Invasion of privacy occurs when personal information is accessed, disclosed, or used without consent, violating an individual's right to confidentiality and autonomy. This issue spans various contexts, including digital data breaches, unauthorized surveillance, and identity theft, posing significant risks to personal security and trust. Explore the rest of the article to understand how you can protect your privacy in today's interconnected world.
Table of Comparison
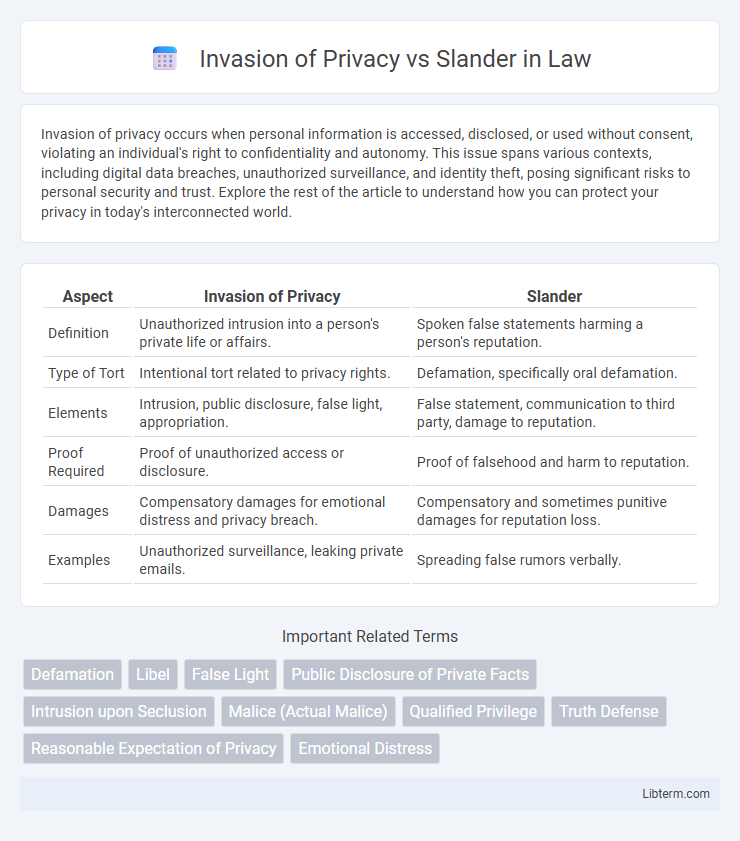
| Aspect | Invasion of Privacy | Slander |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unauthorized intrusion into a person's private life or affairs. | Spoken false statements harming a person's reputation. |
| Type of Tort | Intentional tort related to privacy rights. | Defamation, specifically oral defamation. |
| Elements | Intrusion, public disclosure, false light, appropriation. | False statement, communication to third party, damage to reputation. |
| Proof Required | Proof of unauthorized access or disclosure. | Proof of falsehood and harm to reputation. |
| Damages | Compensatory damages for emotional distress and privacy breach. | Compensatory and sometimes punitive damages for reputation loss. |
| Examples | Unauthorized surveillance, leaking private emails. | Spreading false rumors verbally. |
Introduction to Privacy Invasion and Slander
Invasion of privacy involves unauthorized intrusion into an individual's private life, including actions like unauthorized use of personal information or surveillance. Slander, a form of defamation, refers to false spoken statements that damage a person's reputation. Both legal concepts protect personal rights but address different types of harm--privacy invasion safeguards personal information, while slander protects against harmful untrue verbal attacks.
Defining Invasion of Privacy
Invasion of privacy refers to the unauthorized intrusion into an individual's personal life or private information, violating their right to confidentiality and solitude. This tort includes acts such as unauthorized surveillance, public disclosure of private facts, and misappropriation of identity. Unlike slander, which involves spoken false statements damaging a person's reputation, invasion of privacy protects against breaches of personal boundaries and confidentiality.
Understanding Slander: Key Elements
Slander involves making false spoken statements that damage a person's reputation, requiring proof of the statement's falsity and harmful impact. Key elements include the defamatory nature of the statement, its communication to a third party, and actual damages suffered by the victim. Unlike invasion of privacy, slander specifically centers on spoken defamation that causes reputational harm.
Legal Distinctions Between Privacy Invasion and Slander
Invasion of privacy involves the unauthorized intrusion into an individual's private life or personal information, while slander refers specifically to the oral communication of false statements that damage a person's reputation. Legal distinctions hinge on the nature of the harm: invasion of privacy protects against breaches of confidentiality, unauthorized publicity, or intrusion, whereas slander addresses defamatory speech that causes reputational harm. Courts require proof of falsehood and damages for slander cases, whereas invasion of privacy claims often focus on violating reasonable expectations of privacy without necessarily involving false statements.
Common Examples of Privacy Invasion
Common examples of invasion of privacy include unauthorized use of personal photos, eavesdropping on private conversations, and unauthorized access to confidential information such as medical or financial records. In contrast, slander involves spoken false statements that damage a person's reputation, such as spreading unfounded rumors or accusations in public settings. Both invasion of privacy and slander can result in legal actions, but privacy invasion centers on violating personal boundaries, while slander concerns harmful verbal defamation.
Notable Cases of Slander
Notable cases of slander include the 2011 defamation lawsuit filed by Hulk Hogan against Gawker Media, which resulted in a $140 million verdict highlighting the impact of false spoken statements on reputation. The 2016 case of Johnny Depp versus Amber Heard brought widespread attention to slander in the context of public figures, emphasizing the blurred lines between personal allegations and defamation claims. These cases underscore the critical legal distinctions between slander--spoken defamatory statements--and invasion of privacy, which involves unauthorized public disclosure of private facts.
Harm and Consequences: Privacy Invasion vs Slander
Invasion of privacy causes harm by exposing personal and confidential information, leading to emotional distress, reputation damage, and potential financial loss. Slander inflicts harm through false spoken statements that damage a person's reputation, resulting in social humiliation and lost opportunities. Both offenses carry legal consequences, including civil lawsuits and financial compensation, but invasion of privacy often involves breaches of confidentiality, whereas slander centers on defamatory speech.
Defenses Against Privacy Invasion Claims
Defenses against invasion of privacy claims commonly include consent, where the plaintiff agreed to the disclosure or use of personal information, and the absence of a reasonable expectation of privacy in the circumstances. Another critical defense is the truthfulness of the information disclosed, especially when the invasion involves private facts, which may align with the public's legitimate interest. Courts also consider whether the information falls under privileged communications, such as those made during judicial proceedings, which can protect defendants from liability in privacy invasion cases.
Defenses in Slander Lawsuits
Defenses in slander lawsuits primarily include truth, which establishes the statement's factual accuracy as a complete protection against liability. Other key defenses are privileged communications, such as those occurring in legislative or judicial proceedings, offering immunity to defendants. Consent and lack of negligence in cases involving public figures also play significant roles in mitigating slander claims.
Protecting Yourself: Legal Strategies and Prevention
Protecting yourself against invasion of privacy and slander requires understanding distinct legal strategies for each tort; invasion of privacy involves unauthorized use of personal information or images, while slander refers to spoken false statements damaging reputation. Legal measures include obtaining restraining orders, documenting incidents thoroughly, and consulting attorneys specializing in defamation and privacy law to evaluate case specifics. Preventive actions such as managing online privacy settings, avoiding sharing sensitive information publicly, and responding promptly to defamatory statements can mitigate risks effectively.
Invasion of Privacy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com