Administrative Regulation Interpretation involves understanding the meaning and application of rules set by government agencies that govern various sectors. Accurate interpretation ensures compliance with legal standards and helps avoid potential disputes or penalties. Explore this article to deepen your knowledge and effectively navigate administrative regulations.
Table of Comparison
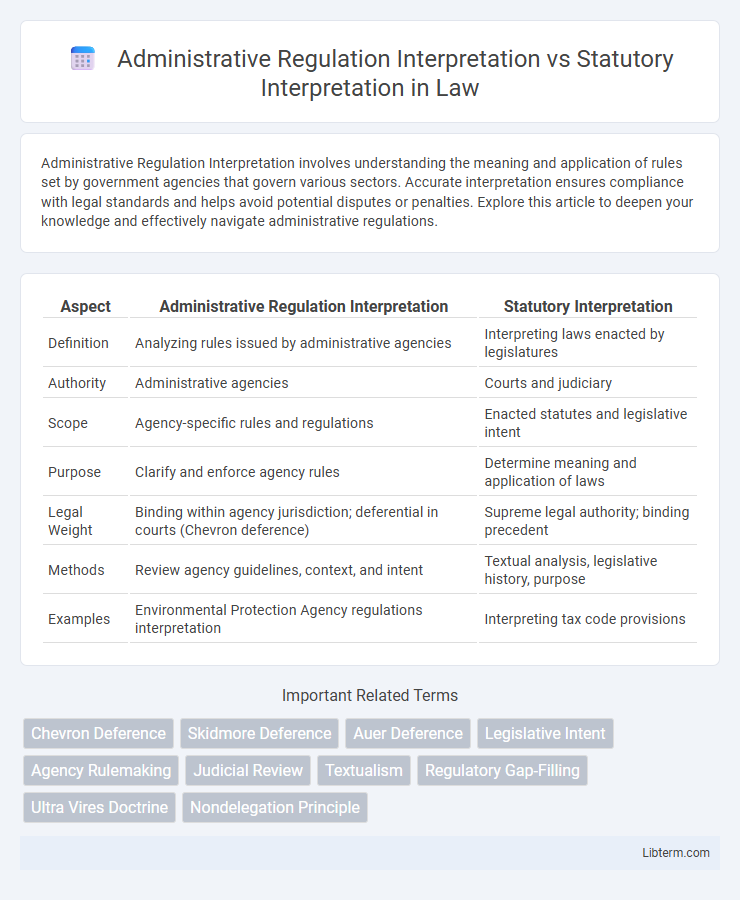
| Aspect | Administrative Regulation Interpretation | Statutory Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzing rules issued by administrative agencies | Interpreting laws enacted by legislatures |
| Authority | Administrative agencies | Courts and judiciary |
| Scope | Agency-specific rules and regulations | Enacted statutes and legislative intent |
| Purpose | Clarify and enforce agency rules | Determine meaning and application of laws |
| Legal Weight | Binding within agency jurisdiction; deferential in courts (Chevron deference) | Supreme legal authority; binding precedent |
| Methods | Review agency guidelines, context, and intent | Textual analysis, legislative history, purpose |
| Examples | Environmental Protection Agency regulations interpretation | Interpreting tax code provisions |
Introduction to Legal Interpretation Frameworks
Administrative regulation interpretation involves analyzing rules created by government agencies to determine their meaning and application within the scope of delegated authority. Statutory interpretation focuses on understanding and applying legislative statutes enacted by legislatures based on textual, purposive, and contextual frameworks. Both frameworks require methods such as textual analysis, examination of legislative intent, and review of administrative context to resolve ambiguities and guide legal decision-making.
Defining Administrative Regulation Interpretation
Administrative regulation interpretation involves analyzing and clarifying the meaning and application of rules established by government agencies, ensuring their enforcement aligns with legislative intent and policy goals. It requires understanding the context, purpose, and language of the regulation, often considering agency expertise and precedent in decision-making. This process differs from statutory interpretation, which primarily focuses on deciphering the language and intent of legislative statutes passed by governing bodies.
Understanding Statutory Interpretation
Understanding statutory interpretation involves analyzing legislative language to determine the legislature's intent, ensuring laws are applied as intended. It requires examining the text, context, purpose, and legislative history to resolve ambiguities or inconsistencies in statutes. This process contrasts with administrative regulation interpretation, which focuses on how agencies enforce or implement those statutes within their regulatory frameworks.
Sources of Authority: Statutes vs. Regulations
Statutory interpretation derives authority directly from legislatures enacting laws that courts interpret to apply legal rules, while administrative regulation interpretation is grounded in agencies' expertise and authority delegated by statutes to create detailed rules. Courts give deference to administrative regulations when agencies act within their statutory mandate, as established by doctrines like Chevron or Auer deference. The source of authority for statutes is the sovereign legislative body, whereas regulations gain authority through formal rulemaking processes authorized by the underlying statutes.
Principles Guiding Administrative Regulation Interpretation
Administrative regulation interpretation emphasizes agency expertise and the purpose behind regulatory language, relying on principles such as deference to agency interpretations under the Chevron doctrine and the reasonable construction of ambiguous terms. Statutory interpretation prioritizes legislative intent by examining the text, context, and legislative history of statutes without giving default deference to administrative agencies. The core principles guiding administrative regulation interpretation include consistency with statutory mandates, avoiding conflicts with established laws, and ensuring regulations fulfill their intended regulatory objectives.
Core Methods in Statutory Interpretation
Core methods in statutory interpretation include textualism, which emphasizes the ordinary meaning of the statute's language; intentionalism, focusing on the legislature's intent behind the law; and purposivism, seeking to understand the broader purpose and objectives of the statute. Administrative regulation interpretation often relies on Chevron deference, whereby courts defer to an agency's reasonable interpretation of ambiguous statutes within its jurisdiction. In contrast, statutory interpretation prioritizes the plain text, legislative history, and legislative purpose to resolve ambiguities without deferring to agency interpretations.
Judicial Approaches to Regulatory vs. Statutory Texts
Judicial approaches to administrative regulation interpretation prioritize deference to agency expertise, often applying the Chevron two-step test to uphold regulatory interpretations unless they are unreasonable. In contrast, statutory interpretation emphasizes the courts' independent examination of legislative text using tools like the plain meaning rule, legislative history, and canons of construction. This distinction reflects the judiciary's recognition of agencies' specialized role in rulemaking while maintaining ultimate authority in interpreting statutory mandates.
Conflicts Between Statutes and Administrative Regulations
Conflicts between statutes and administrative regulations arise when an agency's rules appear to exceed or contradict legislative mandates established by statutes. Courts resolve these conflicts by applying the Chevron deference framework, which grants agencies interpretive authority when statutes are ambiguous and regulations are reasonable. When a statute clearly prohibits certain provisions, administrative regulations in conflict are invalidated to uphold legislative supremacy and statutory interpretation principles.
Impact on Legal Outcomes and Precedents
Administrative regulation interpretation often grants agencies deference under doctrines like Chevron, influencing legal outcomes by allowing flexible application of statutes within agency expertise, which can solidify specific regulatory policies as binding precedent. Statutory interpretation relies on judicial analysis of legislative intent and textual meaning, providing courts with a framework to evaluate laws independently, thereby shaping legal precedents grounded in statutory language. The balance between these interpretations affects how courts uphold agency actions and the stability of legal doctrines in subsequent cases.
Conclusion: Harmonizing Interpretative Approaches
Harmonizing Administrative Regulation Interpretation with Statutory Interpretation requires recognizing the complementary roles each plays in legal analysis, where statutory interpretation establishes legislative intent and administrative interpretation applies that intent within agency expertise. Courts tend to defer to administrative interpretations under frameworks like Chevron when regulations fill gaps left by statutes, promoting consistency and flexibility in law application. This synergy enhances legal clarity by integrating statutory mandates with detailed regulatory implementation, ensuring effective governance and judicial efficiency.
Administrative Regulation Interpretation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com