Constitutional interpretation involves analyzing the text, context, and purpose of constitutional provisions to determine their meaning and application in contemporary cases. Various methods, such as textualism, originalism, and purposivism, guide jurists in resolving ambiguities and adapting principles to modern challenges. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding of how these interpretive approaches shape legal decisions and impact your rights.
Table of Comparison
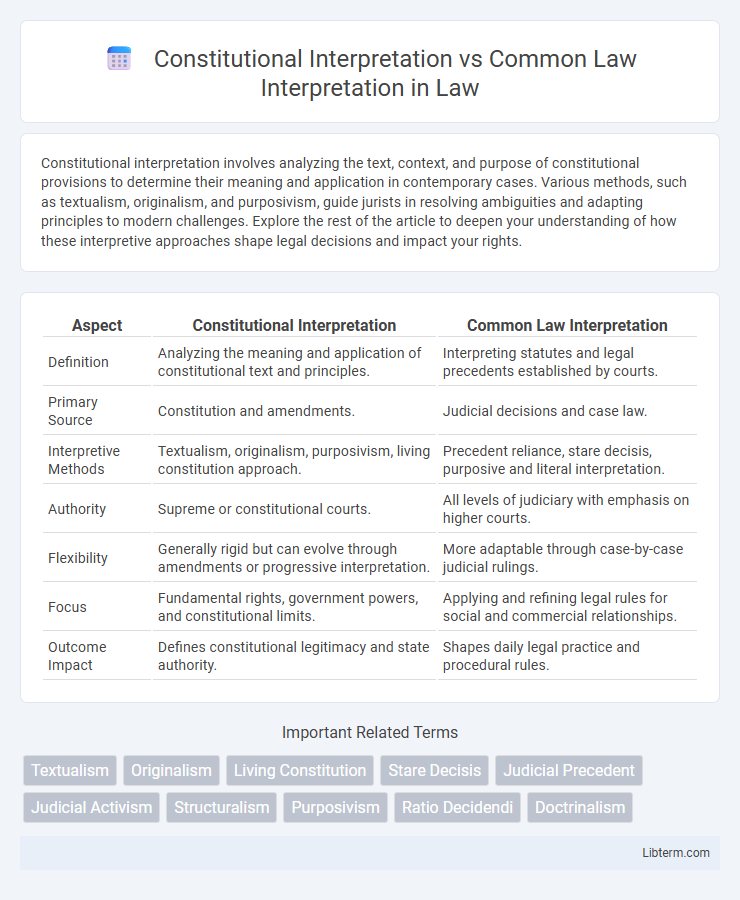
| Aspect | Constitutional Interpretation | Common Law Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzing the meaning and application of constitutional text and principles. | Interpreting statutes and legal precedents established by courts. |
| Primary Source | Constitution and amendments. | Judicial decisions and case law. |
| Interpretive Methods | Textualism, originalism, purposivism, living constitution approach. | Precedent reliance, stare decisis, purposive and literal interpretation. |
| Authority | Supreme or constitutional courts. | All levels of judiciary with emphasis on higher courts. |
| Flexibility | Generally rigid but can evolve through amendments or progressive interpretation. | More adaptable through case-by-case judicial rulings. |
| Focus | Fundamental rights, government powers, and constitutional limits. | Applying and refining legal rules for social and commercial relationships. |
| Outcome Impact | Defines constitutional legitimacy and state authority. | Shapes daily legal practice and procedural rules. |
Introduction to Constitutional and Common Law Interpretation
Constitutional interpretation involves analyzing and applying the principles and provisions outlined in a nation's constitution to legal cases and governance structures, emphasizing the constitution's supreme authority. Common law interpretation relies on judicial precedent and the evolving body of case law to resolve legal disputes, adapting to societal changes over time. Understanding the distinctions between these interpretative methods highlights their roles in shaping legal frameworks and ensuring justice within different legal systems.
Defining Constitutional Interpretation
Constitutional interpretation involves analyzing the text, context, and purpose of a constitution to determine its application in legal cases, emphasizing principles such as originalism or living constitutionalism. It differs from common law interpretation, which primarily relies on judicial precedents and case-by-case analysis to develop legal principles. Constitutional interpretation ensures the fundamental framework of government and individual rights are upheld according to the constitution's intended meaning and evolving societal values.
Defining Common Law Interpretation
Common law interpretation involves the judicial process of interpreting statutes and legal principles based on precedent, judicial decisions, and customary practices rather than fixed statutory text. It emphasizes case law evolution, adapting legal rules to changing societal contexts through judicial reasoning and analogy. This method contrasts with constitutional interpretation, which focuses on construing the terms and intentions of constitutional provisions, often with greater rigidity and foundational legal authority.
Historical Evolution of Interpretive Methods
Constitutional interpretation has historically evolved through methods such as originalism, which seeks to understand the framers' intent, and living constitutionalism, which adapts the text to contemporary contexts. In contrast, common law interpretation developed through judicial precedents, emphasizing case-by-case analysis and the doctrine of stare decisis to ensure consistency and predictability. These divergent approaches reflect the differing foundations of constitutional texts as supreme law and common law as judge-made law shaped incrementally over time.
Key Principles of Constitutional Interpretation
Constitutional interpretation centers on deciphering the text, structure, and intent of the Constitution, emphasizing principles such as originalism, textualism, and the living Constitution doctrine to guide judicial decisions. It prioritizes the Constitution's supremacy and foundational role in shaping laws and protecting fundamental rights, ensuring interpretations align with democratic values and constitutional fidelity. Unlike common law interpretation, which evolves through judicial precedents, constitutional interpretation demands a stable framework to maintain the Constitution's authoritative status and balance of powers.
Key Principles of Common Law Interpretation
Common law interpretation prioritizes the intent of the legislature and the context of statutory language, emphasizing precedent and judicial decisions to resolve ambiguities. Courts rely on the plain meaning rule, purposive approach, and the golden rule to interpret statutes, ensuring that the law is applied consistently with established legal principles. This method contrasts with constitutional interpretation, which often involves broader considerations of fundamental rights and the underlying values of the constitution.
Contrasts in Judicial Approaches
Constitutional interpretation involves applying principles and original intent to constitutional texts, emphasizing the fixed meaning or evolving standards within a supreme legal framework. Common law interpretation relies on precedents, judicial decisions, and evolving customs, allowing flexibility and adaptability to changing societal contexts. Judges in constitutional cases often prioritize textual fidelity and structural coherence, while common law judges emphasize case-by-case analysis and pragmatic outcomes.
Impact on Legal Precedents and Jurisprudence
Constitutional interpretation shapes legal precedents by establishing foundational principles that guide judiciary decisions and ensure government powers align with the constitution's intent. Common law interpretation influences jurisprudence through case-by-case analysis, allowing courts to adapt past rulings to new circumstances and evolving social norms. The interplay between these approaches creates a dynamic legal system where constitutional mandates provide overarching stability while common law fosters flexibility and incremental legal development.
Contemporary Debates and Challenges
Contemporary debates on constitutional interpretation often center on originalism versus living constitutionalism, reflecting divergent views on how rigidly courts should adhere to the framers' intent or adapt to societal changes. Common law interpretation faces challenges in balancing precedent stability with evolving social norms and technological advancements, sparking discussions on judicial activism and restraint. Both frameworks grapple with maintaining legal consistency while ensuring justice in rapidly changing cultural and political landscapes.
Conclusion: Implications for Legal Systems
Constitutional interpretation establishes foundational legal principles that guide the entire legal system, emphasizing stability and uniformity in applying fundamental rights and government powers. Common law interpretation evolves through judicial decisions, allowing flexibility and adaptability to changing societal norms and circumstances. The interaction between these interpretative methods shapes the dynamic balance between legal certainty and responsiveness within diverse legal systems.
Constitutional Interpretation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com