Judicial interpretation plays a crucial role in shaping the application of laws by clarifying ambiguous legal texts and adapting statutes to contemporary issues. Courts analyze legislative intent, precedent, and constitutional principles to resolve disputes and ensure justice is served effectively. Explore the rest of the article to understand how judicial interpretation impacts your legal rights and societal norms.
Table of Comparison
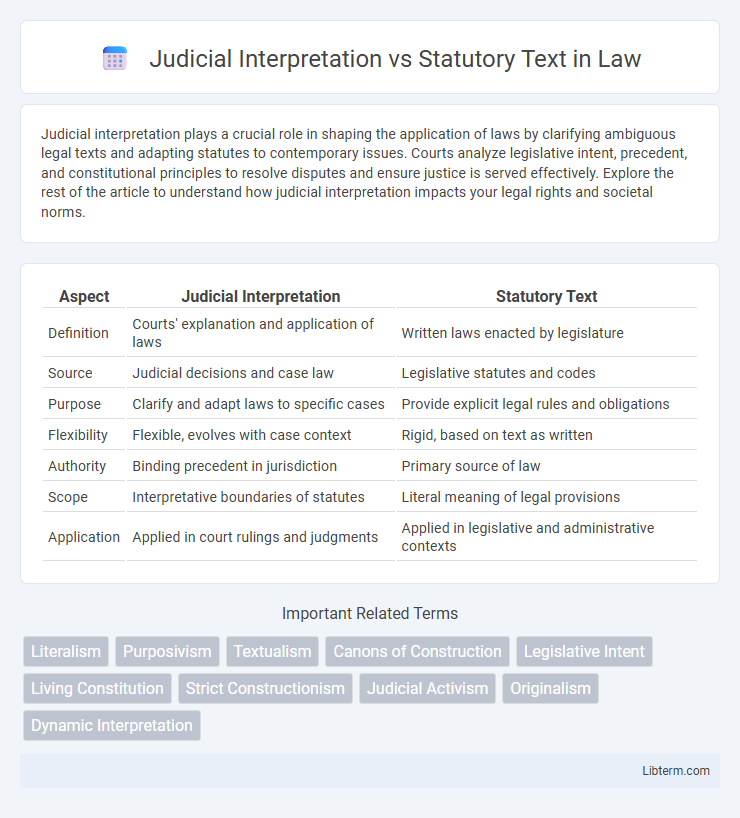
| Aspect | Judicial Interpretation | Statutory Text |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Courts' explanation and application of laws | Written laws enacted by legislature |
| Source | Judicial decisions and case law | Legislative statutes and codes |
| Purpose | Clarify and adapt laws to specific cases | Provide explicit legal rules and obligations |
| Flexibility | Flexible, evolves with case context | Rigid, based on text as written |
| Authority | Binding precedent in jurisdiction | Primary source of law |
| Scope | Interpretative boundaries of statutes | Literal meaning of legal provisions |
| Application | Applied in court rulings and judgments | Applied in legislative and administrative contexts |
Introduction to Judicial Interpretation and Statutory Text
Judicial interpretation involves courts analyzing and clarifying the meaning of statutory text to apply laws correctly in specific cases. Statutory text refers to the exact language written in legislation, embodying the lawmakers' intent at the time of enactment. Understanding the relationship between judicial interpretation and statutory text is essential for accurately enforcing laws and ensuring legal consistency.
Defining Judicial Interpretation
Judicial interpretation involves courts analyzing and clarifying the meaning of statutory text when ambiguities or uncertainties arise in legislation. This process ensures laws are applied consistently with legislative intent while adapting to evolving social and legal contexts. Courts rely on interpretative tools, such as the plain meaning rule, legislative history, and precedent, to define and enforce statutory provisions accurately.
Understanding Statutory Text
Understanding statutory text requires a precise analysis of the language and structure used by the legislature to convey legal obligations and rights. Judicial interpretation often involves examining the plain meaning of the text, legislative history, and context to resolve ambiguities while maintaining fidelity to the statutory framework. Clear comprehension of statutory text ensures that courts apply laws consistently and uphold the intent behind legislative enactments.
Historical Development of Statutory Interpretation
The historical development of statutory interpretation traces back to early common law principles where judges emphasized the literal meaning of the text, adhering closely to the statute's language. Over time, courts incorporated broader interpretative methods, including the purposive approach and consideration of legislative intent, reflecting shifts in legal philosophy and societal values. This evolution highlights the tension between strict textualism and more dynamic judicial interpretation frameworks that adapt statutory meaning to contemporary contexts.
Methods of Judicial Interpretation
Methods of judicial interpretation include textualism, which emphasizes the plain meaning of statutory text at the time of enactment, and purposivism, where courts consider the legislative intent and purpose behind the law. Originalism focuses on the framers' intent during the Constitution's drafting, while dynamic interpretation allows statutes to evolve with societal changes. Courts also apply canons of construction, such as ejusdem generis and expressio unius, to resolve ambiguities within statutory language.
Textualism vs. Purposivism: A Comparative Approach
Textualism emphasizes interpreting laws based solely on the ordinary meaning of the statutory text at the time of enactment, prioritizing clarity and predictability in judicial decisions. Purposivism, by contrast, considers the broader legislative intent and purpose behind the statute, allowing judges to apply principles that promote the law's intended objectives even if not explicitly stated in the text. The debate between textualism and purposivism centers on whether courts should adhere strictly to statutory language or incorporate legislative purpose to resolve ambiguities and adapt laws to contemporary contexts.
The Role of Precedents in Judicial Interpretation
Precedents play a crucial role in judicial interpretation by providing authoritative guidance on how statutory texts should be understood and applied in future cases. Courts rely on prior decisions to ensure consistency, predictability, and stability in the law, interpreting ambiguous or vague statutory language in light of established legal principles. The adherence to stare decisis reinforces the legitimacy of judicial interpretations while allowing the law to evolve through incremental adjustments based on precedent.
Challenges in Interpreting Statutory Text
Interpreting statutory text presents challenges due to ambiguous language, evolving societal contexts, and conflicting legislative intentions. Judicial interpretation must balance the plain meaning of the text with the purpose and spirit of the law, often requiring judges to resolve gaps or inconsistencies without overstepping their authority. This complexity intensifies when statutes contain broad or vague provisions, resulting in varied judicial outcomes and debates over originalism versus purposivism.
Impact of Judicial Interpretation on Legal Outcomes
Judicial interpretation shapes legal outcomes by clarifying ambiguous statutory text, allowing courts to adapt laws to evolving societal contexts and address gaps left by legislators. This interpretive process influences precedent, impacting the consistency and predictability of legal decisions across jurisdictions. The dynamic between judicial interpretation and statutory text determines how laws are applied, potentially altering the intent and scope of legislative provisions.
Conclusion: Striking a Balance Between Text and Interpretation
Effective judicial decision-making requires balancing the literal statutory text with the broader purpose and context of the law. Sole reliance on textualism can lead to rigid outcomes that ignore legislative intent, while excessive interpretivism risks judicial overreach and unpredictability. Striking this balance ensures laws are applied consistently while adapting to evolving societal values and complexities.
Judicial Interpretation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com