Subject matter defines the core topic or theme of any content, shaping its focus and relevance for the audience. Understanding your subject matter helps tailor information precisely to meet your reader's needs and enhance engagement. Explore the rest of the article to discover how mastering subject matter can elevate your content's impact.
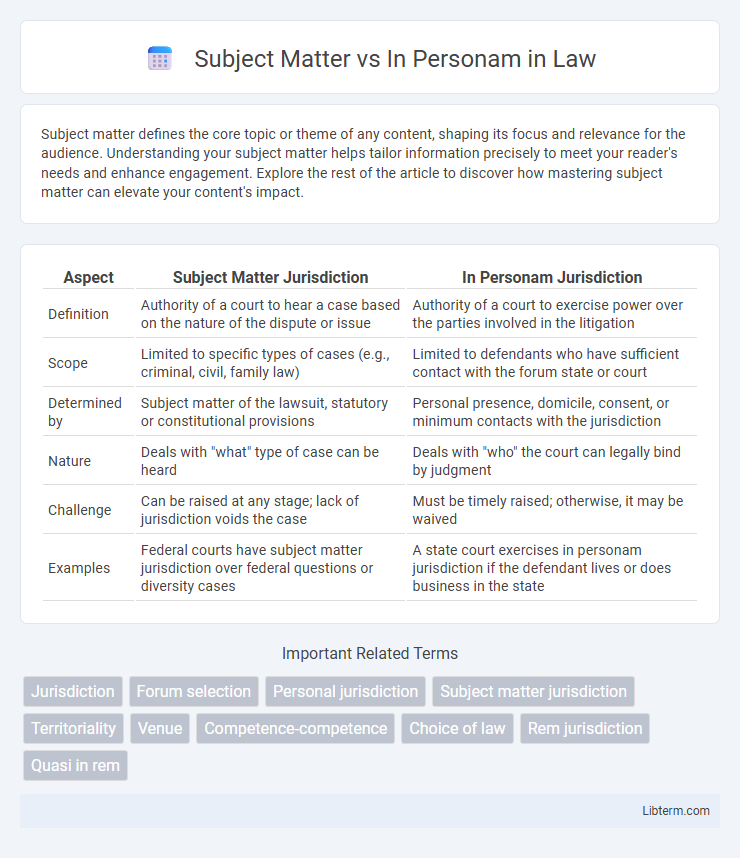
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Subject Matter Jurisdiction | In Personam Jurisdiction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Authority of a court to hear a case based on the nature of the dispute or issue | Authority of a court to exercise power over the parties involved in the litigation |
| Scope | Limited to specific types of cases (e.g., criminal, civil, family law) | Limited to defendants who have sufficient contact with the forum state or court |
| Determined by | Subject matter of the lawsuit, statutory or constitutional provisions | Personal presence, domicile, consent, or minimum contacts with the jurisdiction |
| Nature | Deals with "what" type of case can be heard | Deals with "who" the court can legally bind by judgment |
| Challenge | Can be raised at any stage; lack of jurisdiction voids the case | Must be timely raised; otherwise, it may be waived |
| Examples | Federal courts have subject matter jurisdiction over federal questions or diversity cases | A state court exercises in personam jurisdiction if the defendant lives or does business in the state |
Understanding the Concepts: Subject Matter and In Personam
Subject matter jurisdiction refers to a court's authority to hear cases of a specific type or cases relating to a particular subject, ensuring the legal issue falls within the court's designated scope. In personam jurisdiction relates to the court's power over the parties involved in the litigation, based on their connection to the forum state, such as residency, consent, or conduct within the jurisdiction. Understanding these concepts is crucial to determining whether a court can lawfully adjudicate a dispute, where subject matter jurisdiction addresses the nature of the case and in personam jurisdiction concerns the parties' legal ties to the court's location.
Defining Subject Matter Jurisdiction
Subject Matter Jurisdiction refers to a court's authority to hear cases of a particular type or cases relating to specific subject matter, determining whether the court is competent to adjudicate the issues presented. This jurisdiction is essential for ensuring that cases are brought before a proper judicial forum, unlike In Personam jurisdiction, which focuses on the court's power over the parties involved. Without subject matter jurisdiction, any judgment rendered by the court is void, highlighting its critical role in the judicial process.
Exploring In Personam Jurisdiction
In Personam jurisdiction refers to a court's authority over the parties involved in a legal dispute, allowing it to render judgments that bind those specific individuals. This jurisdiction is established through the defendant's presence within the court's geographical territory, consent, or sufficient minimum contacts with the forum state. Understanding In Personam jurisdiction is essential for determining where a plaintiff can sue a defendant, ensuring due process and fair legal proceedings.
Key Differences Between Subject Matter and In Personam
Subject matter jurisdiction determines a court's authority to hear cases of a specific type or category, such as criminal, probate, or family law cases, ensuring the court does not exceed its legal bounds. In personam jurisdiction refers to a court's power over the parties involved in the litigation, typically established through the defendant's residency, presence, or consent within the forum state. The key difference lies in subject matter jurisdiction's focus on case type restrictions, while in personam jurisdiction concerns the court's reach over individuals or entities in the dispute.
Legal Importance of Subject Matter Jurisdiction
Subject matter jurisdiction determines a court's authority to hear a case based on the nature of the dispute, making it fundamental to legal proceedings. Without proper subject matter jurisdiction, any judgment rendered is null and void, emphasizing its critical role in ensuring lawful adjudication. Unlike in personam jurisdiction, which concerns the court's power over parties, subject matter jurisdiction safeguards the legal system's integrity by limiting courts to cases they are empowered to resolve.
When Does In Personam Jurisdiction Apply?
In personam jurisdiction applies when a court has authority over a specific individual or entity based on their personal connections to the forum state, such as residency, physical presence, or consent to jurisdiction. This jurisdiction is essential for adjudicating cases that involve enforcing personal obligations or rights directly against the party. Courts determine in personam jurisdiction by evaluating factors like minimum contacts, purposeful availment, and whether exercising jurisdiction aligns with fairness and due process principles.
Subject Matter in Civil vs Criminal Cases
Subject matter jurisdiction refers to a court's authority to hear a specific type of case, distinct from in personam jurisdiction which concerns authority over the parties involved. In civil cases, subject matter jurisdiction often depends on the nature of the dispute, such as family law, contract issues, or tort claims, and whether the case falls within state or federal court boundaries. In criminal cases, subject matter jurisdiction is determined by the seriousness of the offense and whether it is classified as a misdemeanor or felony under state or federal law, influencing which court has the power to adjudicate.
Establishing In Personam Jurisdiction: Legal Requirements
Establishing In Personam jurisdiction requires the defendant to have minimum contacts with the forum state, ensuring fairness and due process under the Fourteenth Amendment. Courts assess factors such as the defendant's purposeful availment of conducting activities within the state and whether exercising jurisdiction aligns with traditional notions of fair play. Personal jurisdiction is distinct from subject matter jurisdiction, which relates to a court's authority over the type of case rather than the parties involved.
Common Misconceptions About Jurisdiction Types
Subject matter jurisdiction refers to a court's authority to hear cases of a particular category, while in personam jurisdiction involves the court's power over the parties involved in the lawsuit. A common misconception is that having in personam jurisdiction automatically grants subject matter jurisdiction, which is incorrect because both must independently exist for a valid case. Confusing these jurisdiction types can lead to procedural errors, such as improper case dismissals due to lack of jurisdiction.
Subject Matter vs In Personam: Case Law Examples
Subject matter jurisdiction refers to a court's authority to hear cases of a specific type or relating to a particular subject, while in personam jurisdiction concerns the court's power over the parties involved. In *Pennoyer v. Neff*, 95 U.S. 714 (1878), the U.S. Supreme Court emphasized that proper in personam jurisdiction requires personal service within the state, contrasting with subject matter jurisdiction that is determined by the nature of the dispute. In *International Shoe Co. v. Washington*, 326 U.S. 310 (1945), the Court clarified the standard for in personam jurisdiction based on a defendant's minimum contacts, illustrating the distinction from subject matter jurisdiction governed by statutory or constitutional provisions.
Subject Matter Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com