Judicial precedent ensures that courts follow previous rulings to maintain consistency and predictability in the legal system. This principle guides judges in making decisions based on established case law, thereby reinforcing legal stability and fairness. Explore the rest of the article to understand how judicial precedent impacts your rights and legal outcomes.
Table of Comparison
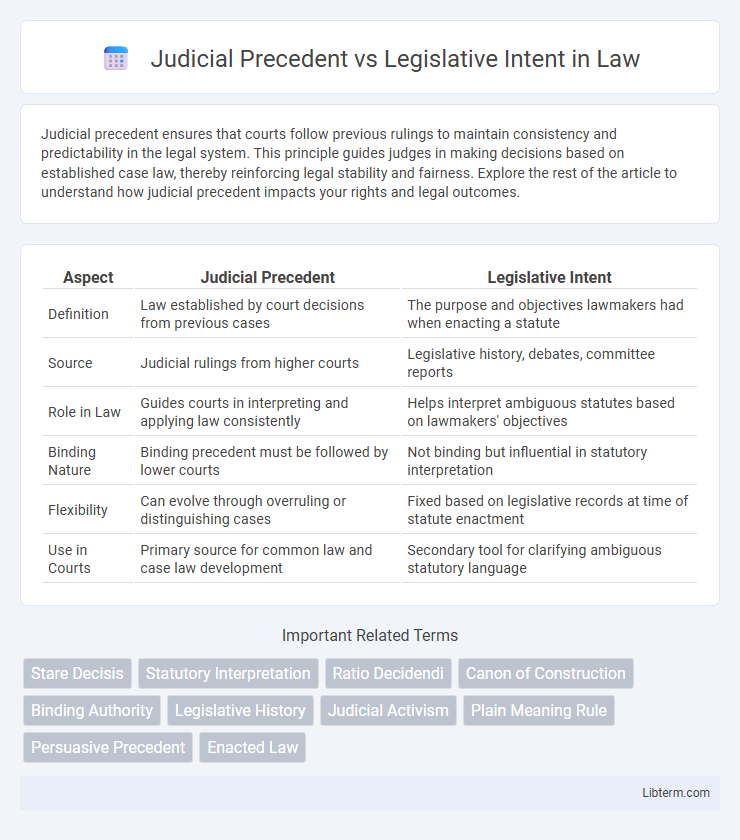
| Aspect | Judicial Precedent | Legislative Intent |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Law established by court decisions from previous cases | The purpose and objectives lawmakers had when enacting a statute |
| Source | Judicial rulings from higher courts | Legislative history, debates, committee reports |
| Role in Law | Guides courts in interpreting and applying law consistently | Helps interpret ambiguous statutes based on lawmakers' objectives |
| Binding Nature | Binding precedent must be followed by lower courts | Not binding but influential in statutory interpretation |
| Flexibility | Can evolve through overruling or distinguishing cases | Fixed based on legislative records at time of statute enactment |
| Use in Courts | Primary source for common law and case law development | Secondary tool for clarifying ambiguous statutory language |
Introduction to Judicial Precedent and Legislative Intent
Judicial precedent refers to past court decisions that guide judges in resolving similar future cases, ensuring consistency and predictability in the legal system. Legislative intent involves understanding the purpose and objectives lawmakers had when enacting statutes, guiding the interpretation and application of laws. Both concepts are essential for interpreting legal texts, with judicial precedent emphasizing case law and legislative intent focusing on the statutory framework.
Defining Judicial Precedent
Judicial precedent refers to the principle where past judicial decisions serve as authoritative guidelines for deciding future cases with similar facts or legal issues. It ensures consistency and predictability in the legal system by obligating courts to follow established rulings, known as stare decisis. This doctrine contrasts with legislative intent, which relies on interpreting the purpose and objectives behind statutes enacted by legislative bodies.
Understanding Legislative Intent
Understanding legislative intent involves analyzing the purpose and objectives lawmakers aimed to achieve when enacting a statute. Courts examine legislative history, including committee reports, debates, and drafts, to interpret ambiguous or unclear statutory language. This approach ensures that judicial decisions align with the law's intended meaning and policy goals.
Historical Development of Both Doctrines
Judicial precedent originated from the English common law system, evolving over centuries through the formalization of case law and the principle of stare decisis, which mandates courts to follow previous judicial decisions for consistency and predictability. Legislative intent emerged as statutory interpretation became necessary to understand lawmakers' objectives, particularly during the rise of codified legal systems in the 19th and 20th centuries, emphasizing the purpose behind legislative texts. Both doctrines developed historically to balance stability in law with flexibility, with judicial precedent anchoring legal continuity and legislative intent ensuring that statutes are applied according to the evolving societal context envisioned by lawmakers.
Key Differences Between Judicial Precedent and Legislative Intent
Judicial precedent relies on past court decisions to guide the interpretation and application of laws, emphasizing consistency and predictability in legal rulings. Legislative intent centers on the purpose and objectives lawmakers had when drafting statutes, focusing on the original meaning and aims behind the legislation. Key differences include judicial precedent's basis in established case law versus legislative intent's foundation in the legislative history and statute text, affecting how laws are interpreted in varying contexts.
Role in Statutory Interpretation
Judicial precedent plays a critical role in statutory interpretation by providing courts with past rulings that clarify ambiguous legislation and guide consistent application of laws. Legislative intent focuses on understanding the purpose and objectives behind a statute, using legislative history, debates, and committee reports to inform judicial decisions. Courts often balance these approaches to ensure that statutes are applied in ways that align with both the letter and the spirit of the law.
Advantages and Limitations of Judicial Precedent
Judicial precedent provides consistency and predictability in legal rulings by adhering to established decisions, enabling courts to apply the law uniformly across similar cases. Its main advantage lies in promoting stability and efficiency within the legal system, as lower courts follow higher courts' interpretations, reducing ambiguity. However, the limitation of judicial precedent is its rigidity, which can hinder legal development and adaptation to societal changes, often requiring legislative intervention to address outdated or unjust rulings.
Strengths and Challenges of Relying on Legislative Intent
Relying on legislative intent ensures that courts interpret laws according to the original purpose and objectives envisioned by lawmakers, promoting consistency with democratic principles. However, challenges arise due to ambiguities in legislative history, potential shifts in societal values since enactment, and conflicting interpretations of lawmakers' intent that can lead to judicial uncertainty. Moreover, legislative intent may be difficult to ascertain definitively, making it necessary for courts to balance intent with the text and context of statutes.
Case Studies Illustrating the Conflict
In the landmark case of *Youngstown Sheet & Tube Co. v. Sawyer*, judicial precedent clashed with legislative intent as the Supreme Court limited executive power despite prior decisions favoring broad authority. Similarly, *Chevron U.S.A., Inc. v. Natural Resources Defense Council, Inc.* highlights the tension between courts deferring to administrative agency interpretations and Congress's original legislative purpose. These case studies underscore the ongoing conflict where courts balance respect for precedent against interpreting the true legislative intent behind statutes.
Conclusion: Balancing Judicial Precedent and Legislative Intent
Balancing judicial precedent and legislative intent requires courts to respect established case law while interpreting statutes in light of lawmakers' original purposes. Maintaining this equilibrium ensures legal stability without sacrificing flexibility for evolving societal values and legislative changes. Effective judicial decisions harmonize precedent adherence with faithful execution of legislative objectives, promoting consistency and justice.
Judicial Precedent Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com