Impleader is a legal procedure allowing a defendant to bring a third party into a lawsuit, claiming that this third party is liable for all or part of the plaintiff's claim. This process helps allocate responsibility and can streamline complex litigation involving multiple parties. Explore the rest of the article to understand how impleader might impact your legal strategy and case outcomes.
Table of Comparison
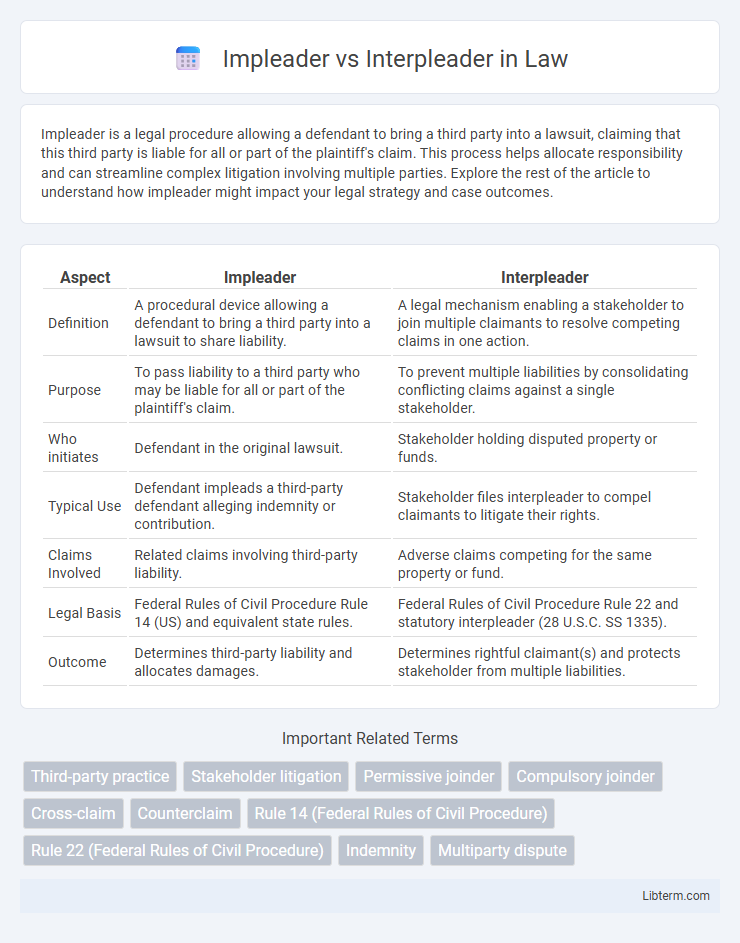
| Aspect | Impleader | Interpleader |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A procedural device allowing a defendant to bring a third party into a lawsuit to share liability. | A legal mechanism enabling a stakeholder to join multiple claimants to resolve competing claims in one action. |
| Purpose | To pass liability to a third party who may be liable for all or part of the plaintiff's claim. | To prevent multiple liabilities by consolidating conflicting claims against a single stakeholder. |
| Who initiates | Defendant in the original lawsuit. | Stakeholder holding disputed property or funds. |
| Typical Use | Defendant impleads a third-party defendant alleging indemnity or contribution. | Stakeholder files interpleader to compel claimants to litigate their rights. |
| Claims Involved | Related claims involving third-party liability. | Adverse claims competing for the same property or fund. |
| Legal Basis | Federal Rules of Civil Procedure Rule 14 (US) and equivalent state rules. | Federal Rules of Civil Procedure Rule 22 and statutory interpleader (28 U.S.C. SS 1335). |
| Outcome | Determines third-party liability and allocates damages. | Determines rightful claimant(s) and protects stakeholder from multiple liabilities. |
Understanding Impleader and Interpleader
Impleader involves a defendant bringing a third party into a lawsuit who may be liable for part or all of the plaintiff's claim, allowing the court to determine liability among multiple parties. Interpleader allows a party holding property or money with competing claims from two or more others to initiate a lawsuit to have the court decide who is entitled to the asset, preventing multiple liabilities. Understanding the procedural differences and purposes of impleader and interpleader is crucial for effectively managing multi-party disputes and protecting interests in complex litigation.
Definitions: Impleader vs Interpleader
Impleader is a procedural mechanism allowing a defendant to bring a third party into a lawsuit who may be liable for all or part of the plaintiff's claim, typically used to shift liability. Interpleader involves a stakeholder initiating a lawsuit to compel two or more parties with conflicting claims to the same property or funds to litigate their rights, preventing multiple liabilities. Both serve distinct legal functions: impleader addresses derivative liability, while interpleader resolves competing claims to a single asset.
Purpose and Legal Significance
Impleader allows a defendant to bring a third party into a lawsuit to share liability, ensuring all related claims are resolved in one proceeding and avoiding multiple lawsuits. Interpleader enables a stakeholder holding property or funds to initiate a lawsuit compelling claimants to litigate their competing claims, preventing the stakeholder from multiple liabilities. Both procedures streamline dispute resolution, enhance judicial efficiency, and protect parties from inconsistent obligations.
Key Differences Between Impleader and Interpleader
Impleader involves a defendant bringing a third party into a lawsuit to share liability, typically when the defendant claims the third party is responsible for all or part of the plaintiff's claim. Interpleader allows a stakeholder holding property or money to initiate a lawsuit to compel multiple claimants to litigate their entitlement, preventing multiple liabilities or inconsistent obligations. Key differences include the purpose: impleader seeks to transfer liability, while interpleader resolves competing claims over the same asset.
Parties Involved in Impleader vs Interpleader
Impleader involves three parties: the original plaintiff, the original defendant, and a third party who may be liable for all or part of the plaintiff's claim. Interpleader typically includes two or more claimants disputing ownership or rights over the same property or fund, with a stakeholder holding the disputed asset joining as a neutral party. Understanding these distinct roles clarifies how impleader shifts liability to a third party, while interpleader resolves competing claims among multiple parties.
Procedural Requirements and Rules
Impleader requires the defendant to bring a third party into the lawsuit, typically through a third-party complaint filed within a specific time frame after answering the original complaint, following Federal Rule of Civil Procedure 14. Interpleader involves a stakeholder initiating a suit to compel multiple claimants to litigate competing claims over the same property or funds, governed by Federal Rule of Civil Procedure 22 or the Interpleader Act, often requiring diversity jurisdiction or minimal diversity along with an amount in controversy exceeding $75,000 for statutory interpleader. Procedurally, impleader focuses on asserting derivative liability, while interpleader focuses on resolving conflicting claims to property within a single proceeding.
Common Scenarios for Impleader and Interpleader
Impleader commonly arises in situations where a defendant brings a third party into a lawsuit, typically to seek indemnity or contribution, such as in product liability cases when a manufacturer sues a supplier. Interpleader is frequently used when a stakeholder holds property or funds claimed by multiple parties, like an insurance company facing competing claims on a policy payout. Both procedural tools aim to resolve multiple claims efficiently but apply in distinct contexts--impleader to shift liability among parties and interpleader to consolidate competing claims to the same asset.
Advantages and Limitations
Impleader allows a defendant to bring a third party into a lawsuit, facilitating the resolution of related claims and potentially shifting liability, which streamlines litigation and preserves judicial resources. However, impleader can complicate the case by introducing additional parties and issues, potentially increasing the time and cost of resolution. Interpleader is advantageous in situations with multiple claimants to the same property or funds, as it consolidates all claims into a single proceeding, effectively preventing multiple liabilities and inconsistent judgments, but its limitations include strict procedural requirements and the necessity that claimants have conflicting claims to the same subject matter.
Practical Examples and Case Studies
Impleader allows a defendant to bring a third party into a lawsuit to share liability, such as a contractor suing a subcontractor after a construction defect claim, whereas interpleader resolves disputes between multiple parties claiming the same property or funds, exemplified by a bank holding a disputed escrow account that several parties claim ownership over. In case studies, impleader has been used in product liability suits where manufacturers seek contribution from component suppliers, while interpleader often arises in insurance disputes where multiple beneficiaries claim the same policy proceeds. Practical application of impleader reduces litigation complexity by consolidating related claims, while interpleader protects stakeholders by centralizing competing claims into a single legal action.
Choosing the Right Approach: Impleader or Interpleader
Choosing between impleader and interpleader hinges on the nature of the liability and the parties involved in a lawsuit. Impleader allows a defendant to bring a third party who may be liable for all or part of the plaintiff's claim, optimizing claim consolidation and reducing multiple suits. Interpleader is suitable when a stakeholder holds funds or property claimed by multiple parties, enabling a single action to determine the rightful claimant and limit liability exposure.
Impleader Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com