A defective title can undermine the credibility and effectiveness of any content by failing to accurately reflect its subject or grabbing the reader's attention. Crafting a clear, concise, and relevant title is essential for ensuring your audience understands the topic and is enticed to engage with the material. Discover practical tips and strategies in the rest of the article to create powerful titles that boost your content's impact.
Table of Comparison
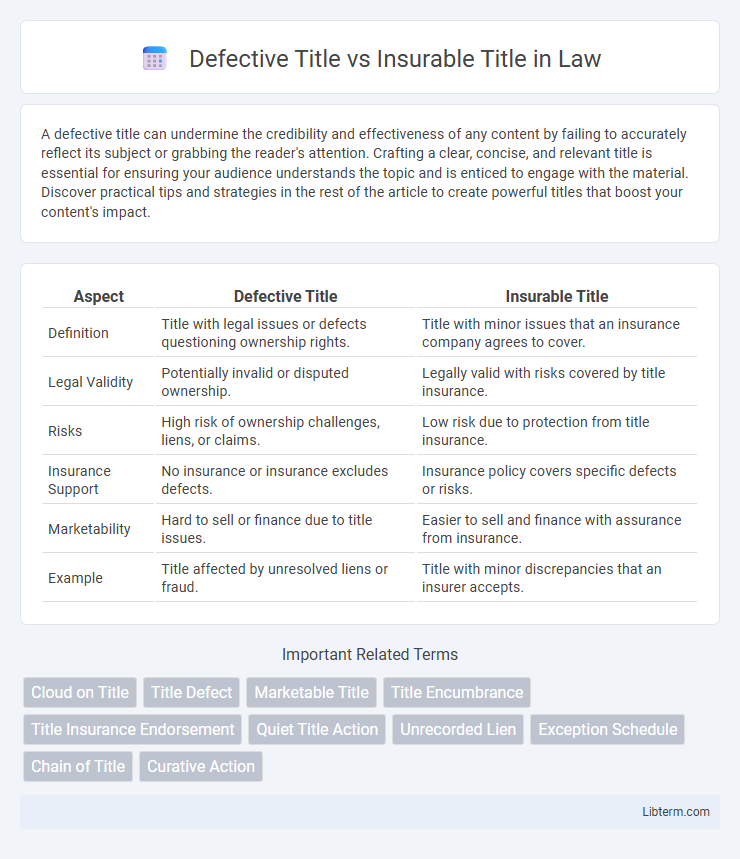
| Aspect | Defective Title | Insurable Title |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Title with legal issues or defects questioning ownership rights. | Title with minor issues that an insurance company agrees to cover. |
| Legal Validity | Potentially invalid or disputed ownership. | Legally valid with risks covered by title insurance. |
| Risks | High risk of ownership challenges, liens, or claims. | Low risk due to protection from title insurance. |
| Insurance Support | No insurance or insurance excludes defects. | Insurance policy covers specific defects or risks. |
| Marketability | Hard to sell or finance due to title issues. | Easier to sell and finance with assurance from insurance. |
| Example | Title affected by unresolved liens or fraud. | Title with minor discrepancies that an insurer accepts. |
Understanding Defective Title: Key Concepts
A defective title contains legal flaws such as liens, undisclosed heirs, or forged signatures that can hinder property ownership and transfer. Understanding defective title involves recognizing issues that may cause disputes or financial losses, making it crucial to identify these defects early. Insurable title, by contrast, offers protection through title insurance against potential defects, ensuring clear ownership despite unknown risks.
What Constitutes an Insurable Title?
An insurable title refers to a property title that may have minor defects or irregularities but can be guaranteed by a title insurance company, ensuring protection against potential future claims or legal disputes. These titles typically lack significant liens, encumbrances, or unresolved ownership issues that would impair marketability, making them eligible for insurance coverage. Title insurance policies provide financial protection for buyers and lenders, covering losses arising from defects such as forgery, undisclosed heirs, or errors in public records.
Major Causes of Defective Title
Major causes of defective title include unresolved liens, improper property descriptions, unknown heirs, and fraudulent conveyances, all of which compromise ownership clarity. Defective title can result from errors in public records, forgery, or undisclosed encumbrances that cloud legal ownership rights. Insurable title, by contrast, protects against losses arising from these defects through title insurance policies that validate ownership despite underlying title issues.
Legal Risks Associated with Defective Titles
Defective titles pose significant legal risks including ownership disputes, unresolved liens, and potential foreclosure, which can jeopardize property rights and lead to costly litigation. In contrast, insurable titles have been vetted by title insurance companies, mitigating risks by providing coverage against defects and undisclosed claims. Purchasing a property with a defective title requires thorough legal scrutiny to avoid future encumbrances and ensure clear ownership transfer.
How Insurable Titles Protect Property Buyers
Insurable titles protect property buyers by providing a guarantee from title insurance companies that any defects or liens not found during the title search will be covered, ensuring financial security against unforeseen claims. Unlike a defective title, which may have unresolved claims or legal issues, an insurable title confirms the property is free of significant legal encumbrances or that any risks have been acknowledged and accepted by the insurer. This protection empowers buyers with confidence in their ownership rights and safeguards their investment against future title disputes.
Common Title Defects Insurers Cover
Common title defects covered by insurable title include undisclosed heirs, forged documents, and clerical errors in public records, which often lead to disputes in property ownership. Defective titles may arise from boundary disputes, missing signatures, or fraud, but title insurers mitigate risk by guaranteeing clear ownership against these hidden hazards. Title insurance protects against financial loss resulting from these defects, ensuring secure property transactions despite underlying title irregularities.
Title Insurance vs. Clear Title: What’s the Difference?
Title insurance protects against financial loss from defects in a property's title, even if the title appears clear. A defective title contains unresolved issues like liens or ownership disputes that can jeopardize ownership, while an insurable title may have defects but is guaranteed by the title insurance company to be resolved or covered. Clear title means the ownership is free of liens or claims, but title insurance provides added security against hidden risks not evident during a standard title search.
Curing Title Defects: Legal Remedies and Processes
Curing title defects involves legal remedies such as quiet title actions, where courts resolve ownership disputes to establish clear title. Title insurance companies often facilitate the correction of title defects by investigating liens, encumbrances, or errors in public records to provide an insurable title status. Recording affidavits, obtaining releases, or correcting deeds through reformation are common processes used to transform a defective title into an insurable one, ensuring marketable property ownership.
Choosing Title Insurance: What Homebuyers Need to Know
Choosing title insurance involves understanding the difference between defective title and insurable title to protect your real estate investment from potential ownership disputes or liens. A defective title may contain errors, unresolved claims, or legal issues that could jeopardize property ownership, while an insurable title meets legal criteria and can be covered by a title insurance policy ensuring financial protection. Homebuyers should carefully review title search reports and policies to ensure the title is insurable, minimizing risks during property transactions.
Defective Title vs. Insurable Title: Practical Scenarios
Defective title arises when there are legal issues such as liens, unknown heirs, or improper documentation, complicating ownership transfer and potentially leading to disputes or loss of property rights. Insurable title, on the other hand, may contain minor defects that a title insurance company is willing to insure against, providing protection to the buyer despite underlying issues. In practical scenarios, homeowners encountering unresolved liens often face defective titles, whereas insurable titles commonly apply in transactions where minor clerical errors exist but can be covered by title insurance policies.
Defective Title Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com