Doctrine serves as a foundational set of principles guiding legal, religious, or military practices, ensuring consistency and clarity in application. Understanding how doctrine influences your decisions can empower you to navigate complex frameworks effectively. Explore the rest of this article to uncover key insights and practical examples of doctrine in action.
Table of Comparison
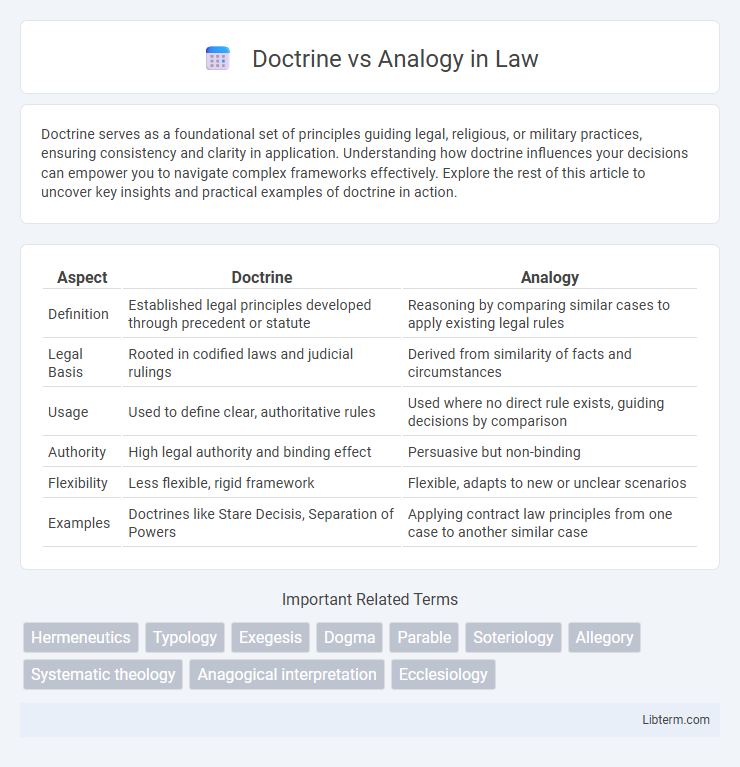
| Aspect | Doctrine | Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Established legal principles developed through precedent or statute | Reasoning by comparing similar cases to apply existing legal rules |
| Legal Basis | Rooted in codified laws and judicial rulings | Derived from similarity of facts and circumstances |
| Usage | Used to define clear, authoritative rules | Used where no direct rule exists, guiding decisions by comparison |
| Authority | High legal authority and binding effect | Persuasive but non-binding |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, rigid framework | Flexible, adapts to new or unclear scenarios |
| Examples | Doctrines like Stare Decisis, Separation of Powers | Applying contract law principles from one case to another similar case |
Understanding Doctrine: Definition and Importance
Doctrine refers to a formalized set of principles or teachings, often established by authoritative bodies to guide beliefs, decisions, or practices within a particular field. Understanding doctrine is crucial because it provides a structured framework for interpreting complex information and maintaining consistency across related topics. Its importance is evident in legal, religious, and academic contexts where doctrine shapes policy, ethical standards, and educational curricula.
What is Analogy? A Conceptual Overview
Analogy is a cognitive process that involves drawing comparisons between two different concepts or entities based on shared characteristics or relational similarities. It serves as a fundamental tool in reasoning, problem-solving, and communication by enabling individuals to transfer understanding from a familiar domain to an unfamiliar one. Unlike doctrine, which is a formalized set of principles or beliefs, analogy functions as an informal, intuitive method for generating insights and facilitating comprehension across diverse fields.
Key Differences Between Doctrine and Analogy
Doctrine refers to a formalized set of principles or beliefs that guide a particular field or practice, often codified and authoritative in nature. Analogy involves drawing parallels between two distinct concepts or situations to facilitate understanding, relying on similarity rather than formal authority. The key difference lies in doctrine's prescriptive and established framework compared to analogy's descriptive and comparative function used for explanation.
Historical Context: Origins of Doctrine and Analogy
Doctrine originates from formalized principles established in religious, legal, and philosophical traditions, often codified through authoritative texts and institutional teachings. Analogy emerged as a cognitive and rhetorical tool in ancient philosophy, notably within Aristotelian logic, to draw parallels and infer conclusions based on similarity rather than direct authority. The historical context reveals doctrine as a mechanism for preserving consistent belief systems, while analogy serves to adapt and interpret knowledge across different contexts.
Applications of Doctrine in Law and Theology
Doctrine serves as a foundational framework in law, providing established principles and precedents that guide judicial decisions and maintain legal consistency. In theology, doctrine defines core beliefs and dogmas that shape religious teachings and community practices. Both fields rely on doctrine to preserve authority, ensure coherence, and support systematic interpretation of complex concepts.
The Role of Analogy in Critical Thinking
Analogy plays a crucial role in critical thinking by enabling individuals to draw parallels between unfamiliar concepts and known experiences, facilitating deeper understanding and problem-solving. Unlike doctrine, which involves accepting established principles or rules, analogy promotes flexible reasoning and creative insight by highlighting similarities that reveal new perspectives. This method enhances cognitive processes by allowing thinkers to transfer knowledge across different domains, improving decision-making and argumentation skills.
Strengths and Limitations of Doctrine
Doctrine provides a solid framework based on established legal principles, ensuring consistency and predictability in judicial decisions. Its strength lies in the clarity and authority it offers, guiding courts and practitioners through well-defined rules. However, doctrine can be rigid and may struggle to adapt to novel cases or evolving societal values, limiting its flexibility and relevance in dynamic legal contexts.
Advantages and Challenges of Using Analogy
Using analogy in reasoning facilitates understanding by linking unfamiliar concepts to known experiences, enhancing cognitive retention and problem-solving efficiency. It simplifies complex subjects through relatable comparisons, making abstract or technical information more accessible. Challenges include potential oversimplification, the risk of misleading or inaccurate conclusions if analogies are not carefully selected, and difficulties in ensuring relevancy across different contexts.
Doctrine vs Analogy: Impact on Decision-Making
Doctrine provides a structured framework based on established principles and precedents, offering consistency and predictability in decision-making processes. Analogy relies on comparing current cases to previous ones with similar circumstances, enabling flexible and context-sensitive judgments that adapt to unique situations. The impact on decision-making lies in Doctrine's emphasis on authoritative rules fostering stability, while Analogy promotes adaptability and nuanced interpretation in evolving scenarios.
Selecting the Right Approach: When to Use Doctrine or Analogy
Selecting between doctrine and analogy depends on the context and purpose of legal reasoning. Doctrine applies established legal principles and precedents for predictable and consistent outcomes in well-defined cases. Analogy is effective in novel or ambiguous situations, drawing comparisons to similar cases to extend or adapt legal principles where doctrine lacks direct application.
Doctrine Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com