Declaratory relief is a legal remedy that allows a court to determine the rights, duties, or obligations of parties without ordering any specific action or awarding damages. It provides clarity and helps prevent further legal disputes by resolving uncertainties in contracts, statutes, or other legal relationships. Explore the rest of the article to understand how declaratory relief can protect your interests in various legal scenarios.
Table of Comparison
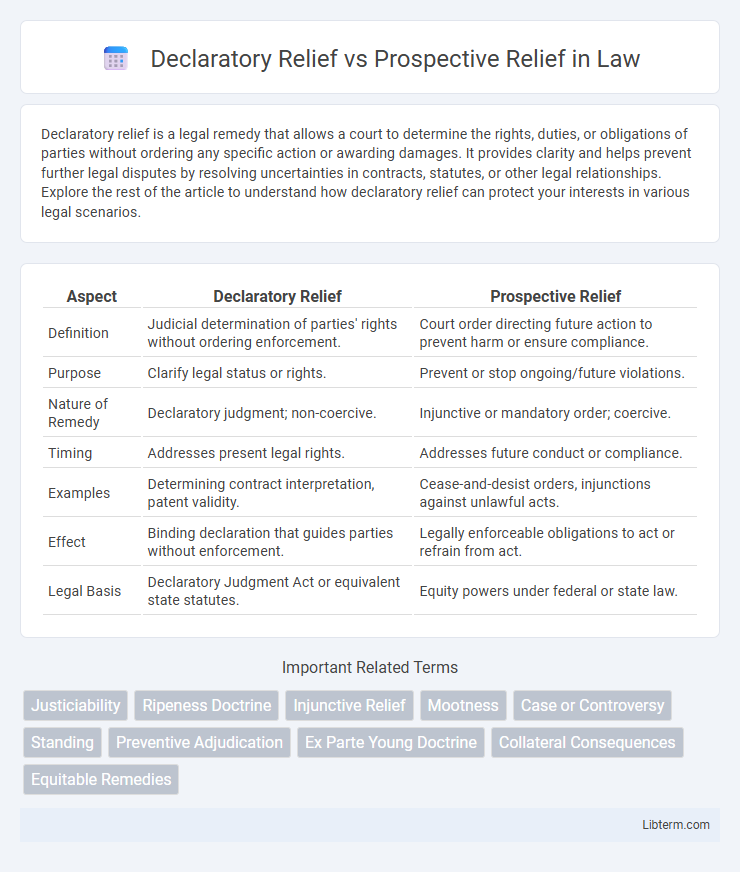
| Aspect | Declaratory Relief | Prospective Relief |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Judicial determination of parties' rights without ordering enforcement. | Court order directing future action to prevent harm or ensure compliance. |
| Purpose | Clarify legal status or rights. | Prevent or stop ongoing/future violations. |
| Nature of Remedy | Declaratory judgment; non-coercive. | Injunctive or mandatory order; coercive. |
| Timing | Addresses present legal rights. | Addresses future conduct or compliance. |
| Examples | Determining contract interpretation, patent validity. | Cease-and-desist orders, injunctions against unlawful acts. |
| Effect | Binding declaration that guides parties without enforcement. | Legally enforceable obligations to act or refrain from act. |
| Legal Basis | Declaratory Judgment Act or equivalent state statutes. | Equity powers under federal or state law. |
Introduction to Declaratory and Prospective Relief
Declaratory relief provides a court's official determination on the rights and obligations of parties without ordering any specific action or awarding damages, clarifying legal uncertainties. Prospective relief, often seen as injunctive relief, aims to prevent future harm by requiring parties to act or refrain from certain behaviors. Both remedies serve to address ongoing or anticipated legal disputes by defining rights clearly or shaping future conduct.
Defining Declaratory Relief
Declaratory relief is a legal remedy that determines the rights, duties, or obligations of parties without ordering any specific action or awarding damages. It allows courts to clarify legal uncertainties by issuing a binding declaration on the status or interpretation of a law, contract, or constitutional issue. This form of relief is often pursued to prevent future disputes by establishing legal relationships before actual harm occurs.
Understanding Prospective Relief
Prospective relief is a legal remedy designed to prevent future harm by ordering parties to take or refrain from specific actions, ensuring compliance with the law moving forward. Unlike declaratory relief, which merely establishes the rights or legal relationships between parties without mandating action, prospective relief enforces proactive measures such as injunctions or restraining orders. Courts issue prospective relief to maintain ongoing legal compliance and avoid irreparable damage, emphasizing its preventive and forward-looking nature.
Key Legal Principles Involved
Declaratory relief involves a court's formal statement clarifying the legal rights or obligations of parties without ordering any specific action, aiming to resolve legal uncertainty. Prospective relief, by contrast, directs future conduct through injunctions or orders requiring parties to act or refrain from specific behaviors to prevent ongoing or future harm. Both remedies rely on principles such as justiciability, standing, and the existence of a genuine legal dispute ripe for resolution, with declaratory relief emphasizing legal clarity and prospective relief focusing on preventing irreparable damage.
Differences in Purpose and Function
Declaratory relief serves to establish the rights, duties, or obligations of parties without ordering any specific action, often clarifying legal positions before disputes escalate. Prospective relief, on the other hand, mandates future conduct or restrains actions to prevent ongoing or imminent harm, typically through injunctions or orders that have a forward-looking effect. The key difference lies in declaratory relief's role in legal clarification, whereas prospective relief functions to proactively enforce or prohibit behaviors.
Procedural Requirements for Each Relief
Declaratory relief requires a plaintiff to establish an actual controversy and demonstrate immediate legal uncertainty, often necessitating a filed complaint that explicitly requests a judicial declaration to ascertain rights or legal status before any breach or harm occurs. Prospective relief, such as injunctions or specific performance, demands proof of imminent harm or ongoing violation of rights, alongside clear evidence that monetary damages are inadequate, typically requiring detailed factual allegations and a showing of irreparable injury in the pleadings. Both remedies involve distinct procedural steps including jurisdictional prerequisites, the presence of concrete legal disputes, and compliance with relevant statutes or court rules governing equitable remedies.
Common Situations for Declaratory Relief
Common situations for declaratory relief include contract disputes where parties seek a court's determination on their rights without enforcing a specific action, insurance coverage conflicts requiring clarification of policy obligations, and constitutional challenges where individuals or entities request a judicial declaration on the legality of statutes or government actions. Declaratory relief helps prevent future litigation by resolving legal uncertainties, often in cases involving ambiguous contracts, interpretation of statutes, or potential infringement of rights. Unlike prospective relief, which orders future conduct, declaratory relief solely establishes legal relationships or rights as they exist.
Common Applications of Prospective Relief
Prospective relief commonly addresses ongoing or future harm by preventing actions that would violate rights, often seen in injunctions restricting unlawful business practices or environmental damage. Courts frequently grant prospective relief in cases involving constitutional rights, such as restraining government agencies from enforcing unconstitutional laws or policies. This form of relief proactively ensures compliance with legal standards, contrasting with declaratory relief, which simply clarifies legal rights without enforcing future conduct.
Judicial Trends and Precedents
Judicial trends show an increasing preference for declaratory relief in cases requiring clarification of legal rights without coercive actions, emphasizing clarity and prevention of disputes. Courts historically distinguish prospective relief by its forward-looking injunctions or mandates aimed at shaping future conduct, as seen in landmark rulings like Ex parte Young and Monsanto Co. v. Geertson Seed Farms. Recent precedents highlight courts' cautious application of prospective relief, often requiring a clear legal basis and demonstrable ongoing harm to justify such remedies.
Choosing the Appropriate Relief
Choosing the appropriate relief between declaratory relief and prospective relief hinges on the nature of the legal dispute and the desired outcome. Declaratory relief provides a court's determination of parties' rights or legal status without ordering any specific action, ideal for resolving uncertainties and preventing future conflicts. Prospective relief, often through injunctions or specific performance, compels or prohibits future conduct, making it suitable when immediate or ongoing intervention is necessary to prevent harm.
Declaratory Relief Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com