Joint custody ensures that both parents share legal and physical responsibilities for their child, promoting balanced decision-making and consistent involvement in the child's life. This arrangement supports the child's well-being by maintaining strong relationships with both parents, even after separation or divorce. Explore this article to understand how joint custody can benefit your family and navigate its legal complexities effectively.
Table of Comparison
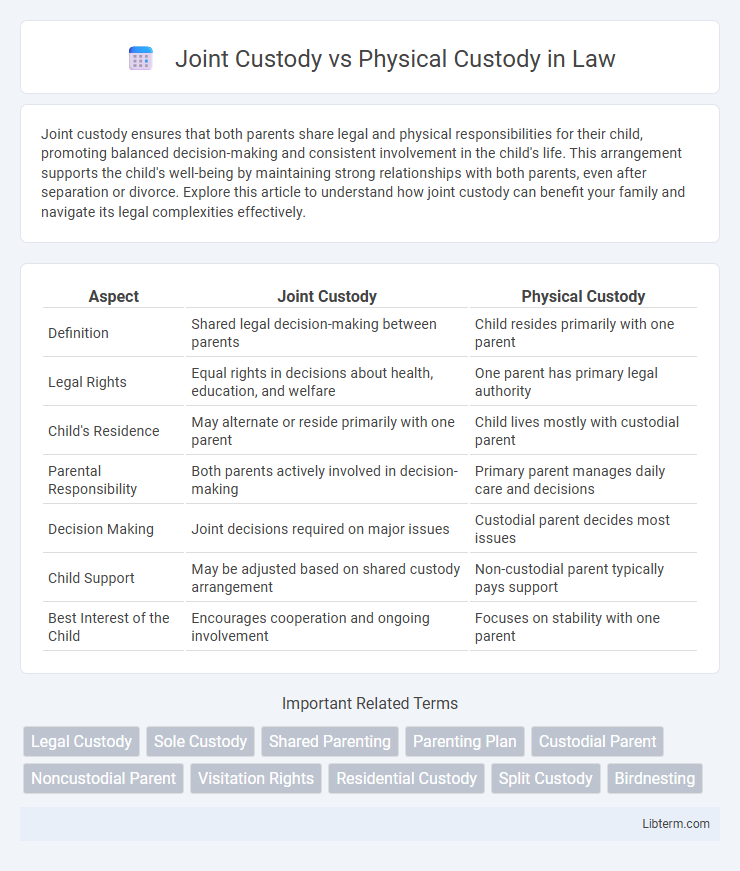
| Aspect | Joint Custody | Physical Custody |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared legal decision-making between parents | Child resides primarily with one parent |
| Legal Rights | Equal rights in decisions about health, education, and welfare | One parent has primary legal authority |
| Child's Residence | May alternate or reside primarily with one parent | Child lives mostly with custodial parent |
| Parental Responsibility | Both parents actively involved in decision-making | Primary parent manages daily care and decisions |
| Decision Making | Joint decisions required on major issues | Custodial parent decides most issues |
| Child Support | May be adjusted based on shared custody arrangement | Non-custodial parent typically pays support |
| Best Interest of the Child | Encourages cooperation and ongoing involvement | Focuses on stability with one parent |
Introduction to Child Custody Types
Child custody primarily divides into joint custody and physical custody, each defining different parental responsibilities and rights. Joint custody involves shared decision-making authority regarding the child's welfare, education, and healthcare, emphasizing co-parenting cooperation. Physical custody determines the child's living arrangements, specifying with which parent the child resides most of the time.
Defining Joint Custody
Joint custody refers to a legal arrangement in which both parents share the decision-making responsibilities regarding their child's upbringing, including education, healthcare, and religious training. This form of custody emphasizes parental cooperation and equal involvement in major aspects of the child's life, regardless of the child's physical living arrangements. Joint custody can coexist with various physical custody setups, such as primary physical custody granted to one parent while both retain legal custody rights.
Understanding Physical Custody
Physical custody refers to the arrangement where a child lives primarily with one parent, determining daily care and supervision responsibilities. It directly impacts the child's routine, schooling, healthcare, and overall well-being. Understanding physical custody is essential for parents to establish clear caregiving roles and ensure stability in the child's environment.
Key Differences Between Joint and Physical Custody
Joint custody refers to both parents sharing legal decision-making responsibilities for the child, while physical custody pertains to where the child primarily resides. Key differences include that joint custody emphasizes shared parental rights and responsibilities, whereas physical custody focuses on the child's living arrangements. Courts often grant joint legal custody to ensure cooperative parenting, but physical custody can be sole or joint depending on the child's best interests.
Legal Considerations in Custody Arrangements
Joint custody involves shared legal decision-making responsibilities between parents, ensuring both have equal rights regarding the child's education, health care, and general welfare. Physical custody determines where the child primarily resides, affecting daily routines and stability, which courts prioritize based on the child's best interests. Legal considerations often require balancing parental rights with the child's emotional and physical needs, emphasizing cooperative parenting and consistent environments.
Pros and Cons of Joint Custody
Joint custody allows both parents to share legal decision-making responsibilities, promoting balanced involvement in a child's upbringing and reducing conflicts over major choices such as education and healthcare. However, joint custody requires effective communication and cooperation, which can be challenging in high-conflict situations, potentially leading to inconsistent parenting and stress for the child. Despite these challenges, joint custody often supports the child's emotional well-being by maintaining strong relationships with both parents.
Pros and Cons of Physical Custody
Physical custody grants a parent the right to have a child live with them, providing daily care and routine management. Pros include fostering closer parent-child relationships and ensuring direct involvement in the child's upbringing, while cons involve the potential burden of full-time caregiving responsibilities and possible conflicts with the other parent over visitation. Balancing physical custody often requires careful consideration of each parent's capacity, living situation, and the child's best interests.
Factors Courts Consider in Custody Decisions
Courts evaluate factors such as the child's best interests, including the ability of each parent to provide a stable, safe environment and nurture emotional well-being when deciding between joint custody and physical custody arrangements. They consider the child's age, wishes, and existing relationship with each parent, alongside each parent's capacity to cooperate and communicate effectively. The court also assesses each parent's mental and physical health, history of abuse or neglect, and the child's adjustment to home, school, and community to ensure consistent, continuous care.
Impact on Children’s Well-being
Joint custody promotes a balanced involvement of both parents, fostering emotional stability and consistent support, which positively impacts children's mental health and development. Physical custody arrangements determine the child's living environment and daily routine, directly influencing their sense of security and familiarity. Studies show children benefit most when both custody types ensure regular, meaningful contact with each parent, reducing feelings of abandonment and enhancing overall well-being.
Tips for Navigating Custody Agreements
Understanding the distinction between joint custody, where both parents share decision-making responsibilities, and physical custody, which determines where the child lives, is crucial for effective co-parenting. Clear communication, flexibility, and prioritizing the child's best interests help parents create balanced custody agreements that minimize conflict. Legal guidance and detailed parenting plans specifying visitation schedules, holidays, and decision authority support smoother transitions and reduce misunderstandings.
Joint Custody Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com