Sole custody grants one parent exclusive legal and physical responsibility for raising a child, making key decisions without input from the other parent. This arrangement often arises when courts determine it is in the child's best interest due to factors like parental fitness or stability. Discover how sole custody impacts your family and what you need to consider moving forward in the full article.
Table of Comparison
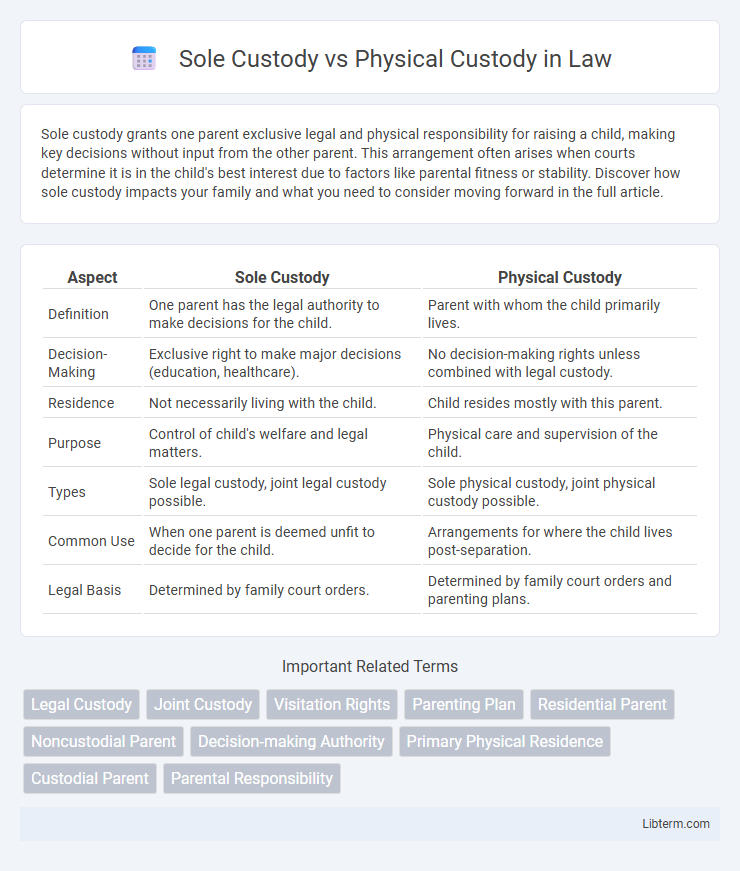
| Aspect | Sole Custody | Physical Custody |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | One parent has the legal authority to make decisions for the child. | Parent with whom the child primarily lives. |
| Decision-Making | Exclusive right to make major decisions (education, healthcare). | No decision-making rights unless combined with legal custody. |
| Residence | Not necessarily living with the child. | Child resides mostly with this parent. |
| Purpose | Control of child's welfare and legal matters. | Physical care and supervision of the child. |
| Types | Sole legal custody, joint legal custody possible. | Sole physical custody, joint physical custody possible. |
| Common Use | When one parent is deemed unfit to decide for the child. | Arrangements for where the child lives post-separation. |
| Legal Basis | Determined by family court orders. | Determined by family court orders and parenting plans. |
Understanding Sole Custody
Sole custody refers to a legal arrangement where one parent has the exclusive right to make major decisions regarding the child's education, healthcare, and welfare, while physical custody determines where the child primarily resides. Understanding sole custody involves recognizing that this parent holds primary responsibility for the child's upbringing without requiring consent from the non-custodial parent for key decisions. Courts typically award sole custody when it serves the child's best interests, such as in cases involving safety concerns or parental incapacity.
Defining Physical Custody
Physical custody refers to the arrangement determining where a child lives and who is responsible for their day-to-day care and supervision. It emphasizes the child's physical presence with a parent or guardian and includes decisions about their daily environment, such as living arrangements, schooling, and healthcare. Sole physical custody means the child resides primarily with one parent, while the other may have visitation rights or limited physical access.
Key Differences Between Sole and Physical Custody
Sole custody refers to one parent having exclusive legal decision-making authority over the child's education, healthcare, and general welfare, while physical custody pertains to where the child primarily resides. Key differences include sole custody granting a parent full legal rights without the need for the other parent's consent, whereas physical custody focuses strictly on the child's living arrangements and daily care. Courts may award sole or joint legal custody alongside various physical custody arrangements based on the child's best interests.
Legal Implications of Sole Custody
Sole custody grants one parent exclusive legal decision-making authority regarding a child's education, healthcare, and religion, significantly impacting parental rights and responsibilities. Courts awarding sole custody often do so based on the child's best interests, considering factors like parental fitness, stability, and history of abuse or neglect. Legal implications include restricted parental involvement for the non-custodial parent, which may affect visitation rights and require compliant behavior to maintain access.
Advantages of Physical Custody Arrangements
Physical custody arrangements provide children with consistent daily routines and stability by having them live primarily with one parent. This setup fosters stronger parent-child bonds through more frequent face-to-face interactions and direct involvement in the child's education, healthcare, and extracurricular activities. Courts often favor physical custody arrangements when prioritizing the child's emotional well-being and continuity of care.
When Courts Award Sole Custody
Courts award sole custody when one parent is deemed unfit due to factors like abuse, neglect, substance abuse, or inability to provide a stable environment, prioritizing the child's safety and well-being. Sole custody grants one parent the exclusive legal right to make major decisions regarding the child's education, healthcare, and religion, while physical custody determines where the child lives. Judges consider the child's best interests, parental fitness, and existing bonds before assigning sole custody to protect the child's emotional and physical health.
Factors Influencing Physical Custody Decisions
Physical custody decisions are primarily influenced by the child's best interests, including stability, emotional bonds, and the ability of each parent to provide a safe, nurturing environment. Courts evaluate factors such as the child's age, health, school schedule, and each parent's living situation and work commitments. Evidence of each parent's involvement in daily routines and willingness to encourage a positive relationship with the other parent also plays a critical role.
Impact on Child’s Well-being
Sole custody grants one parent full legal decision-making authority, while physical custody determines where the child primarily resides, both significantly affecting the child's stability and emotional health. Studies show that consistent physical custody arrangements with minimal conflict promote better psychological outcomes and secure attachments in children. Sole custody decisions should prioritize the child's best interests, ensuring that the custodial parent supports positive relationships and a safe environment.
Modifying Custody Agreements
Modifying custody agreements requires demonstrating a significant change in circumstances affecting the child's welfare, whether altering sole custody or physical custody arrangements. Courts prioritize the child's best interests, considering factors like stability, parental capability, and the child's needs when reviewing modification requests. Legal processes for modifying custody agreements differ by jurisdiction but often require filing a petition and attending hearings to present evidence supporting the proposed changes.
Choosing the Best Custody Option
Choosing the best custody option depends on the child's best interests and the parents' circumstances, balancing stability with parental involvement. Sole custody grants one parent legal decision-making authority, while physical custody concerns where the child primarily lives, often shared to ensure regular contact with both parents. Courts prioritize arrangements that promote the child's well-being, consistent routines, and emotional security when determining sole versus physical custody.
Sole Custody Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com