Unlock the Power of Effective Time Management for Enhanced Productivity and Stress Reduction. Discover practical strategies to optimize your daily schedule, prioritize tasks, and maintain focus throughout the day. Read on to explore techniques that will transform your approach to time and boost your success.
Table of Comparison
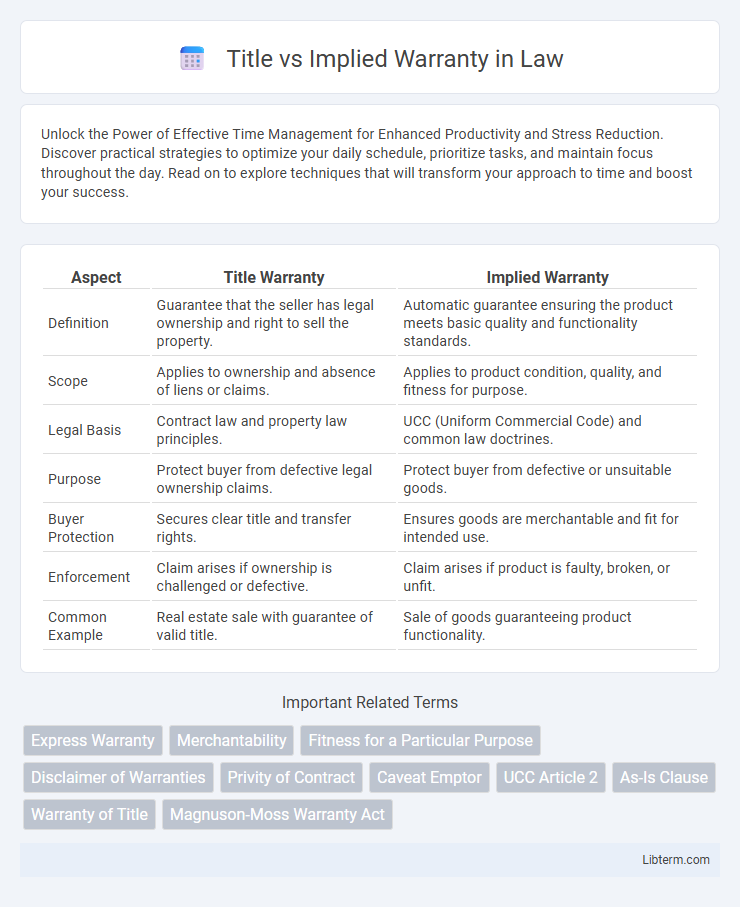
| Aspect | Title Warranty | Implied Warranty |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Guarantee that the seller has legal ownership and right to sell the property. | Automatic guarantee ensuring the product meets basic quality and functionality standards. |
| Scope | Applies to ownership and absence of liens or claims. | Applies to product condition, quality, and fitness for purpose. |
| Legal Basis | Contract law and property law principles. | UCC (Uniform Commercial Code) and common law doctrines. |
| Purpose | Protect buyer from defective legal ownership claims. | Protect buyer from defective or unsuitable goods. |
| Buyer Protection | Secures clear title and transfer rights. | Ensures goods are merchantable and fit for intended use. |
| Enforcement | Claim arises if ownership is challenged or defective. | Claim arises if product is faulty, broken, or unfit. |
| Common Example | Real estate sale with guarantee of valid title. | Sale of goods guaranteeing product functionality. |
Understanding Title Warranty
Title warranty ensures the legal ownership of a property is free from undisclosed claims, providing buyers protection against potential title defects or liens. It guarantees that the seller holds clear ownership and has the right to transfer title, contrasting with implied warranties that cover product quality but not ownership issues. Understanding title warranty is crucial for real estate transactions to avoid future disputes and financial loss.
Defining Implied Warranty
Implied warranty is a legal guarantee automatically granted by law that assures a product meets certain minimum standards of quality and functionality, even if not explicitly stated in a contract. Unlike a title warranty that ensures clear ownership of property, an implied warranty protects consumers by implying that goods are fit for their intended purpose and free from significant defects. This warranty is essential in transactions involving goods, providing a baseline assurance that sellers cannot arbitrarily disclaim.
Key Legal Differences: Title vs Implied Warranty
Title warranty guarantees the seller's legal ownership and the right to transfer clear and marketable title to the buyer, protecting against claims or liens from third parties. Implied warranty ensures the product or property meets certain minimum standards of quality and fitness for a specific purpose, even if not expressly stated in the contract. Key legal differences include title warranty addressing ownership and defects in title, while implied warranty pertains to product condition, usability, and compliance with expectations under the law.
Importance of Title Warranty in Transactions
Title warranty is crucial in real estate transactions as it guarantees the seller has clear ownership and the legal right to transfer property, protecting the buyer from future ownership disputes. Unlike implied warranties, which are automatic and limited, title warranties explicitly assure free and marketable title, providing stronger legal recourse if title defects arise. This assurance enhances buyer confidence and mitigates financial risks associated with unknown liens or encumbrances.
Types of Implied Warranties
Implied warranties primarily include the warranty of merchantability, which ensures that a product will function as expected for ordinary use, and the warranty of fitness for a particular purpose, assuring the product meets specific needs disclosed by the buyer to the seller. Title warranty guarantees legal ownership and the right to sell the product, protecting against claims or liens from third parties. Understanding these distinctions helps consumers and sellers recognize their rights and obligations in sales contracts.
Buyer’s Rights Under Title Warranty
Buyers under a title warranty receive protection ensuring the seller has valid ownership and the right to transfer clear title, free from undisclosed liens or encumbrances. This warranty empowers buyers to seek legal remedies or compensation if a third party challenges ownership or defects arise after purchase. Unlike implied warranties, title warranties specifically guarantee the seller's lawful authority to convey the property, safeguarding the buyer's investment and ownership rights.
Limitations of Implied Warranty
Implied warranty offers protection for buyers by ensuring that a product meets basic quality and functionality standards, but its limitations include lack of coverage for defects disclosed before purchase or those arising from misuse. Unlike a title warranty, implied warranty does not guarantee legal ownership or protect against claims from third parties. Courts often limit implied warranty claims by imposing strict timeframes and excluding consequential damages, restricting the scope of buyer protection.
Common Scenarios: Title Warranty vs Implied Warranty
Title warranty guarantees the legal ownership and clear title of a property, protecting buyers from disputes or claims against the property's ownership. Implied warranty, often relevant in the sale of goods, ensures that products meet basic standards of quality and functionality, such as fitness for a particular purpose or merchantability. Common scenarios include a buyer relying on title warranty to avoid defects in ownership during real estate transactions, while implied warranty is applied when a consumer purchases a product that fails to perform as expected despite no express warranty given.
Protecting Yourself: Choosing the Right Warranty
Selecting the right warranty involves understanding the distinction between title and implied warranties, where a title warranty guarantees legal ownership and freedom from liens, while an implied warranty ensures the product meets basic quality and functionality standards. Protecting yourself requires verifying clear title before purchase to avoid future ownership disputes and relying on implied warranties to address defects not explicitly covered in a sales contract. Prioritize reviewing state-specific warranty laws and obtaining written assurances to maximize legal protection and minimize financial risk.
Legal Consequences of Warranty Breaches
Breach of title warranty, which guarantees clear ownership, can lead to legal consequences such as rescission of the sale, damages, or specific performance to resolve title defects. Violations of implied warranty, particularly implied warranty of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose, expose sellers to claims for damages or contract rescission if the goods fail to meet reasonable quality standards. Courts often award remedies based on the nature of the warranty and the impact of the breach on the buyer's rights and expectations.
Title Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com