Negligent misstatement occurs when incorrect information is carelessly communicated, leading to financial loss or damage. Understanding the legal implications of such statements can protect your rights and help avoid costly errors. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to identify and address negligent misstatements effectively.
Table of Comparison
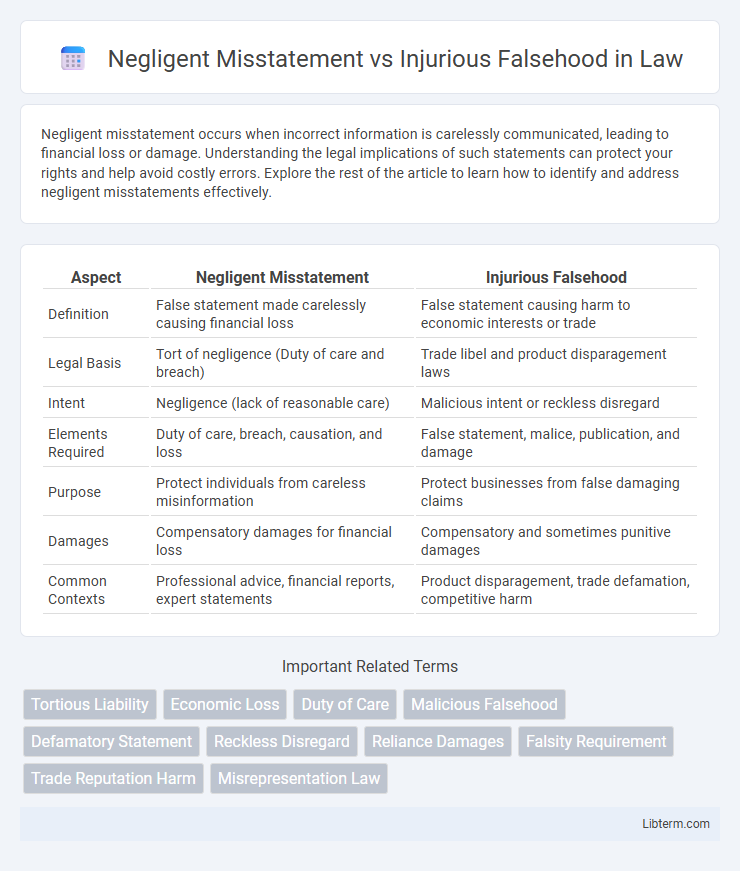
| Aspect | Negligent Misstatement | Injurious Falsehood |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | False statement made carelessly causing financial loss | False statement causing harm to economic interests or trade |
| Legal Basis | Tort of negligence (Duty of care and breach) | Trade libel and product disparagement laws |
| Intent | Negligence (lack of reasonable care) | Malicious intent or reckless disregard |
| Elements Required | Duty of care, breach, causation, and loss | False statement, malice, publication, and damage |
| Purpose | Protect individuals from careless misinformation | Protect businesses from false damaging claims |
| Damages | Compensatory damages for financial loss | Compensatory and sometimes punitive damages |
| Common Contexts | Professional advice, financial reports, expert statements | Product disparagement, trade defamation, competitive harm |
Introduction to Negligent Misstatement and Injurious Falsehood
Negligent misstatement involves inaccurate information provided carelessly, causing economic loss to a reliant party, typically addressed under tort law for pure economic damage. Injurious falsehood, also known as trade libel, concerns false statements that damage a person's business or property interests, requiring proof of malice or intent. Both legal concepts protect against harm from false information but differ in focus, with negligent misstatement centered on careless advice and injurious falsehood on malicious false claims.
Defining Negligent Misstatement
Negligent misstatement occurs when a party owes a duty of care to provide accurate information but fails, causing economic loss to another due to reliance on incorrect advice or statements. It is distinguished from injurious falsehood by its focus on carelessness in communication rather than malicious intent or trade-related falsehoods. Key elements include a duty of care, breach of that duty through faulty information, and resultant financial damage.
Defining Injurious Falsehood
Injurious falsehood, also known as trade libel or commercial disparagement, involves the publication of false statements that cause economic loss to a business by damaging its reputation or products. Unlike negligent misstatement, which arises from carelessly providing incorrect information leading to financial harm, injurious falsehood requires proof of malice or intent to harm and actual damage resulting from the false statement. The tort protects businesses against deliberate falsehoods that disrupt commercial relationships or sales.
Key Legal Elements of Negligent Misstatement
Negligent misstatement requires the existence of a duty of care owed by the defendant to the claimant, a breach of that duty through careless or inaccurate communication, and resultant economic loss directly caused by reliance on the false information. The statement must be made in a professional or business context where the defendant knows the information will be relied upon. Proof of loss and factual reliance are critical to establish liability under negligent misstatement claims, distinguishing it from injurious falsehood which centers on falsehoods causing damage to reputation or trade.
Essential Components of Injurious Falsehood
Injurious falsehood requires the publication of a false statement made maliciously or without just cause, causing direct economic loss to the plaintiff through a malicious intent to damage their business. The essential components include the falsity of the statement, malice or improper motive, publication to a third party, and resulting financial harm. Unlike negligent misstatement, which focuses on carelessness causing economic loss, injurious falsehood demands proof of intentional harm and actual damage.
Differences in Duty of Care
Negligent misstatement involves a duty of care owed when providing information or advice, requiring the defendant to avoid causing economic loss through inaccurate statements. Injurious falsehood centers on protecting business interests from false and malicious statements that harm reputation or trade, focusing on intentional or reckless falsehoods rather than mere negligence. The key difference lies in the duty of care: negligent misstatement demands reasonable care in information accuracy, while injurious falsehood emphasizes wrongful intent or malice behind harmful statements.
Comparison of Damages and Remedies
Damages for negligent misstatement primarily address economic loss caused by reliance on false information, focusing on compensatory damages to restore the claimant's financial position. Injurious falsehood, by contrast, covers harm to business reputation or goodwill, enabling recovery for both pecuniary loss and, in some cases, exemplary damages to deter malicious conduct. Remedies in negligent misstatement often involve rectifying misinformation and financial compensation, whereas injurious falsehood may also include injunctions to prevent further disparagement of the claimant's commercial interests.
Notable Case Law Examples
Notable case law on negligent misstatement includes Hedley Byrne & Co Ltd v Heller & Partners Ltd (1964), where the House of Lords established liability for economic loss caused by reliance on inaccurate information due to a breach of duty of care. In contrast, injurious falsehood was examined in British Motor Trade Association Ltd v Gray (1913), focusing on malicious false statements causing damage to business interests. These cases illustrate the differing legal standards and remedies: negligent misstatement centers on careless inaccuracies, while injurious falsehood involves deliberate or reckless falsehoods causing economic harm.
Practical Applications: Business and Professional Contexts
Negligent misstatement typically arises in business and professional contexts where inaccurate advice or information causes financial loss, such as in consulting, accounting, or legal services, and liability depends on a duty of care owed by the advisor to the plaintiff. Injurious falsehood involves the publication of false statements intended to damage a competitor's goods or business reputation, often seen in commercial disputes where proving malice and actual damage is crucial for recovery. Practical applications in businesses include risk management strategies to avoid negligent misstatements and robust evidence gathering to contest injurious falsehood claims effectively.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Legal Claim
Selecting the appropriate legal claim between negligent misstatement and injurious falsehood hinges on the nature of the harm and the defendant's conduct. Negligent misstatement suits cases involving financial loss due to inaccurate advice lacking reasonable care, while injurious falsehood targets deliberate falsehoods causing economic damage to reputation or products. Understanding these distinctions ensures effective legal strategy and maximizes recovery potential in commercial disputes.
Negligent Misstatement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com