A Writ of Habeas Corpus is a fundamental legal mechanism that protects individual freedom by requiring a person under arrest to be brought before a court to determine the legality of their detention. This writ serves as a crucial safeguard against unlawful imprisonment and ensures that your personal liberty is not violated without due process. Discover how this powerful legal tool operates and why it remains essential in upholding justice throughout the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
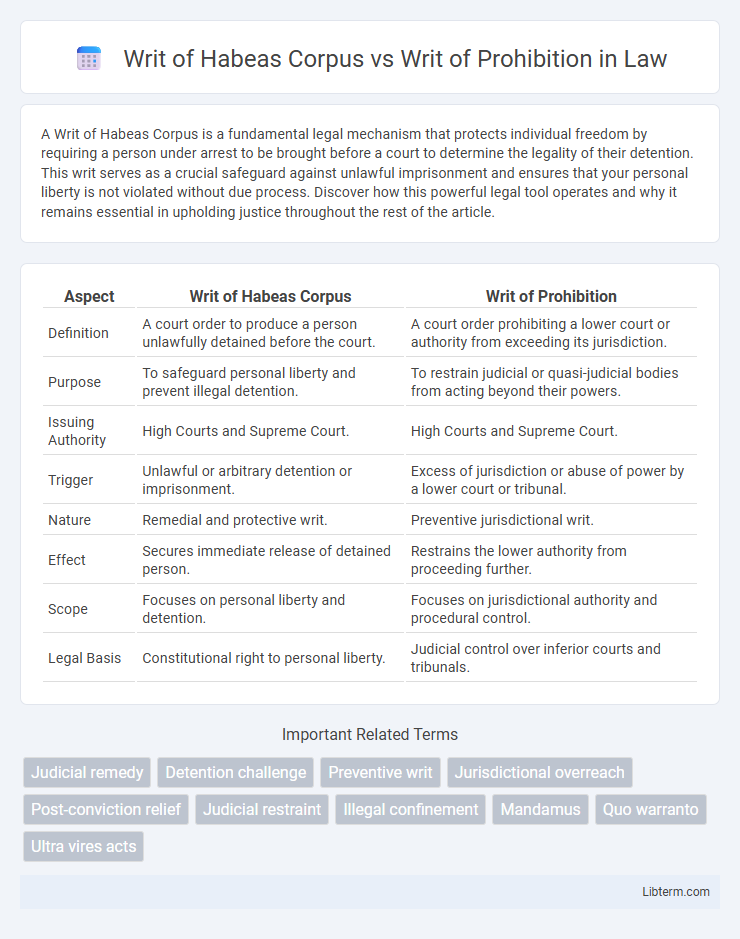
| Aspect | Writ of Habeas Corpus | Writ of Prohibition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A court order to produce a person unlawfully detained before the court. | A court order prohibiting a lower court or authority from exceeding its jurisdiction. |
| Purpose | To safeguard personal liberty and prevent illegal detention. | To restrain judicial or quasi-judicial bodies from acting beyond their powers. |
| Issuing Authority | High Courts and Supreme Court. | High Courts and Supreme Court. |
| Trigger | Unlawful or arbitrary detention or imprisonment. | Excess of jurisdiction or abuse of power by a lower court or tribunal. |
| Nature | Remedial and protective writ. | Preventive jurisdictional writ. |
| Effect | Secures immediate release of detained person. | Restrains the lower authority from proceeding further. |
| Scope | Focuses on personal liberty and detention. | Focuses on jurisdictional authority and procedural control. |
| Legal Basis | Constitutional right to personal liberty. | Judicial control over inferior courts and tribunals. |
Introduction to Writ of Habeas Corpus and Writ of Prohibition
The writ of habeas corpus serves as a fundamental legal remedy designed to protect individual freedom by requiring authorities to justify the lawful detention of a person. In contrast, the writ of prohibition functions as a supervisory writ issued by a higher court to prevent lower courts or tribunals from acting beyond their jurisdiction or exceeding their legal authority. Both writs play a crucial role in the judicial system by safeguarding personal liberty and maintaining the proper exercise of judicial power.
Definition and Legal Basis of Habeas Corpus
The Writ of Habeas Corpus is a legal action or writ through which a person can seek relief from unlawful detention by demanding the detainee be brought before a court to determine the legality of the imprisonment, grounded in constitutional law such as Article 3, Section 15 of the 1987 Philippine Constitution. The Writ of Prohibition, on the other hand, is an order issued by a higher court to a lower court or tribunal to stop proceedings that exceed jurisdiction or violate due process. Habeas Corpus serves as a fundamental safeguard against illegal restraint, affirming personal liberty under the rule of law.
Definition and Legal Basis of Prohibition Writ
The Writ of Habeas Corpus is a legal remedy that protects an individual's freedom by requiring authorities to justify unlawful detention. In contrast, the Writ of Prohibition is a judicial order directing a lower court or tribunal to cease functions overstepping its jurisdiction, rooted in the principle of jurisdictional control and outlined under Rule 65 of the Rules of Court. Its legal basis ensures higher courts prevent inferior courts from proceeding in cases beyond their authority, safeguarding due process and maintaining judicial hierarchy.
Historical Evolution of Both Writs
The Writ of Habeas Corpus, originating in 17th-century English common law, historically served as a crucial safeguard against unlawful detention by ensuring a detainee's right to appear before a court. The Writ of Prohibition, with roots tracing back to medieval English law, evolved as a legal remedy to prevent lower courts or tribunals from exceeding their jurisdiction or acting contrary to established law. Both writs have significantly influenced the development of judicial review and the protection of individual liberties in common law jurisdictions worldwide.
Scope and Applicability: Habeas Corpus vs Prohibition
The Writ of Habeas Corpus specifically addresses unlawful detention or imprisonment, compelling authorities to justify the legality of a person's custody, thus focusing on individual liberty protection. In contrast, the Writ of Prohibition seeks to prevent lower courts or tribunals from exceeding their jurisdiction or acting contrary to the law, primarily serving as a supervisory tool within the judicial system. While Habeas Corpus is applicable only when personal liberty is threatened, the Writ of Prohibition applies broadly to any judicial or quasi-judicial body overstepping legal authority.
Key Differences Between Habeas Corpus and Prohibition
The Writ of Habeas Corpus safeguards individual liberty by compelling authorities to produce a detained person before the court to determine the lawfulness of the detention, whereas the Writ of Prohibition prevents lower courts or tribunals from exceeding their jurisdiction or acting contrary to the rules of natural justice. Habeas Corpus is primarily concerned with unlawful imprisonment or detention, providing a remedy for personal freedom, while Prohibition serves as a supervisory writ ensuring judicial or quasi-judicial bodies refrain from overstepping legal boundaries. The fundamental difference lies in Habeas Corpus addressing the legality of detention, and Prohibition focusing on restraining jurisdictional overreach.
Grounds for Filing Each Writ
The writ of habeas corpus is filed to challenge unlawful detention or imprisonment, asserting that a person's liberty is being restrained without legal justification. In contrast, the writ of prohibition is sought to prevent a lower court or tribunal from exceeding its jurisdiction or acting contrary to the law, thereby stopping a legal proceeding before it causes harm. Habeas corpus centers on personal liberty and unlawful confinement, while prohibition focuses on jurisdictional overreach and procedural errors in judicial or quasi-judicial bodies.
Legal Procedures and Jurisdictions Involved
The writ of habeas corpus is a judicial mandate requiring a person under arrest to be brought before a court to determine if their detention is lawful, primarily utilized in criminal and civil cases involving personal liberty. In contrast, the writ of prohibition is issued by a higher court to a lower court or tribunal, directing it to cease proceedings that exceed its jurisdiction or violate the law, ensuring proper adherence to jurisdictional limits. Habeas corpus predominantly focuses on individual freedom against unlawful detention, while prohibition regulates judicial authority and procedural integrity within hierarchical court systems.
Landmark Cases Demonstrating Both Writs
The Writ of Habeas Corpus, exemplified by the landmark case Ex parte Milligan (1866), protects individual freedom by challenging unlawful detention, ensuring a person cannot be held without just cause. In contrast, the Writ of Prohibition, as demonstrated in the case of Barrow v. Hunton (1913), serves as a judicial check by preventing lower courts from exceeding their jurisdiction and interfering with higher court authority. Both writs play critical roles in maintaining legal boundaries and safeguarding due process within the judicial system.
Conclusion: Importance in Safeguarding Legal Rights
The Writ of Habeas Corpus serves as a vital legal remedy to protect individual liberty by preventing unlawful detention, ensuring that no person is held without just cause. The Writ of Prohibition acts as a preventive measure by restraining lower courts or authorities from exceeding their jurisdiction, maintaining the rule of law. Both writs are essential instruments in upholding due process and safeguarding fundamental legal rights within judicial systems.
Writ of Habeas Corpus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com