Certiorari is a legal writ that allows a higher court to review the decision of a lower court, ensuring that the law was applied correctly and justice was served. This critical process helps maintain consistency in legal interpretations and protects your rights within the judicial system. Explore the rest of the article to understand how certiorari functions and its impact on legal proceedings.
Table of Comparison
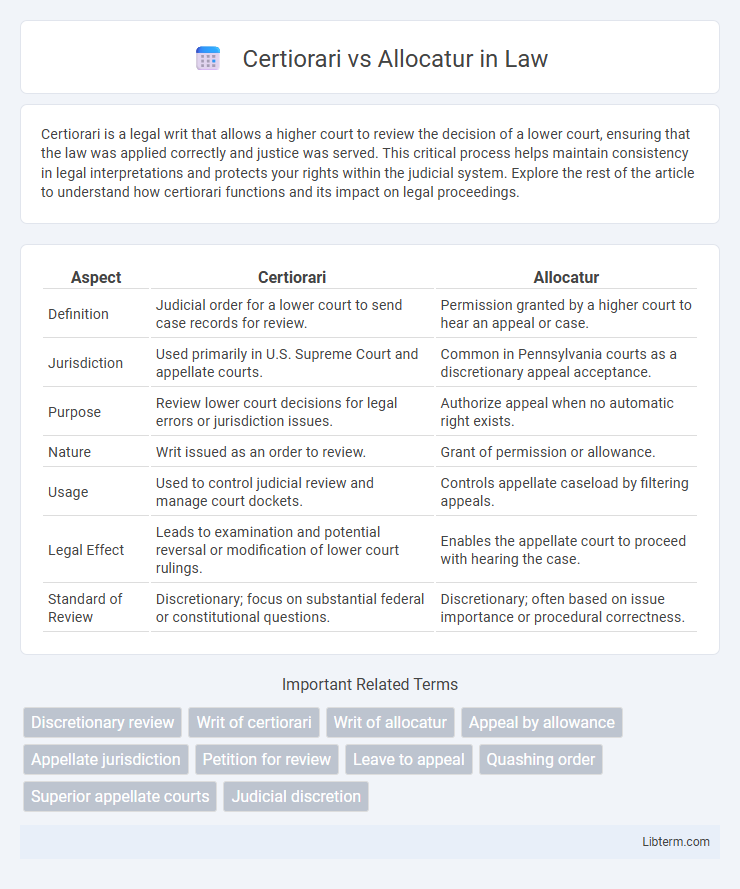
| Aspect | Certiorari | Allocatur |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Judicial order for a lower court to send case records for review. | Permission granted by a higher court to hear an appeal or case. |
| Jurisdiction | Used primarily in U.S. Supreme Court and appellate courts. | Common in Pennsylvania courts as a discretionary appeal acceptance. |
| Purpose | Review lower court decisions for legal errors or jurisdiction issues. | Authorize appeal when no automatic right exists. |
| Nature | Writ issued as an order to review. | Grant of permission or allowance. |
| Usage | Used to control judicial review and manage court dockets. | Controls appellate caseload by filtering appeals. |
| Legal Effect | Leads to examination and potential reversal or modification of lower court rulings. | Enables the appellate court to proceed with hearing the case. |
| Standard of Review | Discretionary; focus on substantial federal or constitutional questions. | Discretionary; often based on issue importance or procedural correctness. |
Introduction to Certiorari and Allocatur
Certiorari is a legal writ issued by a higher court to review the decision and proceedings of a lower court for errors of law or jurisdiction, primarily used in appellate courts to ensure judicial fairness. Allocatur, historically rooted in Pennsylvania practice, refers to the formal allowance or permission by a court to appeal a case, often serving as a procedural gatekeeper before certiorari is granted. Understanding the distinction highlights how certiorari functions as a discretionary review mechanism, while allocatur represents the preliminary approval necessary to escalate legal issues to higher judicial scrutiny.
Historical Background of Certiorari and Allocatur
Certiorari originated in English common law as a writ issued by higher courts to review and correct lower court decisions, serving as a key instrument in judicial oversight since the medieval period. Allocatur developed as a procedural term in Pennsylvania courts during the 19th century, signifying permission granted to appeal or review a case, functioning as a form of appellate approval. Both writs historically facilitated judicial control over case selection but evolved in distinct legal traditions and jurisdictions.
Definitions: What is Certiorari?
Certiorari is a judicial writ issued by a higher court to review the decision or proceedings of a lower court for errors of law or excess of jurisdiction. It primarily serves as a mechanism for appellate review, ensuring the correct application of legal principles and protection of due process. This writ is commonly used by supreme or appellate courts to select cases of significant public importance or to resolve conflicting decisions.
Definitions: What is Allocatur?
Allocatur is a legal term referring to a superior court's grant of permission to review a lower court's decision, primarily used in certain state courts like Pennsylvania. It functions similarly to certiorari, allowing appellate courts discretionary authority to hear appeals. Unlike certiorari, which is more common in federal courts, allocatur is specific to state judicial procedures and signifies acceptance of a case for appellate review.
Jurisdictional Differences: Federal vs State Practice
Certiorari primarily serves as a discretionary appellate review mechanism in federal courts, where the U.S. Supreme Court exercises this power to select cases from lower federal and state courts, emphasizing significant federal or constitutional questions. Allocatur is a term predominantly used in some state court systems, such as Pennsylvania, referring to the discretionary permission by a state appellate court to review an appeal, often highlighting procedural or state law issues under their jurisdiction. The key jurisdictional difference lies in certiorari's role in federal judicial review versus allocatur's function within state appellate processes, reflecting distinct procedural traditions and scopes of legal authority.
Key Procedural Distinctions
Certiorari and Allocatur differ primarily in their procedural application and courts of origin; certiorari is a writ commonly used by appellate courts to review decisions from lower courts, emphasizing error correction and jurisdictional oversight. Allocatur, predominantly found in certain state courts like Pennsylvania, is a permission or writ to allow an appeal, focusing on discretionary review where the court decides whether to hear a case. The key procedural distinction lies in certiorari's automatic or mandatory review of jurisdictional questions versus allocatur's discretionary acceptance of appeals based on the court's interest in the legal issues presented.
Criteria for Granting Certiorari and Allocatur
Certiorari is primarily granted based on the criteria of significant federal or constitutional questions, conflicts among lower courts, or issues of substantial public importance requiring Supreme Court review, often emphasizing cases with national impact. Allocatur, used mainly in Pennsylvania's appellate courts, grants discretionary review based on factors such as the presence of substantial legal questions, errors in lower court rulings, or matters needing clarification of state law precedent. Both mechanisms prioritize cases where addressing legal disputes will promote uniformity, correct serious judicial errors, or resolve significant legal uncertainties.
Case Law Examples Illustrating Each Writ
Certiorari is exemplified by cases like *Marbury v. Madison*, where the Supreme Court reviewed lower court decisions to ensure legal error correction and jurisdictional adherence. Allocatur, historically used in Pennsylvania, appears in cases such as *Commonwealth v. Shaines*, granting discretionary appellate review to refine legal questions or procedural issues. Both writs serve to control court proceedings, with certiorari emphasizing judicial oversight and allocatur focusing on selective appellate permission.
Practical Implications for Litigants and Attorneys
Certiorari and allocatur serve as mechanisms for higher courts to review lower court decisions, with certiorari primarily used in U.S. federal courts and allocatur in certain state jurisdictions like Pennsylvania. For litigants and attorneys, understanding that certiorari petitions require demonstration of significant federal or constitutional questions, whereas allocatur often involves discretionary review focusing on legal errors, guides strategic decisions on appellate advocacy. Effective navigation of these review processes impacts case outcomes by dictating the standards for granting review and shaping the scope of appellate arguments.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Certiorari and Allocatur
Certiorari serves as a discretionary review used primarily by higher courts to examine lower court decisions, particularly in federal appellate and Supreme Court cases. Allocatur functions similarly in some state courts, granting permission to review specific legal questions or cases on a discretionary basis. Choosing between certiorari and allocatur depends on the jurisdictional rules, procedural context, and strategic considerations involved in seeking appellate review.
Certiorari Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com