Bailment occurs when the owner of goods temporarily transfers possession to another party for safekeeping or a specific purpose, without relinquishing ownership. Understanding the duties and liabilities of both the bailor and bailee is crucial to protect Your interests in such agreements. Explore the rest of this article to learn how bailment works and what legal protections are in place.
Table of Comparison
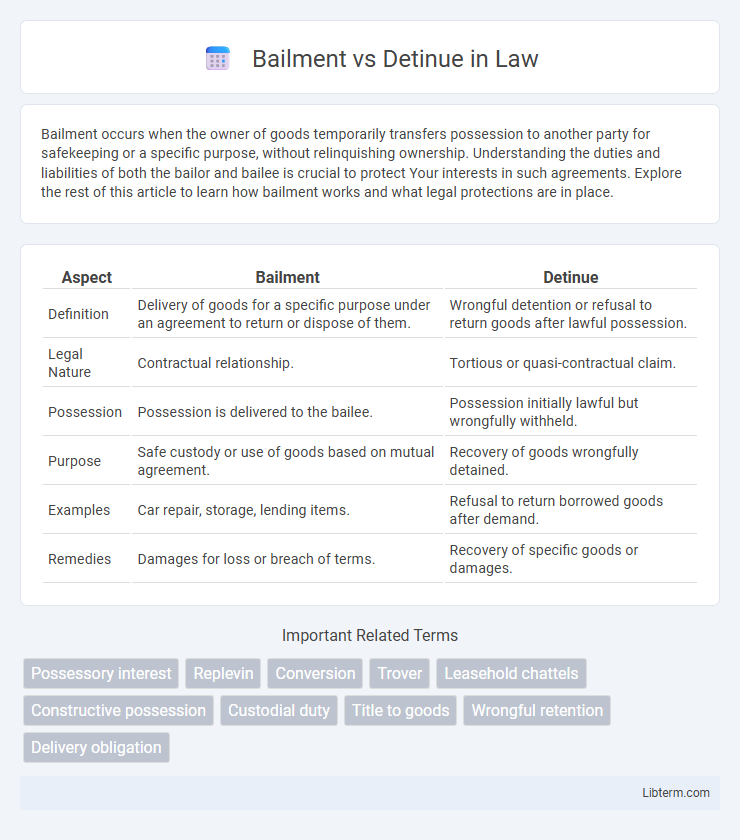
| Aspect | Bailment | Detinue |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Delivery of goods for a specific purpose under an agreement to return or dispose of them. | Wrongful detention or refusal to return goods after lawful possession. |
| Legal Nature | Contractual relationship. | Tortious or quasi-contractual claim. |
| Possession | Possession is delivered to the bailee. | Possession initially lawful but wrongfully withheld. |
| Purpose | Safe custody or use of goods based on mutual agreement. | Recovery of goods wrongfully detained. |
| Examples | Car repair, storage, lending items. | Refusal to return borrowed goods after demand. |
| Remedies | Damages for loss or breach of terms. | Recovery of specific goods or damages. |
Introduction to Bailment and Detinue
Bailment involves the delivery of goods by one party, the bailor, to another, the bailee, for a specific purpose under an agreement that the goods will be returned or otherwise disposed of according to the bailor's instructions. Detinue is a legal action to recover possession of goods wrongfully withheld by a party who initially had lawful possession. While bailment emphasizes the transfer of possession with an expectation of return, detinue focuses on the wrongful detention and recovery of those goods.
Definition of Bailment
Bailment is the legal relationship wherein the owner of goods (bailor) temporarily transfers possession to another party (bailee) for a specific purpose, under an agreement that the goods will be returned or otherwise disposed of as directed. It involves lawful delivery of personal property without transferring ownership, emphasizing the bailee's duty to take reasonable care. Distinct from detinue, which pertains to wrongful detention of property, bailment focuses on consensual possession and the responsibilities arising from it.
Definition of Detinue
Detinue is a common law tort or action arising from the wrongful detention or refusal to return personal property lawfully requested by the rightful owner or possessor. It differs from bailment, which is a consensual relationship where one party temporarily delivers goods to another for safekeeping or specific use. The key element in detinue is the possession being unlawfully withheld, making it distinct from mere disputes over ownership.
Key Elements of Bailment
Bailment involves the delivery of goods by the bailor to the bailee for a specific purpose under an agreement that the goods will be returned or disposed of according to the bailor's instructions. Key elements of bailment include the transfer of possession without transfer of ownership, a mutual agreement or contract between parties, and the obligation of the bailee to take reasonable care of the goods. The distinction from detinue lies in the lawful possession under bailment, whereas detinue concerns wrongful detention of goods without consent.
Key Elements of Detinue
Detinue involves the wrongful detention of goods after a lawful possession was initially granted, emphasizing the owner's right to immediate possession and recovery of the specific chattel. Key elements of detinue include proof of original lawful possession by the defendant, refusal or failure to return the goods upon demand, and the claimant's right to possession rather than ownership alone. Unlike bailment, detinue requires an unlawful withholding, making the defendant liable for the specific item rather than damages for its value.
Differences Between Bailment and Detinue
Bailment involves the transfer of possession of goods from the bailor to the bailee with the expectation of their return, whereas detinue is a legal action to recover goods wrongfully withheld by a party. The key difference lies in possession: bailment is consensual and temporary, while detinue addresses wrongful detention or refusal to return possession. Bailment creates a fiduciary relationship requiring care, whereas detinue focuses on the recovery of specific property through legal remedy.
Legal Rights and Duties in Bailment
Bailment involves the transfer of possession but not ownership of goods from the bailor to the bailee, who has the duty to return or dispose of the goods as agreed, exercising reasonable care. The bailee's legal rights include limited possession rights and protection against unauthorized interference, while the bailor retains ownership and the right to reclaim the property. Unlike detinue, which focuses on wrongful detention and recovery of specific goods, bailment centers on the lawful possession and agreed obligations between parties.
Legal Rights and Duties in Detinue
Detinue involves the wrongful detention of goods by a party who admits possession but refuses to return them upon request, creating a legal duty to return the specific chattel to the rightful owner. The plaintiff's right in detinue is to recover the exact item wrongfully withheld, and they may also claim damages for loss caused by the detention. Unlike bailment, where the bailee has a duty to take reasonable care of the goods entrusted, detinue arises from an unlawful refusal to deliver possession, emphasizing the immediate recovery of the property itself.
Remedies Available in Bailment and Detinue Cases
Remedies available in bailment primarily include the recovery of the specific goods entrusted and compensation for any loss or damages caused by negligence or breach of contract by the bailee. In detinue cases, the plaintiff may recover the actual possession of the goods wrongfully detained and claim damages for the unlawful retention or delay in returning the property. Both legal actions aim to restore possession and provide monetary remedies, but detinue emphasizes the wrongful detention of goods rather than mere misdelivery or loss.
Conclusion: Bailment vs Detinue
Bailment involves the voluntary delivery of goods by the bailor to the bailee for a specific purpose, with the expectation of their return, emphasizing a contractual relationship. Detinue, however, centers on the wrongful detention of goods by a party who originally had lawful possession, focusing on the recovery of the specific property. The key distinction lies in bailment's consensual arrangement versus detinue's legal action addressing unjust retention.
Bailment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com