminary Hearing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com