Rescission is the legal process of canceling a contract and restoring the parties involved to their original positions before the agreement. It often occurs when contracts are entered into based on fraud, misrepresentation, undue influence, or mutual mistake. Discover how understanding rescission can protect your rights by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
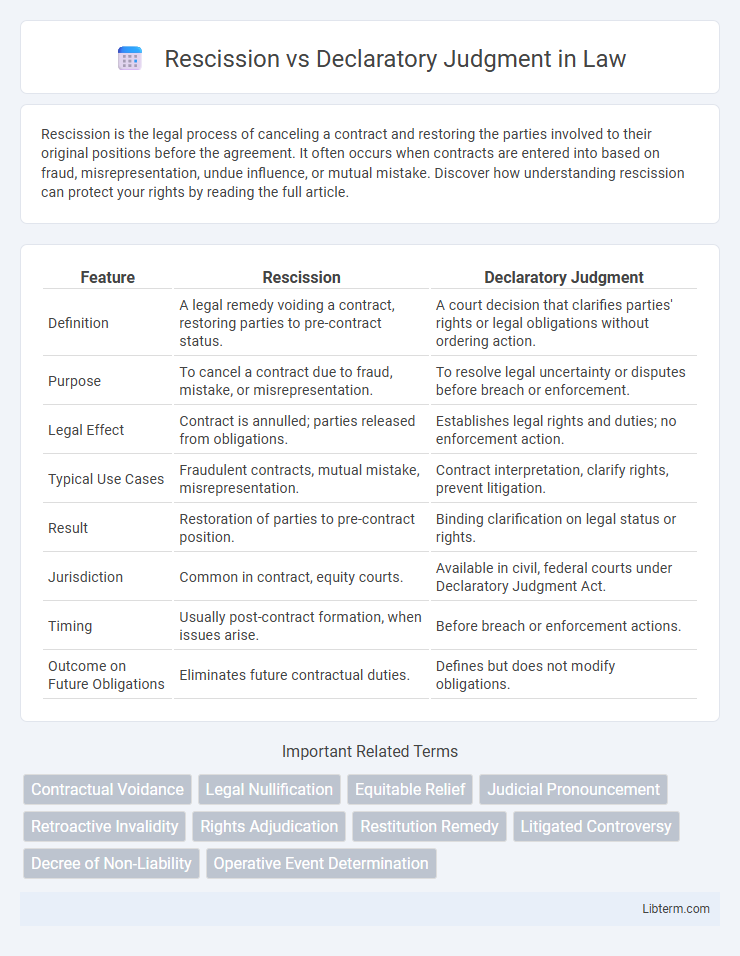
| Feature | Rescission | Declaratory Judgment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A legal remedy voiding a contract, restoring parties to pre-contract status. | A court decision that clarifies parties' rights or legal obligations without ordering action. |
| Purpose | To cancel a contract due to fraud, mistake, or misrepresentation. | To resolve legal uncertainty or disputes before breach or enforcement. |
| Legal Effect | Contract is annulled; parties released from obligations. | Establishes legal rights and duties; no enforcement action. |
| Typical Use Cases | Fraudulent contracts, mutual mistake, misrepresentation. | Contract interpretation, clarify rights, prevent litigation. |
| Result | Restoration of parties to pre-contract position. | Binding clarification on legal status or rights. |
| Jurisdiction | Common in contract, equity courts. | Available in civil, federal courts under Declaratory Judgment Act. |
| Timing | Usually post-contract formation, when issues arise. | Before breach or enforcement actions. |
| Outcome on Future Obligations | Eliminates future contractual duties. | Defines but does not modify obligations. |
Understanding Rescission: Definition and Purpose
Rescission is a legal remedy that voids a contract, returning parties to their pre-contractual position by canceling the agreement due to factors like fraud, mistake, or misrepresentation. Its purpose is to restore fairness and prevent unjust enrichment by nullifying contracts entered under invalid circumstances. Unlike declaratory judgment, which clarifies legal rights without altering party obligations, rescission actively reverses contractual commitments.
What is a Declaratory Judgment? Key Concepts
A declaratory judgment is a court ruling that defines the legal rights and obligations of parties without ordering any specific action or awarding damages. It provides clarity on legal disputes by establishing the status or interpretation of a contract, statute, or law. This judicial determination helps prevent future conflicts by resolving uncertainties proactively.
Legal Grounds for Rescission
Legal grounds for rescission typically include instances of fraud, misrepresentation, mistake, duress, undue influence, or a breach of contract that fundamentally undermines the agreement's validity. Courts require clear evidence that the contract was entered into based on false information or coercion, justifying the unwinding of the contract to restore parties to their original positions. Rescission differs from declaratory judgment as it directly reverses contractual obligations rather than merely clarifying the parties' rights or legal status under a contract.
Legal Grounds for Seeking a Declaratory Judgment
Legal grounds for seeking a declaratory judgment typically involve requests to clarify rights, duties, or obligations under a contract or statute without requesting damages or rescission of the contract. Courts grant declaratory judgments to resolve uncertainty or prevent future litigation by establishing the legal status or validity of an agreement, statute, or regulatory requirement. Unlike rescission, which cancels a contract due to fraud, mistake, or misrepresentation, declaratory judgments focus on affirming the parties' legal positions and obligations.
Rescission vs Declaratory Judgment: Core Differences
Rescission voids a contract by mutual agreement or due to a legal defect, effectively undoing the transaction and restoring parties to their pre-contract positions. Declaratory judgment determines the rights or legal relationships of parties without ordering any specific action or damages, providing clarity on contractual terms or disputes. The core difference lies in rescission's function to cancel contracts, while declaratory judgment resolves uncertainties without altering contractual status.
Procedural Requirements in Rescission Actions
Rescission actions require specific procedural steps such as timely filing, proof of a valid ground like misrepresentation or fraud, and often the restoration of parties to their original positions (restitutio in integrum). Courts typically mandate prompt notice to the opposing party and may require the return of any benefits or consideration exchanged in the contract. In contrast to declaratory judgment actions, rescission demands demonstrating equitable grounds and adherence to strict statutory or common law deadlines to invalidate the contract.
Procedures for Filing a Declaratory Judgment
Filing a declaratory judgment begins with submitting a formal complaint to the appropriate court, specifying the rights or legal status that require clarification. The complaint must include a clear statement of the controversy, relevant facts, and the legal basis for requesting the declaratory relief. Parties must follow jurisdictional rules and serve the complaint on all interested parties, who then have the opportunity to respond before the court issues a binding judgment.
Practical Implications: When to Choose Rescission
Rescission is preferable when a contract's validity is fundamentally compromised due to fraud, misrepresentation, mistake, or duress, allowing parties to void agreements and restore original positions. It suits cases where monetary damages are insufficient, emphasizing equitable relief to unwind contractual obligations. Opting for rescission ensures the annulment of the contract rather than merely establishing rights or interpretations as declaratory judgment does.
Practical Implications: When Declaratory Judgment is Suitable
Declaratory judgment is suitable when parties seek clarity on their rights or legal obligations without requiring immediate enforcement, often preventing potential disputes from escalating into litigation. It is practical in contract interpretation, insurance coverage issues, or property rights where the court's ruling guides future actions without ordering damages or rescinding agreements. Courts prefer declaratory judgments for resolving uncertainties swiftly, conserving resources, and promoting fair settlements.
Comparing Outcomes: Rescission and Declaratory Judgment in Practice
Rescission nullifies a contract, returning parties to their pre-agreement positions and effectively erasing the transaction's legal effects, while declaratory judgment determines the rights and obligations of parties without altering the contract's validity. In practice, rescission resolves disputes by undoing agreements due to misrepresentation, fraud, or mutual mistake, often leading to restitution, whereas declaratory judgment provides clarity and guidance on legal relationships, preventing further litigation. Courts apply rescission typically when fairness demands contract voidance, whereas declaratory judgments are favored to settle uncertainty in ongoing contractual obligations or rights.
Rescission Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com