Declaratory relief provides a court judgment that clarifies legal rights and responsibilities without ordering any specific action or awarding damages. This remedy is essential in resolving disputes early, preventing future legal conflicts by establishing binding interpretations of contracts, statutes, or other legal issues. Explore this article to understand how declaratory relief can protect your interests and guide your legal decisions effectively.
Table of Comparison
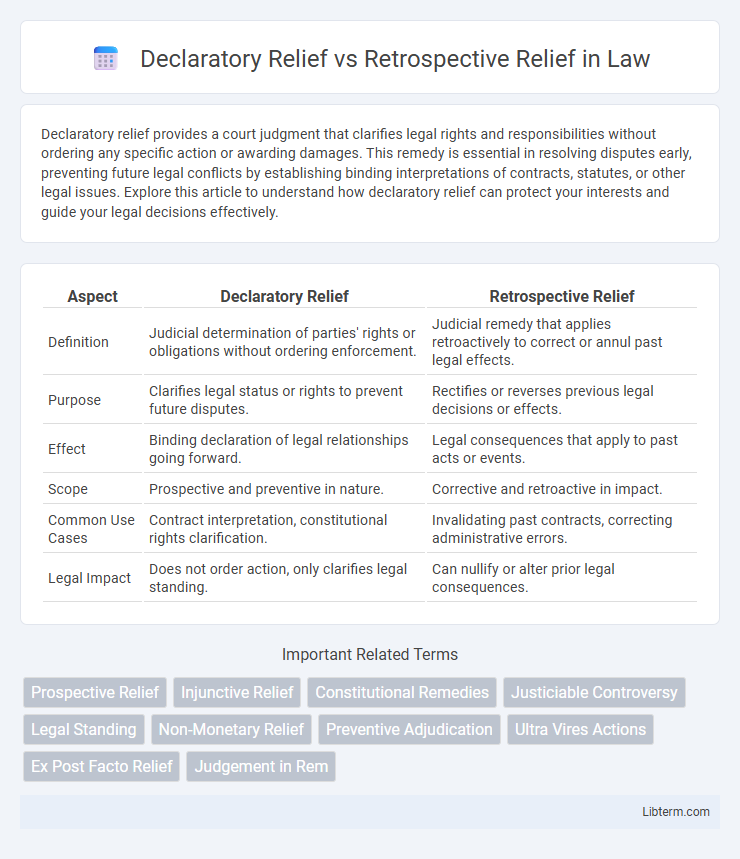
| Aspect | Declaratory Relief | Retrospective Relief |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Judicial determination of parties' rights or obligations without ordering enforcement. | Judicial remedy that applies retroactively to correct or annul past legal effects. |
| Purpose | Clarifies legal status or rights to prevent future disputes. | Rectifies or reverses previous legal decisions or effects. |
| Effect | Binding declaration of legal relationships going forward. | Legal consequences that apply to past acts or events. |
| Scope | Prospective and preventive in nature. | Corrective and retroactive in impact. |
| Common Use Cases | Contract interpretation, constitutional rights clarification. | Invalidating past contracts, correcting administrative errors. |
| Legal Impact | Does not order action, only clarifies legal standing. | Can nullify or alter prior legal consequences. |
Understanding Declaratory Relief
Declaratory relief is a judicial determination that resolves legal uncertainties by affirming the rights, obligations, or legal status of parties without ordering any specific action or awarding damages. It helps prevent future disputes by clarifying the legal relationship, often used in contract or constitutional law cases. Unlike retrospective relief, which addresses past wrongs and may involve compensation or injunctions, declaratory relief focuses solely on providing a clear legal declaration moving forward.
Defining Retrospective Relief
Retrospective relief refers to judicial remedies that address past actions or events by correcting or annulling previous decisions or conduct that violated legal rights. This type of relief aims to restore parties to the position they would have been in had the unlawful acts not occurred, often involving compensation, reversal of penalties, or invalidation of prior rulings. Unlike declaratory relief, which defines the parties' legal rights without ordering specific actions, retrospective relief enforces corrective measures that have an immediate impact on past matters.
Key Differences Between Declaratory and Retrospective Relief
Declaratory relief provides a court judgment that defines the legal rights or obligations of parties without ordering any specific action or awarding damages, while retrospective relief involves remedies that apply to past events, such as compensation or restitution. Key differences include the fact that declaratory relief is forward-looking, clarifying rights to prevent future disputes, whereas retrospective relief addresses harm already suffered by providing compensation or corrective measures. Declaratory judgments do not alter past conduct but establish legal status, whereas retrospective relief actively remedies past violations or damages.
Legal Framework for Declaratory Relief
The legal framework for declaratory relief is established under Rule 57 of the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure, allowing courts to determine the rights and obligations of parties without ordering any specific action or awarding damages. This form of relief provides a binding judicial declaration on legal status or interpretation of law, promoting clarity and preventing future litigation. Unlike retrospective relief, which addresses past actions or wrongs, declaratory relief primarily focuses on resolving legal uncertainties before actual harm occurs.
Legal Basis for Retrospective Relief
Retrospective relief is grounded in equitable principles allowing courts to undo or reverse past actions or decisions to rectify legal wrongs. The legal basis for retrospective relief typically involves doctrines such as restitution, rescission, or judicial review powers to declare past transactions void or invalid. Courts grant retrospective relief to restore parties to their original positions before the contested act occurred, ensuring fairness and justice.
Situations Warranting Declaratory Relief
Situations warranting declaratory relief typically involve disputes where parties seek a court's determination on their rights, duties, or obligations without requiring immediate enforcement or damages. Common scenarios include contract interpretation issues, clarifying legal status in regulatory compliance, or resolving ambiguities in insurance coverage. This relief prevents future litigation by providing a clear legal declaration, helping parties understand their position and avoid costly conflicts.
Common Scenarios for Retrospective Relief
Retrospective relief commonly arises in cases involving breaches of contract, where a party seeks compensation for past losses incurred due to the other party's non-performance. It is also frequently pursued in intellectual property disputes to recover damages for unauthorized use occurring before the lawsuit. Courts often grant retrospective relief in employment law when wrongful termination or discrimination has already caused harm to the employee, necessitating back pay or reinstatement.
Procedural Requirements for Each Relief
Declaratory relief requires a clear legal controversy between parties, often initiated through a petition that presents a substantive question of law or rights without demanding enforcement of a judgment. Procedural requirements mandate proper jurisdiction, pleadings that specify the issue for judicial determination, and compliance with rules on standing and justiciability. Retrospective relief, on the other hand, involves remedies aimed at undoing past actions or validating prior conduct, requiring proof of actual harm or invalidity, strict adherence to statutes of limitations, and often necessitates a motion or claim specifying the relief sought that correlates with the retroactive effect.
Implications and Limitations
Declaratory relief establishes the rights and obligations of parties without ordering specific actions, providing clarity but lacking immediate enforcement, which limits its effectiveness in urgent disputes. Retrospective relief, often involving remedies like damages or compensation, addresses past wrongs but cannot prevent ongoing or future harm, constraining its scope to remedial rather than preventive measures. Both forms impact legal strategy by balancing the desire for certainty against the need for practical enforcement, with declaratory relief offering legal certainty and retrospective relief focusing on reparative outcomes.
Choosing the Appropriate Legal Remedy
Choosing between declaratory relief and retrospective relief depends on the case's specific legal needs and desired outcomes. Declaratory relief provides a court judgment that clarifies legal rights or obligations without ordering enforcement, ideal for preventing future disputes. Retrospective relief addresses past actions by nullifying or correcting legal effects, crucial in cases requiring remedies for prior wrongful acts or contract breaches.
Declaratory Relief Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com