A grantor is an individual or entity that transfers property or rights to another party, known as the grantee, through a legal instrument such as a deed or trust. Your understanding of grantor roles is essential when dealing with real estate transactions, estate planning, or creating trusts. Explore the full article to learn how the grantor's responsibilities impact ownership and legal protections.
Table of Comparison
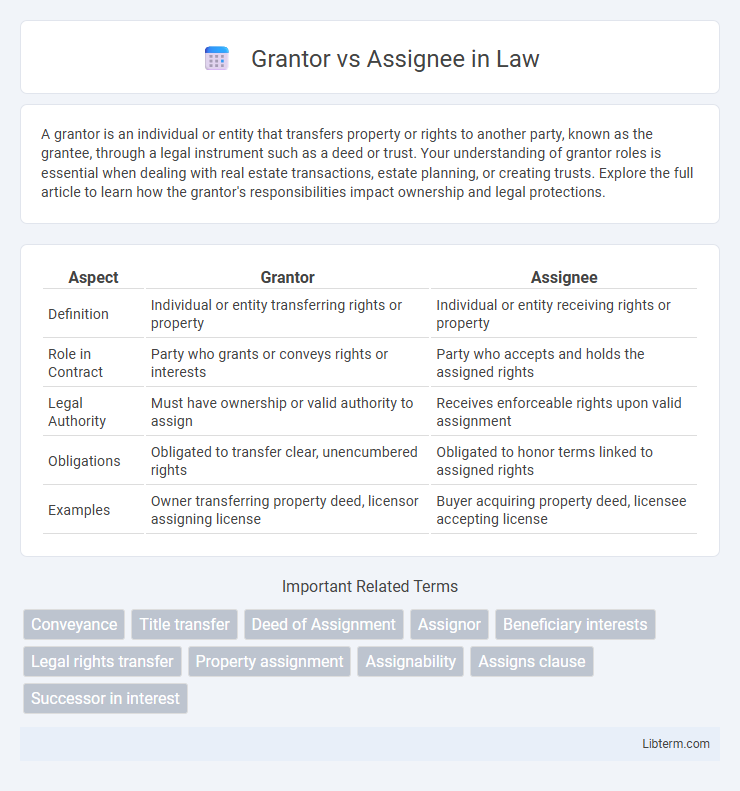
| Aspect | Grantor | Assignee |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual or entity transferring rights or property | Individual or entity receiving rights or property |
| Role in Contract | Party who grants or conveys rights or interests | Party who accepts and holds the assigned rights |
| Legal Authority | Must have ownership or valid authority to assign | Receives enforceable rights upon valid assignment |
| Obligations | Obligated to transfer clear, unencumbered rights | Obligated to honor terms linked to assigned rights |
| Examples | Owner transferring property deed, licensor assigning license | Buyer acquiring property deed, licensee accepting license |
Introduction to Grantor and Assignee
The grantor is the party who transfers rights, property, or interests in a legal agreement, often serving as the original owner or creator of a right. The assignee is the individual or entity receiving these rights or interests through assignment, thereby gaining the legal capacity to enforce or benefit from the transferred rights. Understanding the roles of grantor and assignee is crucial for interpreting property law, contract assignments, and related legal transactions.
Definitions: Who is a Grantor?
A grantor is an individual or entity that transfers property rights, interests, or ownership to another party through a legal document such as a deed, trust, or assignment. This party holds the original rights or title before the transfer and initiates the conveyance process. The grantor's role is crucial in real estate and legal transactions to establish clear ownership and facilitate the transfer of assets.
Definitions: Who is an Assignee?
An assignee is a party to whom rights or property interests, such as leases, contracts, or deeds, are transferred from the original holder, known as the grantor. The assignee assumes the rights and obligations associated with the transferred interest, effectively stepping into the shoes of the grantor. This role is critical in legal and real estate transactions where transfer of ownership or contractual rights occurs.
Key Differences Between Grantor and Assignee
The grantor is the original party transferring rights or property, typically involved in deeds or trusts, while the assignee is the recipient of those rights or property through assignment. Key differences include the grantor's role in creating or conveying an interest, whereas the assignee obtains rights but usually assumes no prior obligations. Legal terminology and responsibilities differ, with the grantor often bearing warranties or covenants, and the assignee primarily stepping into the grantor's position without original liability.
Legal Roles and Responsibilities
The grantor holds the original ownership rights and authority to transfer property or interests through a legal document such as a deed, maintaining responsibilities to ensure clear and rightful conveyance. The assignee receives those rights or interests from the grantor and assumes responsibilities to uphold and manage the transferred property or contractual benefits under the terms agreed upon. Both parties bear distinct legal roles where the grantor guarantees valid title transfer while the assignee enforces and utilizes the rights acquired.
Types of Agreements Involving Grantor and Assignee
Types of agreements involving grantor and assignee primarily include assignment agreements, where the grantor transfers rights or interests in a contract or property to the assignee. Lease assignments and intellectual property assignments are common, enabling the assignee to assume the grantor's rights and obligations. These agreements must clearly define the scope of transfer, effective date, and responsibilities to avoid disputes.
Common Scenarios: Grantor vs Assignee
In common legal and real estate transactions, the grantor is the party who transfers ownership or interest in a property or asset, while the assignee receives the rights or benefits through assignment. Grantors often initiate conveyances such as deeds, leases, or contracts, and assignees step into the position of the original party to enforce or utilize those rights. Scenarios include real estate deeds where the grantor conveys title to the assignee, or contract assignments where the assignee gains the ability to perform or collect under the contract originally held by the grantor.
Legal Implications for Grantors
Grantors face significant legal implications when transferring interests to assignees, as they remain liable for obligations unless explicitly released. The transfer of rights or property interests requires clear documentation to prevent disputes and ensure enforceability under contract law. Failure to properly assign or terminate obligations can result in continued legal responsibility and potential litigation against the grantor.
Legal Rights and Obligations of Assignees
Assignees acquire legal rights from the assignor, enabling them to enforce assigned contracts or claims, but also assume corresponding obligations unless explicitly excluded. They must perform duties under the contract and are subject to defenses available against the assignor, ensuring continuity of contractual performance. Courts often scrutinize the scope of assignment to protect the interests of all parties involved, emphasizing the assignee's responsibility to uphold all contractual terms.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Party for Your Needs
Selecting between a grantor and an assignee depends on your specific transaction goals and legal responsibilities. A grantor typically initiates the transfer of rights or property, holding initial ownership and control, whereas an assignee receives those rights or property, assuming obligations agreed upon in the assignment. Understanding the implications of control, liability, and intended outcomes ensures an informed decision aligning with your contractual and financial objectives.
Grantor Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com