Codification organizes laws and regulations into a systematic collection, making legal references clearer and more accessible. This process ensures consistency and simplifies legal research for professionals and the public alike. Explore the rest of the article to understand how codification can impact Your legal experience.
Table of Comparison
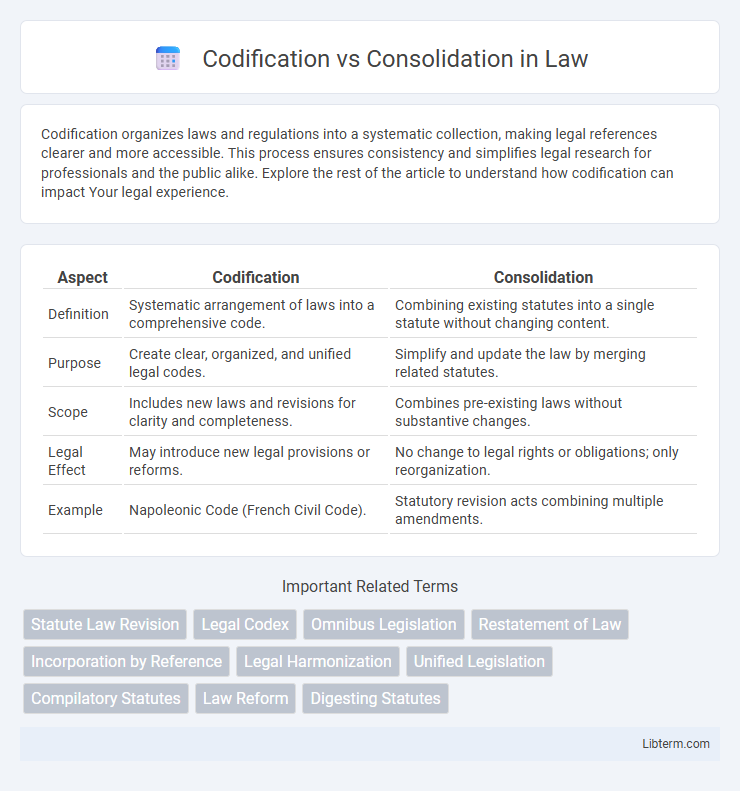
| Aspect | Codification | Consolidation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic arrangement of laws into a comprehensive code. | Combining existing statutes into a single statute without changing content. |
| Purpose | Create clear, organized, and unified legal codes. | Simplify and update the law by merging related statutes. |
| Scope | Includes new laws and revisions for clarity and completeness. | Combines pre-existing laws without substantive changes. |
| Legal Effect | May introduce new legal provisions or reforms. | No change to legal rights or obligations; only reorganization. |
| Example | Napoleonic Code (French Civil Code). | Statutory revision acts combining multiple amendments. |
Introduction to Codification and Consolidation
Codification refers to the systematic arrangement and classification of laws or financial statements into a coherent code or framework, enhancing accessibility and consistency. Consolidation involves combining multiple financial statements or legal provisions from different entities into a single, unified presentation to provide a comprehensive overview. Both processes aim to improve clarity and usability but address different organizational challenges in legal and financial contexts.
Defining Codification in Legal Contexts
Codification in legal contexts refers to the systematic process of arranging and setting down laws or legal principles into a comprehensive, written code. This method transforms scattered statutes and case laws into an organized structure, enhancing accessibility and clarity for legal interpretation and application. Unlike consolidation, which merges various laws without altering content, codification often involves reformatting and harmonizing laws to create a coherent legal framework.
Understanding Consolidation in Law
Consolidation in law refers to the process of combining multiple related statutes or legal provisions into a single, organized code to enhance clarity and accessibility. This approach ensures all relevant laws on a particular subject are integrated coherently, eliminating inconsistencies and redundancies. Unlike codification, which involves systematic arrangement and restatement of laws, consolidation emphasizes merging existing laws to facilitate easier legal reference and application.
Key Differences Between Codification and Consolidation
Codification involves systematically organizing and integrating accounting standards or rules into a single, coherent framework, while consolidation refers to combining financial statements of multiple subsidiaries into one comprehensive report for the parent company. Codification standardizes accounting principles to enhance clarity and consistency, whereas consolidation focuses on presenting the financial position of a group of companies as a single entity. Key differences include the purpose: codification targets standardization of accounting guidance, and consolidation addresses financial reporting of corporate groups.
Historical Evolution of Codification
The historical evolution of codification dates back to ancient legal systems such as the Code of Hammurabi and Roman law, which aimed to organize and unify laws into systematic collections. Codification systematically transforms unwritten customs and judicial precedents into written statutes, facilitating legal clarity and public accessibility. Unlike consolidation, which merges and updates existing laws, codification establishes a coherent, authoritative legal code that serves as the foundation for civil law jurisdictions worldwide.
Historical Development of Consolidation
Consolidation originated in the 19th century as a method to unify fragmented statutes into a single comprehensive code, improving legal clarity and accessibility. Early consolidation efforts were driven by the need to streamline complex legal systems and reduce inconsistencies across jurisdictions. The development of consolidation reflects a shift towards systematic law reform, enabling easier updates and amendments within an integrated legislative framework.
Advantages of Codification
Codification organizes laws into a systematic code, improving legal clarity and accessibility for practitioners and the public. It reduces ambiguity by standardizing statutes, which facilitates consistent interpretation and enforcement across jurisdictions. Codified laws also enhance legislative efficiency by providing a clear reference framework, streamlining legal research and policymaking processes.
Benefits of Consolidation
Consolidation streamlines financial statements by combining multiple entities into a single reporting entity, enhancing clarity and reducing complexity for stakeholders. It improves decision-making through a comprehensive view of the entire organization's financial health, supporting better resource allocation and strategic planning. Consolidated reports also facilitate compliance with regulatory requirements by presenting unified financial data that reflects the group's overall performance.
Practical Examples of Codification and Consolidation
Codification involves organizing laws into systematic codes, such as the Codex of Hammurabi or the United States Code, where statutes are arranged by subject for clarity and accessibility. Consolidation merges multiple related laws or regulations into a single comprehensive document, exemplified by the Consolidated Appropriations Act in the U.S., which combines various funding bills into one. Practical codification streamlines legal research by categorizing legislation, while consolidation simplifies compliance by uniting fragmented statutes under unified provisions.
Choosing Between Codification and Consolidation
Choosing between codification and consolidation depends on the complexity and scope of legal materials involved. Codification organizes laws systematically by subject, enhancing clarity and accessibility for specific legal areas. Consolidation merges multiple related statutes or amendments into a single document, ensuring legal coherence and minimizing contradictions across overlapping regulations.
Codification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com