Rehabilitative justice focuses on reforming offenders through therapy, education, and skill-building to reduce recidivism and promote positive societal reintegration. This approach prioritizes understanding the root causes of criminal behavior and tailoring interventions specific to each individual's needs. Discover how rehabilitative justice can transform lives and communities by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
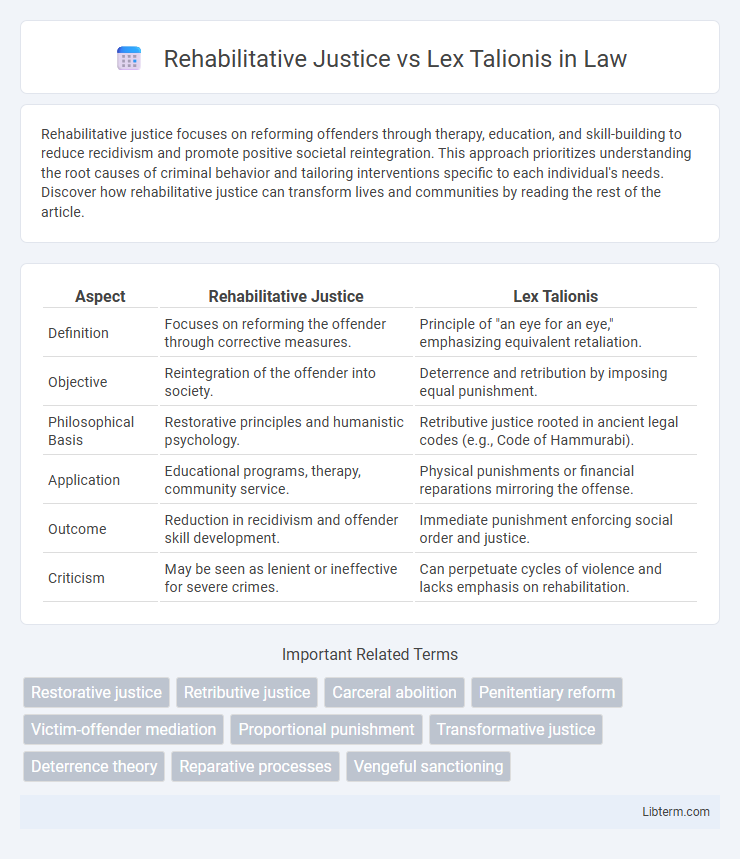
| Aspect | Rehabilitative Justice | Lex Talionis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on reforming the offender through corrective measures. | Principle of "an eye for an eye," emphasizing equivalent retaliation. |
| Objective | Reintegration of the offender into society. | Deterrence and retribution by imposing equal punishment. |
| Philosophical Basis | Restorative principles and humanistic psychology. | Retributive justice rooted in ancient legal codes (e.g., Code of Hammurabi). |
| Application | Educational programs, therapy, community service. | Physical punishments or financial reparations mirroring the offense. |
| Outcome | Reduction in recidivism and offender skill development. | Immediate punishment enforcing social order and justice. |
| Criticism | May be seen as lenient or ineffective for severe crimes. | Can perpetuate cycles of violence and lacks emphasis on rehabilitation. |
Introduction to Rehabilitative Justice and Lex Talionis
Rehabilitative justice focuses on reforming offenders through therapeutic interventions and social reintegration, aiming to reduce recidivism by addressing underlying causes of criminal behavior. Lex Talionis, or the law of retaliation, embodies the principle of "an eye for an eye," emphasizing proportional retribution to ensure punishment mirrors the offense. These contrasting justice models highlight differing societal goals: correction and restoration versus strict retribution and deterrence.
Historical Origins of Lex Talionis
The historical origins of Lex Talionis trace back to ancient legal codes such as the Code of Hammurabi, where the principle of "an eye for an eye" established a direct correlation between the crime and its punishment. This retributive justice system aimed to limit excessive retaliation and maintain social order in early Mesopotamian societies by enforcing proportional penalties. Rehabilitative justice, in contrast, emerged as a more modern approach focusing on offender reform and societal reintegration rather than mere retribution.
Principles and Goals of Rehabilitative Justice
Rehabilitative justice centers on principles of healing, restoration, and reintegration of offenders into society through tailored interventions and support programs. The primary goals include addressing underlying causes of criminal behavior, reducing recidivism rates, and promoting social rehabilitation rather than mere punishment. This approach contrasts with Lex Talionis, which emphasizes proportional retribution and the principle of "an eye for an eye" to maintain justice through equivalence in punishment.
Moral Philosophies: Retribution vs. Restoration
Rehabilitative justice centers on restoration, aiming to repair harm by addressing offenders' underlying issues and reintegrating them into society, reflecting a moral philosophy of restoration. Lex Talionis, or the law of retaliation, embodies retribution by enforcing proportional punishment to uphold moral balance and deter wrongdoing. These opposing moral philosophies highlight a fundamental debate between prioritizing societal healing versus punitive justice.
Legal Frameworks: Comparing Approaches to Punishment
Rehabilitative justice emphasizes restoring offenders through therapy, education, and community integration, aiming to reduce recidivism within progressive legal frameworks. In contrast, lex talionis, rooted in the principle of "an eye for an eye," prioritizes proportional retribution based on strict legal codes found in ancient and some modern punitive systems. Legal frameworks under rehabilitative justice promote individualized sentencing and restorative practices, whereas lex talionis supports standardized punitive measures focusing on equivalence of harm.
Impact on Recidivism and Crime Prevention
Rehabilitative justice significantly reduces recidivism by addressing the root causes of criminal behavior through counseling, education, and skill development, which promotes reintegration into society. Lex Talionis, or the principle of "an eye for an eye," often emphasizes punishment over rehabilitation, potentially perpetuating cycles of crime due to lack of offender reform. Empirical studies show lower crime rates in jurisdictions prioritizing rehabilitative approaches, highlighting its effectiveness in long-term crime prevention and societal safety.
Victims’ Rights and Community Role in Justice
Rehabilitative justice centers on restoring victims' dignity and addressing harm through community involvement, emphasizing healing and reintegration over punishment. Lex Talionis, the principle of "an eye for an eye," prioritizes retributive justice that focuses on proportional punishment rather than victim restoration or community healing. Victims' rights under rehabilitative frameworks include participation in mediation and support services, while lex talionis often limits victims to passive roles in the justice process.
Case Studies: Practical Outcomes of Each System
Rehabilitative justice prioritizes offender reintegration through tailored interventions, demonstrated by Norway's recidivism rate of approximately 20%, significantly lower than the U.S. average of around 50%, reflecting the system's effectiveness in reducing repeat offenses. Lex Talionis enforces proportional retribution and strict penalties, evident in cases like Saudi Arabia's legal system where corporal punishments aim to deter crime but face criticism for lacking rehabilitative support, leading to variable recidivism outcomes. Comparative studies show rehabilitative justice fosters long-term societal benefits by addressing root causes of criminal behavior, whereas lex talionis emphasizes immediate, often severe consequences without necessarily improving offender reform.
Contemporary Debates and Policy Shifts
Rehabilitative justice prioritizes offender rehabilitation and social reintegration, reflecting contemporary shifts toward restorative approaches in criminal justice systems globally. Lex talionis, or the law of retaliation, emphasizes proportional punishment, often criticized for perpetuating cycles of violence and failing to address underlying social causes of crime. Current policy debates highlight a growing preference for evidence-based rehabilitation programs and victim-centered practices over strict retributive paradigms rooted in lex talionis principles.
Future Prospects: Integrating Justice Paradigms
Future prospects in criminal justice emphasize integrating rehabilitative justice and lex talionis to balance restoration and retribution. Emerging models advocate for restorative practices that prioritize offender accountability and victim healing while respecting proportionality principles central to lex talionis. Innovations in policy and legal frameworks aim to create hybrid systems fostering social reintegration and equitable punishment.
Rehabilitative Justice Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com