A victim is an individual who suffers harm or loss due to the actions or negligence of others, often in contexts such as crimes, accidents, or natural disasters. Understanding the psychological and legal aspects surrounding victims is vital for providing appropriate support and justice. Explore the rest of the article to learn how victim assistance programs and legal frameworks can impact Your recovery and rights.
Table of Comparison
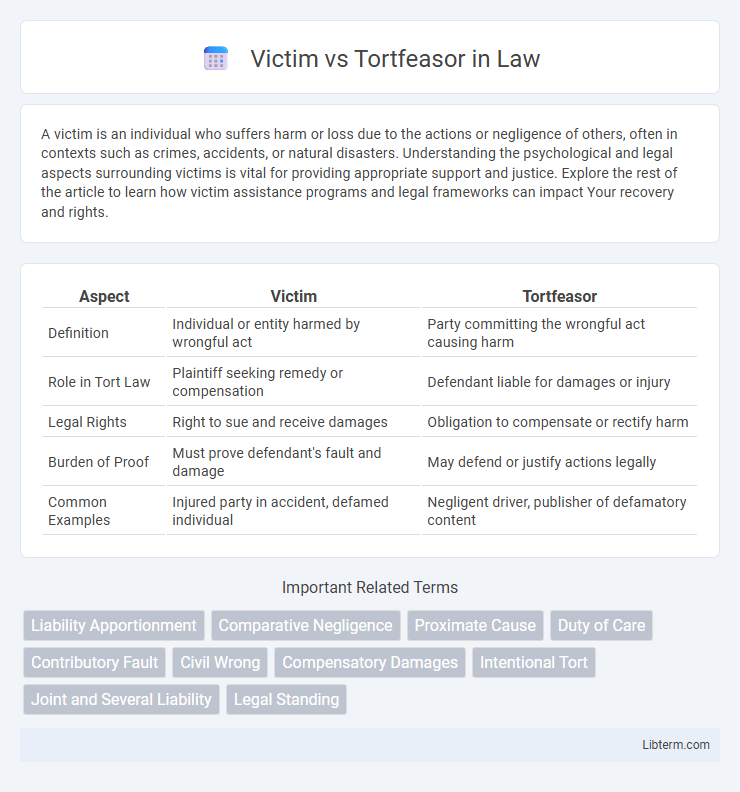
| Aspect | Victim | Tortfeasor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual or entity harmed by wrongful act | Party committing the wrongful act causing harm |
| Role in Tort Law | Plaintiff seeking remedy or compensation | Defendant liable for damages or injury |
| Legal Rights | Right to sue and receive damages | Obligation to compensate or rectify harm |
| Burden of Proof | Must prove defendant's fault and damage | May defend or justify actions legally |
| Common Examples | Injured party in accident, defamed individual | Negligent driver, publisher of defamatory content |
Understanding the Legal Definitions: Victim and Tortfeasor
A victim is an individual who suffers harm or loss due to another party's wrongful act or negligence, often seeking compensation through legal claims. A tortfeasor, in legal terms, is the person or entity responsible for committing a tort, causing injury or damage to the victim. Understanding these roles is essential for navigating civil litigation, where the victim pursues remedies and the tortfeasor may be held liable for damages.
Key Differences Between Victim and Tortfeasor
The victim is the individual or entity harmed or injured due to the actions or negligence of another party, whereas the tortfeasor is the person or organization responsible for causing the harm through a wrongful act or omission. Victims seek compensation or remedies through legal claims, while tortfeasors are liable for damages and legal penalties resulting from their conduct. The legal distinction impacts liability assessment, evidentiary burdens, and the pursuit of justice in tort law cases.
Rights and Responsibilities: Comparing Victims and Tortfeasors
Victims possess the right to seek compensation for harm suffered through civil lawsuits, enabling them to obtain restitution for injuries or losses caused by tortfeasors. Tortfeasors hold the responsibility to repair damages resulting from their negligent or intentional actions, which may include paying monetary damages, implementing corrective measures, or facing legal penalties. The legal system balances victim rights to restitution with tortfeasor duties to be accountable for wrongful conduct, ensuring justice and deterrence in civil liability cases.
Common Scenarios: Victim and Tortfeasor in Civil Law
In civil law, common scenarios involving victims and tortfeasors include personal injury cases where the victim suffers harm due to the tortfeasor's negligence or intentional misconduct. Property damage disputes frequently arise when a tortfeasor's actions result in destruction or loss affecting the victim's ownership rights. Medical malpractice and product liability cases also illustrate interactions where injured victims seek compensation from tortfeasors responsible for breach of duty or defective products.
Legal Protections for Victims
Victims benefit from comprehensive legal protections designed to ensure their rights and safety, including compensation through civil lawsuits against tortfeasors. Statutes like victims' rights laws and crime victim compensation programs provide financial restitution and support services, enhancing recovery and participation in legal proceedings. Courts impose liability on tortfeasors to hold them accountable, reinforcing deterrence and justice within tort law frameworks.
Legal Liabilities Faced by Tortfeasors
Tortfeasors face legal liabilities including compensatory damages, punitive damages, and injunctions to prevent further harm. They may be held accountable for negligence, intentional misconduct, or strict liability depending on the nature of the tort. Courts assess liability based on the duty of care breached and the resulting damages suffered by the victim.
The Role of Evidence in Identifying Victim vs Tortfeasor
Evidence plays a critical role in distinguishing the victim from the tortfeasor by providing objective facts that establish liability in civil cases. Physical evidence, witness testimonies, and expert analyses help reconstruct events to determine who caused harm and who suffered it. Clear documentation of injury, intent, and causation ensures accurate identification of parties responsible for legal accountability.
Compensation and Remedies for Victims
Victims in tort law are entitled to compensation aimed at making them whole, including economic damages such as medical expenses, lost wages, and property damage, as well as non-economic damages like pain and suffering. Tortfeasors, or those who commit torts, bear the legal responsibility to provide these remedies through monetary awards or equitable relief determined by the court. The primary purpose of compensation is to restore the victim's position prior to the harm, ensuring accountability and promoting justice in civil litigation.
Defenses Available to Tortfeasors
Tortfeasors can invoke several defenses to mitigate or eliminate liability, such as consent, where the victim agrees to the conduct; self-defense, allowing reasonable force to prevent harm; and comparative negligence, which reduces damages based on the victim's share of fault. The defense of necessity applies when the tortfeasor's actions aim to prevent greater harm, while duress may excuse conduct performed under threat. These defenses are critical in tort law as they shift or limit responsibility, impacting damage awards and legal outcomes.
Preventing Harm: Reducing Victimization and Tortious Conduct
Implementing comprehensive safety measures and clear legal frameworks effectively reduces victimization and tortious conduct by deterring potential tortfeasors. Enhanced public awareness campaigns and education on rights and responsibilities empower individuals to avoid risky situations and seek legal recourse promptly. Proactive enforcement of regulations and prompt dispute resolution mechanisms further minimize harm and promote accountability among tortfeasors.
Victim Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com